|
Volume 47 (year 2016), parts: 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 |
| Part 1 |
up |
Adamian G.G., Antonenko N.V., Kalandarov Sh.A.
Description of the Quasifission Reactions in the Framework of Dinuclear System Model (rus, 1.8 Mb)
Formation and evolution of dinuclear system in quasifission reactions are considered. In the framework of dinuclear system concept
the processes of formation of reaction products are investigated. Isotopic dependence of formation cross sections of superheavy
nuclei in quasifission reactions is considered. The yields of new neutron-rich isotopes of nuclei with Z = 64 — 80 in quasifission
reactions are predicted. The mechanism of complex fragment formation in complete fusion and quasifission reactions is analyzed.
|
Artukh A.G., Klygin S.A., Kononenko G.A., Kyslukha D.A., Lukyanov S.M., Mikhailova T.I., Oganessian Yu.Ts.,
Penionzhkevich Yu.E., Sereda Yu.M., Vorontsov A.N., Erdemchimeg B.
Radioactive Nuclear Beams of COMBAS Facility (eng, 1.2 Mb)
The basic ion-optical characteristics of the high-luminosity and high-resolution kinematic separator COMBAS, realized
for the first time on the strong focusing principle, are presented. The developed facility allows one to separate the
high-intensity secondary radioactive beams in a wide range of mass numbers A and atomic numbers Z, which are produced
in heavy-ion reactions in the energy range of 20 ⩽ E ⩽ 100 MeV/A (Fermi energy domain). Two distinct detector systems,
such as realized Si strip-detector telescope and the three-dimensional time-projection chamber of promising development,
are discussed. A program of the investigations of nuclear reaction mechanisms at intermediate energies of 20-100 MeV/A,
measurement of the radii of unstable nuclei, study of the cluster structure of light nuclei near the nuclear drip-line,
and search for 26,28Î resonances in exchange reactions is proposed. The upgrading of experimental facility by the
integration of COMBAS separator with the ion catcher is discussed.
|
Tsyganov Yu.S.
Experiment Automation at the Dubna Gas-Filled Recoil Separator (rus, 3.3 Mb)
Different approaches to solving tasks related to the automation of main processes in long-term experiments with heavy-ion beams
at the Dubna gas-filled recoil separator (DGFRS) are examined. Techniques in the field of spectroscopy of rare α-decays
of superheavy nuclei and approaches to the development of control systems which ensure fail-safety when conducting experiments
with extremely radioactive targets and registration of the main parameters of experiments are described. The specificity of DSSSD
(Double Side Silicon Strip Detector) detectors is examined. A special emphasis is placed on the role of edge phenomena of neighboring p-n junctions when the method for "active correlations" is applied. An example of a beam-free experiment is briefly examined
in an attempt to observe the Zeno effect. The main examples are specified for nuclear complete fusion reactions with beams
of 48Ca accelerated by the U-400 cyclotron at FLNR, JINR.
|
Zalikhanov B.Zh.
From the Electron Avalanche to Lightning Discharge (rus, 650 Kb)
The work gives a qualitative description of the physics of the processes beginning with an electron avalanche and ending with a lightning discharge.
A streamer model is considered that is based on the investigation of the observed new processes occurring in the prestreamer region.
The study and analysis of these processes allow a conclusion that they are actually accompanying processes to support transition of an electron avalanche to a streamer and can be interpreted as a manifestation of the properties of the double charge layer in an external electric field.
Important problems of physical processes underlying formation of a lightning discharge are considered on the basis of the new concept of streamer formation and intergrowth.
Causes for coherent microwave leader radiation and neutron generation in a lightning discharge that have not yet been explained in the gas discharge theory are disclosed.
A simple globe lightning model is also proposed on the basis of the new concept, which allows answering all questions arising from the observation of the globe lightning behavior, and a necessity of changing over from the traditional lightning rod to a lightning guard of a new design is discussed.
|
Synopsis (rus, 51 Kb)
|
Publisher's imprint
|
| Part 2 |
up |
Rodionov V.N., Kravtsova G.A.
Algebraic PT-Symmetric Quantum Theory with a Maximal Mass (rus, 400 Êb)
In this article we want to draw attention to the fact
that the approaches developed by V.G.Kadyshevsky in the
course of several decades and devoted to the geometric construction of quantum field theory with fundamental
mass containing non-Hermitian mass extensions have recently gained a powerful development in the
form of construction of the non-Hermitian algebraic approach. The
central point of these theories is the construction of new scalar
products in which the average values of non-Hermitian Hamiltonians
are valid. Among numerous works on this subject there are both purely mathematical and containing a discussion of experimental
results. In this regard, we consider the development of
algebraic relativistic pseudo-Hermitian quantum theory with a
maximal mass and discuss its experimentally significant consequences.
|
Sargsyan V.V., Kanokov Z., Adamian G.G., Antonenko N.V.
