P11-2016-4 (255.5)
Amirkhanov I.V. et al.
Investigation of Quasi-Stationary States in the Double-Barrier Open Well
In this paper an investigation of solutions of quasi-stationary states in
the framework of the Schroedinger equation with complex energies with
piecewise constant potentials for various values of the parameters of the
potential is conducted. Quasi-levels are found for the under- and
above-barrier cases. For the given potential barrier heights the number of
under-barrier quasi-levels for the double-barrier potential is more than for
the single-barrier potential. The calculations show that the real part of
the energy varies smoothly and the imaginary part of the energy changes
irregularly when changing the parameters of the potential.
|
p9-2016-6 (927.7)
Nozdrin M.A. et al.
Diagnostics at JINR LHEP Photogun Bench
The photoinjector electron beam quality dramatically depends on the laser driver beam quality. For laser beam diagnostics a "virtual cathode"
system was realized at the JINR LHEP photogun bench. The system allows one to image laser beam profile at the cathode. The AVINE software complex developed in
DESY Zeuthen is being used for imaging. Equipment for emittance measurement using the slit method was installed. The original emittance calculation software
EmCa was created and tested with the laser beam.
|
E17-2016-8 (116.0)
Bogolubov N.N. (Jr.), Soldatov A.V.
Variational Master Equation Approach to Dynamics of Magnetic Moments
Non-equilibrium properties of a model system comprised of a
subsystem of magnetic moments strongly coupled to a selected Bose
field mode and weakly coupled to a heat bath made of a plurality
of Bose field modes were studied on the basis of non-equilibrium
master equation approach combined with the approximating
Hamiltonian method. A variational master equation derived within
this approach is tractable numerically and can be readily used to
derive a set of ordinary differential equations for various
relevant physical variables belonging to the subsystem of magnetic
moments. Upon further analysis of the thus obtained variational
master equation, an influence of the macroscopic filling of the
selected Bose field mode at low enough temperatures on the
relaxation dynamics of magnetic moments was revealed.
|
P13-2016-10 (405.9)
Pepelyshev Yu.N., Tsogtsaikhan Ts.
Prediction of the Thermal Dynamic Parameters Fluctuation of Coolant System of the IBR-2M Reactor Using Neural Networks
This paper presents an artificial neural network method for long-term
prediction of the thermal dynamic parameters of primary coolant circuit of
the IBR-2M reactor. The main goal is to predict the temperature and liquid
sodium flow rate through the core and thermal power. It is shown that the
prediction can reduce three times the effects of slow reactivity
fluctuations in power and decrease the requirements for the automatic power
stabilization system. Nonlinear autoregressive neural network (NAR) with
local feedback connection has been considered. The results of prediction
error ~ 5% coincide with the experimental ones.
|
P13-2016-20 (1.004.3)
Pepelyshev Yu.N. et al.
Application of the Properties of Toeplitz Matrices of the Noise Correlation Characteristics to the Diagnostics of the IBR-2M Pulsed Reactor
The safeguarding of a nuclear reactor during the operation process is one of
the most significant tasks. The difficulty is in the necessity to use
nondestructive methods. One of such perspective methods is the neutron noise
diagnostics of a nuclear reactor.
Possibility of the noise diagnostics by the new method of norms of positive
definite Toeplitz correlation matrices is studied. The advantage of this
method is its purely mathematical nature; no model of the process is
employed.
The neutron noise analysis of the IBR-2M pulse energy has been carried out
by the represented method. Both the static state and dynamic
state of the reactor have been studied.
Frequency analysis of unstable components of the reactor noise has been
carried out. The main unstable components of the neutron noise are
frequencies of 0.8 and 1.6 Hz, which are conditional on the vibration of the
movable reflector blades of the reactivity modulator. The results of this
diagnostics have been compared with the results of the classical spectral
analysis.
|
E7-2016-21 (292.6)
Volkov V.V., Cherepanov E.A., Kalandarov Sh.A.
Interpretation of the Mechanism of Spontaneous Fission of Heavy Nuclei in the Framework of Dinuclear System Conception
A new approach to the interpretation of the process of spontaneous fission
of heavy nuclei is suggested. It is based on nuclear physics data which are
obtained in heavy ion collisions. The process of spontaneous fission
consists of three sequential stages: clusterization of the valent nucleons
of a heavy nucleus into a light nucleus-cluster, which leads to the
formation of a dinuclear system; evolution of the dinuclear system which
proceeds by nucleon transfer from the heavy to light nucleus; and decay of
the dinuclear system from the equilibrium configuration into two fragments.
|
E14-2016-24 (664.7)
Nyamdavaa E. et al.
Preparation and Characterization of La1-xCexCoO3 Perovskite Oxides for Energy Materials
Cerium-doped lanthanum cobaltite perovskites (La1-xCexCoO3
with x=0, 0.2, 0.4) were prepared by the sol-gel method (calcined for 5 h at
750 ºC) and characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray absorption
(XAS), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), and BET surface area
analysis. The results showed that the cerium doping promoted the structural
transformation of LaCoO3 from rhombohedral into the cubic structure.
High specific surface area and small crystallite size are achieved at x=0.2.
The XAS results confirmed the formation of compound La1-xCexCoO3.
|
P11-2015-19 (210.013)
Volokhova A.V., Zemlyanaya E.V., Rikhvitskiy V.S.
Parallel Optimization Method for Numerical Solving of the Polaron
Equations System Using the Partitions Algorithm
Previously developed method for the numerical simulation of the polaron
states formation in condensed matter has been modified using the partitions
algorithm that provides a significant speedup in the parallel calculations
on multiprocessor systems. Software implementation is based on the MPI
technology. Methodical calculations are carried out on a multiprocessor
cluster CICC LIT JINR (Dubna) with a different processors number and a
different choice of computational parameters. The calculations confirm the
effectiveness of the developed approach for numerical solution of the system
of nonlinear differential equations describing the polaron dynamical model.
|
P4-2015-20 (200.415)
Pupyshev V.V.
Two-Dimensional Coulomb Scattering of a Quantum Particle.
The Structure of the Radial Wave Functions
By assumption, a charged quantum particle moves in the
two-dimensional plane of the three-dimensional configuration space
and is scattered by the fixed Coulomb center lying in the same
plane. It is shown that the radial wave functions of this particle
satisfy the Coulomb equation with half-integer index. The structure
of these functions is studied. Three physically interesting limits - the non-Coulomb limit and the limits of
high and low energies -
are considered. The main differences of the two-dimensional Coulomb
scattering from the three-dimensional one are clarified.
|
P13-2015-21 (310.506)
Morozov V.A., Morozova N.V.
Gas Discharge Processes in the Standard and Metal Channel PMTs
The effect of the potential difference at the focusing chamber electrodes of
the XP2020, FEU-85, FEU-87, and FEU-93 photomultipliers on the intensity of
afterpulses resulting from gas discharge processes is investigated. The time distribution of the afterpulses in the metal
channel PMTs - H6780 and R7600U-200 - is studied as well.
|
E6-2015-24 (128.121)
Maslov O.D.
Results of High-Temperature Processing of High-Carbon Materials from the Lower Cambrian Period of the Earth's History
The paper reports the observation of the spontaneously fissioning nuclides (SFN), concentrated in fly ash during combustion of high-carbon
(graphite) material, chemogenic siliceous-carbonaceous rocks and carbonaceous shale in the mixture with brown coal. In the samples obtained,
the spontaneous fission was measured by track method. The zones of precipitation of SFN and their light homologues on the
thermochromatographic column were determined. The nuclide detected in the alkaline trap has T1/2 = 62 d. It is precipitated with
iron hydroxide, dissolved in the NH4OH + H2O2 solution, distilled by heating up to 100 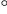 C, and precipitated
with AgI. This nuclide belongs to the halides. The content of the parent nuclide in high-carbon (graphite) material and chemogenic
siliceous-carbonaceous rock corresponds to 10-14 g/g. C, and precipitated
with AgI. This nuclide belongs to the halides. The content of the parent nuclide in high-carbon (graphite) material and chemogenic
siliceous-carbonaceous rock corresponds to 10-14 g/g.
|
P1-2015-28 (554.327)
Kurilkin A.K. et al.