Application of the Theory of Open Quantum Systems in Nuclear Physics (rus, 3550 Êb)
Quantum diffusion equations with transport coefficients, explicitly depending on time, are derived from the generalized non-Markovian Langevin equations.
The asymptotic behavior of the friction and diffusion coefficients is studied in the cases of FC- and RWA-couplings between the collective and internal subsystems.
The asymptotics of the propagator of the density matrix of open quantum system is obtained in the general case of quadratic Hamiltonian linearly coupled
(in coordinate and momentum) with internal degrees of freedom.
The influence of different sets of transport coefficients on decoherence and decay rate of the metastable state is studied by using the master equation for the
reduced density matrix of open quantum systems.
The developed approach is used to study the capture of the projectile by the target nucleus at energies near the Coulomb barrier.
With the calculated capture probabilities, a good agreement between the calculated capture cross sections and experimental data is obtained.
Specific cases where the dissipation promotes penetration through the potential barrier are revealed.
The analytical derivation of the generalized Kramers formula is presented for the quasi-stationary decay rate of quantum metastable systems.
|
Kuklin S.N., Adamian G.G., Antonenko N.V.
Description of Alpha Decay and Cluster Radioactivity in the Dinuclear System Model (rus, 500 Êb)
The description of the cluster radioactivity and 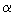 decay of the cold nuclei is suggested
in the dinuclear system model.
The quantum fluctuation of the dynamic coordinate in the charge (mass) asymmetry determines the
value of spectroscopic factor, and tunneling in the coordinate relative distance determines the
amount of the barrier penetrability of the nucleus-nucleus interaction potential. A new method
of calculation of the spectroscopic factor is suggested. The hindrance factors for the transfer
of orbital angular momentum are studied. For α decays of neutron-deficient nuclei 194,196Rn, we give the possible explanation of the deviations of the half-lives from the
Geiger-Nuttall law. The fine structure of α decays of isotopes of U and Th is described
and predicted. The model is employed to describe the α decay from the states of the
rotational band of the even-even nuclei. For the regions of "lead" and "tin" cluster
radioactivities, the half-lives are well described and the most probable cluster yields are
predicted. The cluster decay from the excited nuclei is considered. The connection of cluster
radioactivity with spontaneous fission as well as with highly deformed nuclear states is discussed. decay of the cold nuclei is suggested
in the dinuclear system model.
The quantum fluctuation of the dynamic coordinate in the charge (mass) asymmetry determines the
value of spectroscopic factor, and tunneling in the coordinate relative distance determines the
amount of the barrier penetrability of the nucleus-nucleus interaction potential. A new method
of calculation of the spectroscopic factor is suggested. The hindrance factors for the transfer
of orbital angular momentum are studied. For α decays of neutron-deficient nuclei 194,196Rn, we give the possible explanation of the deviations of the half-lives from the
Geiger-Nuttall law. The fine structure of α decays of isotopes of U and Th is described
and predicted. The model is employed to describe the α decay from the states of the
rotational band of the even-even nuclei. For the regions of "lead" and "tin" cluster
radioactivities, the half-lives are well described and the most probable cluster yields are
predicted. The cluster decay from the excited nuclei is considered. The connection of cluster
radioactivity with spontaneous fission as well as with highly deformed nuclear states is discussed.
|
Logachev P.V., Meshkov O.I., Starostenko A.A., Nikiforov D.A., Andrianov A.V., Maltseva Yu.I., Levichev A.E., Emanov F.A.
Non-Destructive Diagnostic Methods for the Charged Particle Beams (rus, 2025 Êb)
The article provides an overview of the main methods of the non-destructive diagnostic and losses registration of the
charged particle beams used in the accelerator technology. It can help to choose diagnostic and beam loss registration
systems, and gives the qualitative understanding of the devices operation principles. Quantitative characteristics
are presented for each type of diagnostic to define the boundaries of the application.
|
Gongadze A.L.
Micromegas Chambers for the Experiment ATLAS at the LHC (rus, 2007 Êb)
The increase in luminosity and energy of the LHC in the next upgrade (Phase-1) in 2018-2019 will lead to a significant
increase in radiation load on the ATLAS detector, primarily in the areas close to the interaction point of the LHC proton
beams. One of these regions is the Small Wheel of the ATLAS Muon Spectrometer. It is planned to replace it with the
New Small Wheel that will have Micromegas chambers as main coordinate detectors. The paper gives an overview of all existing
types of Micromegas detectors with special focus on the Micromegas chambers for the ATLAS detector upgrade.
|
Synopsis (rus, 52 Kb)
|
Publisher's imprint
|
| Part 3 |
up |
Buchbinder I.L., Ivanov E.A., Pletnev N.G.
Superfield Approach to Construction of the Effective Action in Quantum Field Theory with Extended Supersymmetry (rus, 1.1 Ìb)
This is a review of the modern status of research on construction of the effective actions in supersymmetric quantum field theory.
A special attention is paid to gauge models with extended supersymmetry in the superfield approach. The advantages of formulating such models in N=2 harmonic superspace are emphasized. We describe the manifestly supersymmetric and manifestly covariant methods
of constructing the low-energy effective actions, deriving the corrections to them and obtaining the exact results. We consider
in detail the calculations of the one-loop effective actions in N=2 supersymmetric Yang-Mills theories coupled to
hypermultiplets and in N=4 supersymmetric Yang-Mills theory. The relationship between the effective action in supersymmetric
quantum field theory and the low-energy limits of the superstring theory is discussed.
|
Dorokhov A.E., Radzhabov A.E., Shamakhov F.A., Zhevlakov A.S.
The Nonlocal Chiral Quark Model and the Muon g-2 Problem (eng, 390 Êb)
In the first part of the review we discuss the effective nonlocal approach in the quantum field theory. It concerns primarily
the historical retrospective of this approach, and then we concentrate on the interaction of matter particles (fermions and
bosons) with the (Abelian and non-Abelian) gauge fields. In the second part of the review we consider the hadronic corrections (vacuum polarization) to the anomalous magnetic moment of the muon g-2 factor discussed within the SUf(2) nonlocal
chiral quark model. This is considered in the leading and, partially, in the next-to-leading orders (the effect of the fermion propagator dressing due to pion field)
of expansion in small parameter 1/Nc (Nc is the number of colors in QCD).
|
Adamian G.G., Antonenko N.V., Bezbakh A.N., Jolos R.V.
Influence of Properties of Superheavy Nuclei on Their Formation and Decay (rus, 2.1 Mb)
Properties and stability are discussed for superheavy nuclei obtained in hot fusion reactions.
As shown, the microscopic-macroscopic approach can result in the proton shell closure at Z ⩾ 120.
The isotopic trends of K isomers are predicted in superheavy nuclei.
The evaporation residue cross sections in hot fusion reactions are calculated with
the predicted properties of superheavies.
The interruption of α-decay chain by spontaneous fission is analyzed.
Alpha-decay chains over the isomeric states are considered.
The internal level densities are microscopically calculated in superheavy nuclei.
|
Titov A.I., Kampfer B., Hosaka A., Takabe Hideaki
Quantum Processes in Short and Intensive Electromagnetic Fields (eng, 940 Êb)
This work provides an overview of our recent results in studying two most important and widely discussed quantum processes:
electron-positron pair production off a probe photon propagating through a polarized short-pulsed electromagnetic
(e.g., laser) wave field or generalized Breit-Wheeler process, and a single photon emission off an electron interacting
with the laser pulse, the so-called nonlinear Compton scattering. We show that the probabilities of particle production
in both the processes are determined by interplay of two dynamical effects, where the first one is related to the shape
and duration of the pulse, and the second one is nonlinear dynamics of the interaction of charged fermions with a strong
electromagnetic field.
We elaborate suitable expressions for the production probabilities and cross sections, convenient for studying evolution
of the plasma in presence of strong electromagnetic fields.
|
Synopsis (rus, 48 Kb)
|
Publisher's imprint
|
| Âûïóñê 4 |
íàâåðõ |
Joint Institute for Nuclear Research - 60 (rus, 40 Êb)
|
Volkov M.K., Arbuzov A.B.
Low-Energy Processes of Meson Production in the Extended Nambu-Jona-Lasinio Model (rus, 370 Êb)
In the framework of the extended Nambu-Jona-Lasinio model, low-energy
processes of meson production in electron-positron collisions are described.
It is shown that in these processes intermediate vector mesons, both in the ground
and in the first radial-excited states, play an important role.
Our results are in satisfactory agreement with the existing experimental data.
A set of theoretical predictions, which can be tested experimentally
in the nearest future, is given.
|
Ivanov E.A.
Gauge Fields, Nonlinear Realizations, Supersymmetry (eng, 480 Kb)
This is a brief survey of the all-years research activity in the Sector "Supersymmetry" (the former Markov Group) at the Bogoliubov Laboratory of
Theoretical Physics. The focus is on the issues related to gauge fields, spontaneously broken symmetries in the nonlinear realizations approach, and diverse aspects of supersymmetry.
|
Batyuk P.N., Kekelidze V.D., Kolesnikov V.I., Rogachevsky O.V., Sorin A.S., Voronyuk V.V. (on behalf of the BM@N and MPD collaborations)
Feasibility Study of Heavy Ion Physics Program at NICA (eng, 2.0 Mb)
There is strong experimental and theoretical evidence that in collisions of heavy
ions at relativistic energies the nuclear matter undergoes a phase transition to the
deconfined state - Quark-Gluon Plasma. The caused energy region of such
a transition was not found at high energy at SPS and RHIC, and search for this
energy is shifted to lower energies, which will be covered by the future NICA
(Dubna), FAIR (Darmstadt) facilities and BES II at RHIC. Fixed target and collider experiments
at the NICA facility will work in the energy range from a few AGeV up to 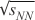 = 11 GeV and will study the most interesting area on the nuclear
matter phase diagram. = 11 GeV and will study the most interesting area on the nuclear
matter phase diagram.