The Vector Ay and Tensor Ayy, Axx, Axz
Analyzing Powers of the   3Hp Reaction at Energy 200 MeV 3Hp Reaction at Energy 200 MeV
The data on the vector Ay and tensor Ayy, Axx,
and Axz analyzing powers of   3Hp
reaction are presented at the kinetic beam energy of 200 MeV in the full angular range in the c.m. frame.
The signs of the tensor analyzing powers Ayy, Axx, and Axz
at forward and backward scattering have demonstrated the sensitivity to the ratio of the D/S components in the
3H and deuteron.
The high-precision experimental results are compared with the theoretical calculations performed in the multiple-scattering model by using standard wave functions
of the three-nucleon bound state and of the deuteron. 3Hp
reaction are presented at the kinetic beam energy of 200 MeV in the full angular range in the c.m. frame.
The signs of the tensor analyzing powers Ayy, Axx, and Axz
at forward and backward scattering have demonstrated the sensitivity to the ratio of the D/S components in the
3H and deuteron.
The high-precision experimental results are compared with the theoretical calculations performed in the multiple-scattering model by using standard wave functions
of the three-nucleon bound state and of the deuteron.
|
P13-2015-30 (233.410)
Turek M. et al.
Tailoring the Evaporator in an Ion Source for Effective Ion Beam Production of Substances with High and Low Melting Points
Two different designs of the internal evaporator in an arc discharge ion
source for low and high melting substances are presented. A matter of the
evaporator size and its placement in order to obtain a stable and intense
ion beam is considered. Basic ion source characteristics, i.e., dependences
of ion current and discharge voltage on discharge and filament currents and
on the external magnetic field flux density are discussed in order to find
optimal working conditions. Results of measurements for both low (P, Zn, Se,
S) and high melting substances (Pd) are presented, which show the
suitability of the designs for ion implantation purposes.
|
P13-2015-31 (282.780)
Turek M. et al.
Thermal Desorption of Helium from Defected Silicon
The TDS (thermal desorption spectroscopy) measurements of He implanted in
silicon samples are reported. The He implantation energy was 90 keV (at a
tilt of 45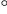 ) while the fluence was 1016 cm-2. Additionally,
the influence of Si preimplantation (fluences in the range
1014-1016 cm-2, E =260 keV) was investigated. The He
releases both from interstitials/vacancies ( ) while the fluence was 1016 cm-2. Additionally,
the influence of Si preimplantation (fluences in the range
1014-1016 cm-2, E =260 keV) was investigated. The He
releases both from interstitials/vacancies (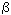 peak) and from cavities (an peak) and from cavities (an 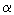 peak or rather a band consisting probably of at least two peaks) were
observed. The
peak or rather a band consisting probably of at least two peaks) were
observed. The 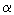 peak disappears for preimplantation fluences larger than
1015 cm-2, while the peak disappears for preimplantation fluences larger than
1015 cm-2, while the 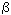 peak becomes broader and shifts toward
higher temperatures. The TDS spectra were collected using heating ramp rates
in the range 0.3-0.7 K/s. Desorption activation energy of the peak becomes broader and shifts toward
higher temperatures. The TDS spectra were collected using heating ramp rates
in the range 0.3-0.7 K/s. Desorption activation energy of the 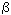 peak for
different preimplantation fluences was found using the Redhead analysis of
the peak for
different preimplantation fluences was found using the Redhead analysis of
the 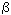 peak shift. peak shift.
|
E16-2015-32 (515.501)
Kuban  k J. et al. k J. et al.
Measurement of Out-of-Field Doses in the Clinical Proton Beam at the Czech Proton Therapy Center
In our paper we describe results of out-of-field doses measurements performed in the clinical
proton beam at the Czech Proton Therapy Center (PTC), Prague, using a pencil-beam delivery mode.
The obtained data were compared with a similar experiment previously performed at the medical center of the Dzhelepov Laboratory of Nuclear Problems
of the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna.
Contrary to the PTC experiment, the clinical proton beam at the JINR Phasotron was formed using passive system of collimators, additional degraders and ridge filters.