The most remarkable results were observed in the study of collective phenomena
occurring in the early stage of nuclear collisions. Investigation of the collective
flow will provide information on Equation of State (EoS) for nuclear matter.
Study of the event-by-event fluctuations and correlations can give us signals
of critical behavior of the system. Femtoscopy analysis provides
the space-time history of the collisions. Also, it was found that baryon stopping
power revealing itself as a "wiggle" in the excitation function of curvature of the
(net) proton rapidity spectrum relates to the order of the phase transition.
The available observations of an enhancement of dilepton rates at low invariant
masses may serve as a signal of the chiral symmetry restoration in hot and dense
matter. Due to this fact, measurements of the dilepton spectra are considered to be
an important part of the NICA physics program. The study of strange particles
and hypernuclei production gives additional information on the EoS and
"strange" axis of the QCD phase diagram.
In this paper a feasibility of the considered investigations is shown by
the detailed Monte Carlo simulations applied to the planned experiments
(BM@N, MPD) at NICA.
|
Ceccucci A., Goudzovski E., Kekelidze V., Madigozhin D., Potrebenikov I.
Kaon Decay Studies at CERN SPS in the Last Decades (eng, 875 Êb)
This review summarizes the kaon experimental results obtained in the last 15 years on the basis of data collected at the CERN SPS with the participation
of JINR physicists. These results contribute essentially to the Standard Model checks and search for its extension, fundamental symmetry violations and low-energy strong interactions theory development. A progress in the
experimental technique and prospects for the future results are also discussed.
|
Filchenkov V.V.
Physical Applications of Muon Catalysis, Muon Capture in Hydrogen (rus, 1.1 Ìb)
The results of theoretical and experimental work on the capture of negative muons in hydrogen are presented.
The accompanying phenomenon of muon catalysis in hydrogen and the features of the experimental method are particularly noted.
The conclusion is made about the importance of determining the precise capture rate for the clarification of the Standard Model.
|
Aksenov V.L., Balagurov A.M., Kozlenko D.P.
Condensed Matter Research at the Modernized IBR-2 Reactor: From Functional Materials to Nanobiotechnologies (rus, 1.6 Ìb)
A review of the main research directions of the condensed matter realized at the IBR-2 high flux pulsed reactor is presented. It is demonstrated that
the spectrometer complex of the modernized reactor has a large potential for studies of the structural, magnetic and dynamical properties of novel functional materials
and nanobiosystems, ensuring the leading JINR positions in neutron scattering studies of condensed matter in the long-term prospect.
|
Frank A.I.
Ultracold Neutrons and Interaction of Waves with Moving Matter (rus, 750 Kb)
This review is devoted to the problem of interaction of neutron waves with moving matter. The validity of the 1/v law for ultracold neutrons and the possibility of
representing neutron interaction with matter by means of the effective potential were tested in the experiments named "Null Fizeau experiment". In such experiments a neutron wave passes through
a flat sample moving parallel to its border. Observation of any physical effects caused by such movement is the evidence of the fact that the concept of the constant effective potential
is not correct. In the second part of the review we describe the prediction and the first observation of the Accelerated Matter Effect, which consists in the change of neutron energy after
passing through the refractive sample moving with acceleration directed along or against the direction of neutron propagation. The characteristic features of this phenomenon in the case of
doubly refractive matter are considered. In conclusion, the problem of propagation of neutron waves in matter moving with giant acceleration is discussed.
|
Manoshin S.A., Belushkin A.V., Ioffe A.I.
Development of Simulation Methods of Neutron Spectrometers and Virtual Neutron Scattering Experiments (rus, 435 Kb)
In this review we present some results of modeling of the polarized neutron
scattering instruments, using developed by the authors' components of the
Monte-Carlo based VITESS simulation package. The work was performed within
the framework of collaboration between the Frank Laboratory of Neutron
Physics JINR and the Juelich Center of Neutron Science (Forschungszentrum
Juelich, Germany). Successful VITESS simulations were carried out for
resonance and adiabatic gradient spin flippers, Drabkin resonator, classical
spin-echo spectrometer, resonance spin-echo spectrometer, spin-echo
diffractometer for small angle neutron scattering, spin-echo spectrometer
with the rotating magnetic fields. Special efforts were undertaken to
introduce in the VITESS the possibility to load the magnetic field
3-dimensional space map from an external source (file), obtained by direct
measurements or calculated by dedicated final elements calculations. A very
good agreement of neutron polarimetric experiments with the VITESS
calculations is demonstrated.
|
Gundorin N.A., Zeinalov Sh.S., Kopatch Yu.N., Popov A.B., Furman W.I.
Investigations of Fission Properties and Correlation Effects in Fission (rus, 1.4 Mb)
This review presents the results of a study on the P-even and P-odd angular
correlations of fission fragments from ($n,f$)-reaction on 235U and 239Pu target nuclei induced by unpolarized and polarized resonance
neutrons, as well the TRI- and ROT-effects in the ternary and binary fission
of actinides caused by polarized thermal neutrons. The results of
measurements of the prompt and delayed neutron yields per fission are presented
too. The experimental data are analyzed on the basis of a new theoretical
approach developed recently by JINR-RNC Kurchatov Institute collaboration,
which allowed to explain consistently the reduction of the multidimensional
phase space fission fragments in space JπK-channels and to
identify the role of interresonance interference in the observed
correlation effects.
|
Kulikov S.A., Prikhodko V.I.
A New Generation of Data Acquisition and Accumulation Systems of the Spectrometers' Complex at the IBR-2 Reactor (rus, 961 Kb)
The paper presents an overview of works on the creation of data acquisition
and accumulation systems, which have been carried out in the Department of
the IBR-2 spectrometers' complex over the past 15 years (before, during and
after the modernization of the IBR-2 reactor). These systems represent a
unified set of identical (from the viewpoint of hardware) modules limited in
type but functionally complete, wherein distinctions in
parameters, functional capabilities, encoding, correction and preliminary
data processing procedures specific to each spectrometer are realized on the
level of microprograms, electronic tables, and unified control software
complex.
|
Synopsis (rus, 65 Kb)
|
Publisher's imprint
|
| Part 5 |
up |
Bednyakov V.A.
Is It Possible to Discover a Dark Matter Particle with an Accelerator? (eng, 4430 Êb)
The paper contains description of the main properties of the galactic dark matter (DM) particles, available approaches for detection
of DM, main features of direct DM detection, ways to estimate prospects for the DM detection, the first collider search for a DM candidate
within an Effective Field Theory (EFT), a complete review of ATLAS results of the DM candidate search with LHC Run~I, and a less complete review
of "exotic" dark particle searches with other accelerators and not only.
From these considerations it follows that one is unable to prove, especially model-independently, a discovery of a DM particle with
an accelerator or a collider. One can only obtain evidence of existence of a weakly interacting neutral particle, which could be or could
not be the DM candidate.
The current LHC DM search program uses only the missing transverse energy signature. Non-observation of any excess above Standard Model
expectations forces the LHC experiments to enter into the same fighting for the best exclusion curve, in which (almost) all direct and
indirect DM search experiments permanently take place. But this fighting has very little (almost nothing) to do with a real possibility
of discovering a DM particle. The true DM particles possess an exclusive galactic signature - annual modulation of a signal, which
is accessible today only for direct DM detection experiments. There is no way for it with a collider or an accelerator.
Therefore, to prove the DM nature of a collider-discovered candidate, one must find the candidate in a direct DM experiment and demonstrate
the galactic signature for the candidate. Furthermore, being observed, the DM particle must be implemented into a modern theoretical framework.
The best candidate is the supersymmetry, which looks today inevitable for coherent interpretation of all available DM data.
|
Morozov A.A.
Conformal Block Properties, AGT Hypothesis and Knot Polynomials (rus, 950 Kb)
In this review we describe different properties of conformal blocks of the
2D conformal field theory. In particular, the connection between conformal
blocks and partition function of 4D supersymmetric theory is discussed.
Besides the interest of such a connection by itself it also provides practical
simplifications of calculations in both theories. For the same purpose the
representation of correlators in conformal theory as a matrix model
varieties can be used. Integral form of such correlators allows one to
generalize the results evaluated for Virasoro algebra to more complicated
cases of $W$-algebras and quantum Virasoro algebras. This leads to the
possible studies of more complicated structures in conformal field theory.
The second part of the review is dedicated to the Chern-Simons theory. The
interest which it arouses at the moment is due to its connection with the
mathematical knot theory. This theory is quite an old subject that appeared in
the 17th century. Its goal is to construct an algorithm which allows one
to distinguish between different knots - contours in 3D space. The main
approach to this problem, which is decribed in this review, is to construct the
so-called knot invariants.
|
Syska J.