In active scanning systems, beam interactions with the patient's body are the only significant source of secondary radiation, whereas in passive scattering beam lines
there are a number of additional collimators, and ridge filters in which secondary radiation is produced.
The out-of-field absorbed doses measured in the Czech PTC were found to be lower and more homogenously distributed than those measured in Dubna.
The main cause of the difference is scattering of the primary beam on the elements of beam formation in the therapy room of JINR.
|
P15-2015-33 (22.385.898)
Didyk A.Yu., Wi niewski R., Semin V.A. niewski R., Semin V.A.
The Synthesis of Microparticles in Helium at a Pressure of 2.4 kbar with a Palladium Rod inside
HeHPC under Irradiation by Braking  -Rays with a Maximum Energy of 10 MeV -Rays with a Maximum Energy of 10 MeV
A helium high-pressure chamber (2.4 kbar) with a palladium rod inside was exposed to
braking  -rays with energies up to 10 MeV during -rays with energies up to 10 MeV during 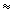 3.5 3.5  105 s. With the opening of the chamber, more
than 10 particles with the size of about 1 mm spilled out, and on the surface of the
entrance window (EW) a set of objects with the element composition
from nitrogen to barium were found. The outer surfaces of EW were covered with a greenish-yellowish
patina of complex composition. 105 s. With the opening of the chamber, more
than 10 particles with the size of about 1 mm spilled out, and on the surface of the
entrance window (EW) a set of objects with the element composition
from nitrogen to barium were found. The outer surfaces of EW were covered with a greenish-yellowish
patina of complex composition.
|
E13-2015-35 (647.226)
Azaryan N. et al.
The Precision Laser Inclinometer Long-Term Sensitivity in Thermo-Stabilized Conditions
The paper presents the latest results of testing of the Precision Laser
Inclinometer in thermostable conditions in Transport Tunnel TT1 at CERN.
Restrictions of the inclinometer's sensitivity in different frequency ranges
have been obtained: 10-6 rad for 10-6-10-4Hz and ~ 10-10 rad for 0.01-1 Hz.
Comparative measurements with two independent inclinometers have been
made and their seismograms almost coincide with each other. The signal
of action of tunnel boring machine has been registered.
|
P10-2015-38 (4.696.444)
Kirilov A.S., Petukhova T.B.
The Set of Components to Create GUI for Neutron Instrument Control Systems on the Base of PyQt
The work is dedicated to the set of visual components (widgets), which facilitates the development of graphical user interface (GUI)
to control the measurements on neutron instruments with software package Sonix+. The kit components correspond to the basic functions of the user interface
for managing the measurement and visualization of spectra, as well as provide program upload/download for the package components and a number of other functions.
The set is used in the development of the universal GUI and tuning programs for instruments of the IBR-2, as well as specialized GUI for some instruments at other centers.
|
P10-2015-39 (677.692)
Kirilov A.S., Murashkevich S.M., Petukhova T.B.
Adaptation of Sonix+ to Control the D3 Diffractometer
The work is devoted to the adaptation of the Sonix+ software tool kit to
control the powder diffractometer D3 at one of the beams of the IVV-2M
reactor at the Neutron Complex for Materials Research in the Institute of
Metal Physics (Zarechny). Sonix+ was designed for instruments at the IBR-2
reactor using the time-of-flight mode of spectra accumulation. However, the
underlying solutions simplified the software adaptation for use at
stationary reactors.
|
P10-2015-40 (715.068)
Kirilov A.S.
New Versions of Instrument Tuning Program and Visualization of Spectra for Reflectometers at the IBR-2 Reactor
The article is devoted to the main features of
the tuning program (ICE) and the spectra visualization program
(SpectraViewer), used at reflectometers of the IBR-2, FLNP, JINR. The ICE
program is implemented as an add-on for the control software Sonix+ and is
designed to adjust the instrument before the main measurement. The
SpectraViewer program is also used at other instruments. Programs have been
written using the PyQt and the graphics library matplotlib.
|
E6-2015-41 (380.166)
Izosimov I.N.