Weak Bound State with the Nonzero Charge Density as the LHC 126.5 GeV State (eng, 440 Êb)
The self-consistent model of classical field interactions formulated as the counterpart of the quantum electroweak model leads
to homogeneous boson ground state solutions in presence of nonzero extended fermionic charge density fluctuations. Two different
types of electroweak configurations of fields are analyzed. The first one has nonzero electric and weak charge fluctuations. The second
one is electrically uncharged but weakly charged. Both types of configurations have two physically interesting solutions which possess
masses equal to 126.67 GeV at the value of the scalar fluctuation potential parameter λ equal to ~ 0.0652. The spin zero
electrically uncharged droplet, formed as a result of the decay of the charged one, is interpreted as the ~ 126.5 GeV state found
in the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) experiment. The other two configurations correspond to solutions with masses equal to 123.7~GeV
and λ equal to ~ 0.0498, and thus the algebraic mean of the masses of two central solutions, i.e., 126.67 and
123.7 GeV, is equal to 125.185 GeV. The problem of a mass of this kind of droplets will be considered on the basis of the phenomenon
of the screening of the fluctuation of charges. Their masses are found in the thin wall approximation.
|
Smirnov V.L., Vorozhtsov S.B.
Modern Compact Accelerators of Cyclotron Type for Medical Applications (eng, 1975 Êb)
Ion beam therapy and hadron therapy are types of external beam radiotherapy. Recently,
the vast majority of patients have been treated with protons and carbon ions.
Typically, the types of accelerators used for therapy were cyclotrons and synchrocyclotrons. It
is intuitively clear that a compact facility fits best to a hospital environment intended for
particle therapy and medical diagnostics. Another criterion for selection of accelerators to
be mentioned in this article is application of superconducting technology to the magnetic
system design of the facility. Compact isochronous cyclotrons, which accelerate protons
in the energy range of 9-30 MeV, have been widely used for production of radionuclides.
Energy of 230 MeV has become canonical for all proton therapy accelerators. Similar
application of a carbon beam requires ion energy of 430 MeV/u. Due to application of
superconducting coils the magnetic field in these machines can reach 4-5 and even 9 T
in some cases. Medical cyclotrons with an ironless or nearly ironless magnetic system
that have a number of advantages over the classical accelerators are at the development
stage. In this work, an attempt is made to describe some conceptual and technical features
of modern accelerators under consideration. The emphasis is placed on the magnetic
and acceleration systems along with the beam extraction unit, which are very important
from the point of view of the facility compactness and compliance with the strict medical
requirements.
|
Drivotin O.I., Ovsyannikov D.A.
Stationary Self-Consistent Distributions for Charged Particle Beam in Magnetic Field (eng, 450 kb)
A review of analytical solutions of the Vlasov equation for a charged particle beam is given. These results are analyzed on the base
of a common approach developed by the authors of the article. According to this method, the space of integrals
of motion is introduced, integrals of motion being regarded as coordinates in it. At that, specifying of a self-consistent distribution
is reduced to specifying of a density in this space. Such an approach allows one to simplify construction and analysis of various
self-consistent distributions. Particularly, in some cases it is possible to obtain new solutions considering linear combinations
of known solutions. This approach also gives a possibility to provide pictorial geometric representation of self-consistent distributions in the space of motion integrals.
|
Synopsis (rus, 54 Kb)
|
Publisher's imprint
|
| Part 6 |
up |
Proceedings of the International Workshop "PROSPECTS OF PARTICLE PHYSICS: NEUTRINO PHYSICS AND ASTROPHYSICS" (PPP 2015)
Valday, Russia, February 1-8, 2015
|
Bezrukov L., Sinev V.
Atmospheric Neutrinos for Investigation of the Earth Interior (eng, 70 kb)
|
Real D., Calvo D. on behalf of the KM3NeT Collaboration
Digital Optical Module Electronics of KM3NeT (eng, 421 kb)
|
Avrorin A. D., Avrorin A. V., Aynutdinov V. M., Bannasch R.,
Belolaptikov I. A., Bogorodsky D. Yu., Brudanin V. B., Budnev N. M.,
Danilchenko I. A., Demidov S. V., Domogatsky G. V., Doroshenko A. A.,
Dyachok A. N., Dzhilkibaev Zh.-A. M., Fialkovsky S. V., Gafarov A. R.,
Gaponenko O. N., Golubkov K. V., Gress T. I., Hons Z., Kebkal K. G.,
Kebkal O. G., Konischev K. V., Korobchenko A. V., Koshechkin A. P.,
Koshel F. K., Kozhin V. A., Kulepov V. F., Kuleshov D. A., Ljashuk V. I.,
Milenin M. B., Mirgazov R. R., Osipova E. A., Panfilov A. I., Pan'kov L. V.,
Pliskovsky E. N., Rozanov M. I., Rjabov E. V., Shaybonov B. A.,
Sheifler A. A., Shelepov M. D., Skurihin A. V., Smagina A. A.,
Suvorova O. V., Tarashchansky B. A., Yakovlev S. A., Zagorodnikov A. V., Zhukov V. A.,
Zurbanov V. L.
Neutrino Signal at the Baikal from Dark Matter
in the Galactic Center (eng, 147 kb)
|
Avrorin A. V., Avrorin A. D., Aynutdinov V. M., Bannasch R.,
Belolaptikov I. A. , Bogorodsky D. Yu., Brudanin V. B., Budnev N. M.,
Danilchenko I. A., Dzhilkibaev Zh.-A. M., Domogatsky G. V.,
Doroshenko A.A., Dyachok A. N., Fialkovsky S. V., Gafarov A. R.,
Gaponenko O.N., Golubkov K. V., Gress T. I., Hons Z., Kebkal K. G.,
Kebkal O.G., Konischev K. V., Korobchenko A. V., Koshechkin A. P.,
Koshel F.K., Kozhin V. A., Kulepov V. F., Kuleshov D. A., Lyashuk V. I.,
Milenin M.B., Mirgazov R. R., Osipova E. A., Panfilov A. I.,
Pan'kov L.V., Pliskovsky E. N., Rozanov M. I., Ryabov E. V.,
Shaybonov B.A., Sheifler A. A., Skurikhin A. V., Smagina A. A.,
Suvorova O.V., Tabolenko V.A., Tarashchansky B.A., Yakovlev S. A.,
Zagorodnikov A. V.,
Zhukov V. A., Zurbanov V. L.
Data Acquisition System for the Baikal-GVD Neutrino Telescope (eng, 268 kb)
|
Suvorova O. V.
Status of Indirect Dark Matter Search with Neutrino Telescopes (eng, 583 kb)
|
Lubsandorzhiev B. Ê.
Multi-TeV Gamma-Ray Astronomy (eng, 599 kb)
|
Lubsandorzhiev B. K.
Evolution of Ideas in Photon Detection (eng, 740 kb)
|
Novoseltseva R. V., Boliev M. M., Dzaparova I. M., Kochkarov M. M.,
Novoseltsev Yu. F., Petkov V. B., Volchenko V. I., Volchenko G. V., Yanin A. F.
The Search for Neutrino Bursts from Supernovae with Baksan
Underground Scintillation Telescope (eng, 194 kb)
|
Petkov V. B.
Prospects of the Search for Neutrino Bursts from Supernovae
with Baksan Large Volume Scintillation Detector (eng, 120 kb)
|
Kochkarov M. M., Alikhanov I. A., Boliev M. M., Dzaparova I. M.,
Novoseltseva R. V., Novoseltsev Yu. F., Petkov V. B., Volchenko V. I.,
Volchenko G. V., Yanin A. F.
Neutron Flux Measurement Using Activated Radioactive Isotopes
at the Baksan Underground Scintillation Telescope (eng, 304 kb)
|
Alexeyev E. N., Gavrilyuk Yu. M., Gangapshev A. M., Kazalov V. V.,
Kuzminov V. V., Panasenko S. I., Ratkevich S. S.
Results of a Search for Daily and Annual Variations
of 214Po Half-Life at the Two-Year Observation Period (eng, 196 kb)
|
Smirnov O. Yu., Agostini M., Appel S., Bellini G., Benziger J., Bick D.,
Bonfini G., Bravo D., Caccianiga B., Calaprice F., Caminata A.,
Cavalcante P., Chepurnov A., Choi K., D'Angelo D., Davini S., Derbin A.,
Di~Noto L., Drachnev I., Empl A., Etenko A., Fomenko K., Franco D.,
Gabriele F., Galbiati C., Ghiano C., Giammarchi M., Goeger-Neff M.,
Goretti A., Gromov M., Hagner C., Hungerford E., Ianni Aldo,
Ianni Andrea, Jedrzejczak K., Kaiser M., Kobychev V., Korablev D.,
Korga G., Kryn D., Laubenstein M., Lehnert B., Litvinovich E.,
Lombardi F., Lombardi P., Ludhova L., Lukyanchenko G., Machulin I.,
Manecki S., Maneschg W., Marcocci S., Meroni E., Meyer M.,
Miramonti L., Misiaszek M., Mosteiro P., Muratova V., Neumair B.,
Oberauer L., Obolensky M., Ortica F., Otis K., Pagani L., Pallavicini M.,
Papp L., Perasso L., Pocar A., Ranucci G., Razeto A., Re A., Romani A.,
Roncin R., Rossi N., Schönert S., Semenov D., Simgen H., Skorokhvatov M.,
Sotnikov A., Sukhotin S., Suvorov Yu., Tartaglia R., Testera G., Thurn J.,
Toropova M., Unzhakov E., Vogelaar R. B., von Feilitzsch F., Wang H.,
Weinz S., Winter J., Wojcik M., Wurm M., Yokley Z., Zaimidoroga O.,
Zavatarelli S., Zuber K. , Zuzel G. (the Borexino Collaboration)
Measurement of Neutrino Flux from the Primary Proton–Proton
Fusion Process in the Sun with the Borexino Detector (eng, 285 kb)
|
Zemskova S. on behalf of the OPERA Collaboration
νμ → νe Oscillations Search in the OPERA Experiment (eng, 446 kb)
|
Nikitenko Ya.