Isospin Quantum Number and Structure of the Excited States in Halo
Nuclei. Halo-Isomers
It has been shown that isobar-analog (IAS), double
isobar-analog (DIAS), configuration (CS), and double configuration
states (DCS) can simultaneously have n-n, n-p, and p-p halo components in their wave
functions. Differences in halo structure of the excited and ground states
can result in the formation of isomers (halo-isomers). Both the Borromean
and tango halo types can be observed for n-p configurations of atomic
nuclei. The structure of the ground and excited states with different isospin
quantum number in halo-like nuclei is discussed. B(M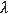 ) and B(E ) and B(E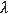 ) for ) for  -transitions
in 6-8Li,
8-10Be, 8,10,11B, 10-14C, 13-17N, 15-17,19O, and 17F
are analyzed. Special attention is given to nuclei whose ground state does
not exhibit halo structure, but the excited state may have one. -transitions
in 6-8Li,
8-10Be, 8,10,11B, 10-14C, 13-17N, 15-17,19O, and 17F
are analyzed. Special attention is given to nuclei whose ground state does
not exhibit halo structure, but the excited state may have one.
|
P16-2015-45 (722.596)
Beskrovnaia L.G., Komochkov M.M., Maurach N.A.
Double Differential Cross Section for Neutron Production in Carbon-Nucleus Interactions at Energies of 135-400 MeV/nucleon, Obtained Using
the Phenomenological NNEP Method
In this work we calculated the double differential cross sections for
neutron production in 12C-A interactions on the basis of the
phenomenological NNEP method and made their comparison with experimental
data. Comparison was performed to verify the semi-empirical method for the
experimental data and to determine the possibility of using the
semi-empirical method for the prediction of radiation situation in the
carbon-ion medical accelerator in the energy range of carbon ions 135-400 MeV/nucleon. There is a good agreement between the calculated and
experimental data.
|
P13-2015-47 (508.853)
Pepelyshev Yu.N., Tsogtsaikhan Ts., Ososkov G.A.
Application of Cluster Analysis and Autoregressive Neural Networks for the Noise Diagnostics of IBR-2M Reactor
The pattern recognition methodologies and artificial neural networks were used widely for the reactor noise diagnostics.
It is very important for the pulsed reactor of periodic operation IBR-2M (Dubna) which has a high sensitivity
to reactivity fluctuations (40 times higher than stationary reactors with a uranium fuel).
It is shown that the power noise is subsequently divided into four stable clusters.
The noise transition region is formed by asymptotically increasing vibration
of the moving reflectors in the process of their heating after maximum power is reached. The study of slow processes
shows that the nonlinear autoregressive neural network predicts an error of ~ 5 %. NAR model allows predicting
changes in reactivity caused by the fluctuation of liquid sodium flow rate up to two days of reactor operation.
|
E13-2015-48 (1.528.640)
Chirikov-Zorin I., Krumshtein Z., Olchevski A.
Design of a Photodetector Unit of a New Shashlyk EM Calorimeter for COMPASS II
A nine-channel photodetector unit with micropixel avalanche photodiodes
(MAPD) and precision thermostabilization based on the compact Peltier module
was designed and constructed. MAPD-3N with a high pixel density of 1.5  104 mm-2
and area 3 104 mm-2
and area 3 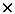 3 mm produced by Zecotek were used. 3 mm produced by Zecotek were used.
|
E13-2015-49 (3.132.219)
Budagov J. et al.
Combined Adapter for the Upgraded Cryomodule of the Linear Collider
As part of work on the ILC Project,
research was performed on the development of
techniques to simplify and make reliable and cheaper the construction of the
cryomodules that are core of the main linac. In the current ILC TDR design
both the helium vessel surrounding the niobium RF cavities and the connected
pipes which channel the exhaust helium gas are made of expensive titanium,
one of the few metals that can be welded to niobium by the electron beam
technique.
In this paper we describe the construction and performance of transition
elements, obtained by explosion welding, that can couple the niobium cavity
with a stainless steel helium vessel, thus saving large amounts of titanium.
A new design, including a minimal titanium intermediate layer,
has been built. Preliminary tests yielded a
very strong resistance of the bond to extreme temperature shocks from
electron beam welding to exposure to cryogenic temperatures.