Antineutrino Direction via Inverse Beta Decay in Double Chooz (eng, 118 kb)
|
Serebrov A. P., Ivochkin V. G., Samoylov R. M., Fomin A. Ê.,
Zinoviev V. G., Neustroev P. V., Golovtsov V. L., Gruzinsky N. V.,
Solovey V. A., Cherniy A. V., Zherebtsov O. M., Martemyanov V.P.,
Zinoev V. G., Tarasenkov V. G., Aleshin V. I., Petelin A. L.,
Pavlov S. V., Izhutov A. L., Sazontov S. À., Ryazanov D. K.,
Gromov M. Î., Afanasiev V. V., Matrosov L. N., Matrosova M. Yu.
Experiment for Search for Sterile Neutrino at SM-3 Reactor (eng, 636 kb)
|
Gorbachev V. V., Gavrin V. N., Ibragimova T. V., Kalikhov A. V.,
Malyshkin Yu. M., Shikhin A. A.
Determination of Activity of 51Cr on Gamma Radiation
Measurements (eng, 95 kb)
|
Gavrin V. N., Kozlova Yu. P., Veretenkin E. P., Logachev A. V.,
Logacheva A. I., Lednev I. S., Okunkova A. A.
Reactor Target from Metal Chromium for “Pure” High-Intensive
Artificial Neutrino Source (eng, 1165 kb)
|
Naumov D. V., Naumov V. A., Shkirmanov D. S.
Inverse-Square Law Violation and Reactor Antineutrino Anomaly (eng, 305 kb)
|
Klimenko A. A., Rumyantseva N. S.
Limits of Majorana Neutrino Mass from Combined Analysis
of Data from 76Ge and 136Xe Neutrinoless Double Beta Decay
Experiments (eng, 218 kb)
|
Vasilyev S., Abgrall N., Arnquist I. J., Avignone F. T. III
Balderrot-Barrera C. X., Barabash A. S., Bertrand F. E., Bradley A. W.,
Brudanin V., Busch M., Buuck M., Byram D., Caldwell A.S., Chan Y.-D.,
Christofferson C. D., Cuesta C., Detwiler J.A., Efremenko Yu., Ejiri H.,
Elliott S. R., Galindo-Uribarri A., Gilliss T., Giovanetti G. K., Goett J.,
Green M. P., Gruszko J., Guinn I., Guiseppe V. E., Henning R., Hoppe E. W.,
Howard S., Howe M. A., Jasinski B. R., Keeter K. E., Kidd M. F.,
Konovalov S. I., Kouzes R. T., LaFerriere B. D., Leon J., MacMullin J.,
Martin R. D., Meijer S. J., Mertens S., Orrell J. L., O'Shaughnessy C.,
Poon A. W. P., Radford D. C., Rager J., Rielage K., Robertson R. G. H.,
Romero-Romero E., Shanks B., Shirchenko M., Snyder N., Suriano A. M.,
Tedeschi D., Trimble J. E., Varner R. L., Vetter K., Vorren K., White B. R.,
Wilkerson J. F., Wiseman C., Xu W., Yakushev E., Yu C.-H., Yumatov V.,
Zhitnikov I. (The Majorana Collaboration)
Status of the Majorana Demonstrator (eng, 515 kb)
|
Alekseenko V. V., Gavrilyuk Yu. M., Gangapshev A. M., Gezhaev A. M.,
Dzhappuev D. D., Kazalov V. V., Kudzhaev A. U., Kuzminov V. V., Panasenko S. I.,
Ratkevich S. S., Tekueva D. A., Yakimenko S. P.
The Study of the Thermal Neutron Flux in the Deep Underground
Laboratory DULB-4900 (eng, 410 kb)
|
Gavrilyuk Yu. M., Gangapshev A. M., Kazalov V. V., Kuzminov V. V.,
Panasenko S. I., Ratkevich S. S., Tekueva D. A., Yakimenko S. P.
Search for 2K(2ν)-Capture of 124Õå (eng, 194 kb)
|
Gavrilyuk Yu. M., Gangapshev A. M., Kazalov V. V., Kuzminov V. V.,
Panasenko S. I., Ratkevich S. S., Tekueva D. A., Yakimenko S. P.
The Origin of the Background Radioactive Isotope 127Xe
in the Sample of Xe Enriched in 124Xe (eng, 189 kb)
|
Minotti A. on behalf of Double Chooz Collaboration
Latest Results from Double Chooz (eng, 470 kb)
|
Chudaykin A. S.
𝒪(1) eV Sterile Neutrino in f(R) Gravity (eng, 205 kb)
|
Subject Index to Volume 47, 2016 (rus)
|
Autor Index to Volume 47, 2016 (rus)
|
| Publisher's imprint |
|
|