The developed
technology allows a trimetallic billet for manufacturing an adapter to be made such that the niobium-titanium bond is free
of intermetallic compounds and the effect of the difference in the linear expansion coefficients of
the ensemble components is eliminated.
|
P13-2015-50 (1.024.723)
Piyadin S.M. et al.
The System of High-Voltage Power PMT for Experiments at the JINR Nuclotron
An 8-channel high-voltage power system based on the use of the module
«Wenzel Elektronik N1130» is described. Specifications of control modules 8DAC-12 and 8ADC-14
designed for the high-voltage systems in CAMAC standard are presented. This system is designed to provide the power for the detectors
used in physics experiments at the JINR Nuclotron.
|
P14-2015-52 (297.865)
Alexakhin V.Yu. et al.
Determination of Elemental Composition of Rocks with Tagged Neutron Method
The technology for determination of the elemental composition of rocks on
the basis of the tagged neutron method is tested in the field conditions. We
discuss the results of experimental studies of rock samples irradiated by
tagged fast neutrons with an energy of 14.1 MeV. The source of the fast
neutrons is a portable neutron generator with a built-in silicon
alpha-detector. Characteristic gamma rays resulting from the inelastic
interaction of neutrons with nuclei of chemical elements that make up the
geological rocks and minerals are registered by gamma-detectors based on BGO
crystals. Comparison of the results on the elemental composition of rocks
obtained by the tagged neutron method with reference values is discussed.
|
P18-2015-55 (905.491)
Bashashin M.V. et al.
NICA Project Management Information System
The science projects growth, changing of the efficiency criteria during the
project implementation require not only increasing of the management
specialization level but also pose the problem of selecting the effective
planning methods, monitoring of deadlines and interaction of participants
involved in research projects. This paper is devoted to choosing the project
management information system for the new heavy-ion collider NICA (Nuclotron
based Ion Collider fAcility). We formulate the requirements for the project
management information system with taking into account the specifics of the
Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR, Dubna, Russia) as an
international intergovernmental research organization, which is developed on
the basis of a flexible and effective information system for the NICA
project management.
|
D10-2015-56_e (327.763)
Dmitriev A.Yu., Dmitriev F.A.
Automation of Registration of Sample Weights for High-Volume Neutron Activation Analysis
at the IBR-2 Reactor of FLNP, JINR
The "Weight" software tool was created at FLNP JINR to
automate the reading of analytical balance readouts and saving these
values in the NAA database. The analytical balance connected to the personal
computer is used to measure weight values. The "Weight" software tool
controls the reading of weight values and the exchange of information with
the NAA database. The weighing process of a large amount of samples is
reliably provided during high-volume neutron activation analysis.
|
P11-2015-58 (756.742)
Akishin P.G., Sapozhnikov A.A.
Automatic Generation of Three-Dimensional Grids
This paper discusses the generation of three-dimensional meshes oriented to
the finite element method. The algorithm used is based on representation of
the problem domain as a combination of standard macroblocks with initial
generation of a two-dimensional mesh on their boundary followed by
generation of a three-dimensional mesh in each block individually. The
possibility of generating meshes using the developed finite element mesh
generator {3DFEMMesh} is discussed.
|
P11-2015-60 (374.473)
Batgerel B. et al.
Mathematical Simulation of Gas Nanocluster Generation Processes for Xenon
This work is devoted to the investigation of temperature regime effects on the process of xenon nanocluster generation and evolution.
Mathematical simulation was based on the molecular dynamics method. Numerical calculations were made for various values of the cooling rate and various
initial xenon densities. As a result of computer simulation it was found that mass distributions of generated nanoclusters depend on the choice of evolution
conditions, initial values of xenon density and a rate of the system cooling.
|
P13-2015-61 (473.718)
Bondarenko G.G. et al.
Investigation of the Distribution of Deuterium and Hydrogen in the
Ta|CD2|Ta, Ta|Ta|СD2|Ta|Ta and Nb|CD2|Nb Assemblies after Exposure to High-Temperature
Argon Plasma at the PF-4 Set-Up
Assemblies of Ta|CD2|Ta, Ta|Ta|CD2|Ta|Ta and
Nb|CD2|Nb foils were
irradiated by 30 pulses of high-temperature argon plasma on the "Plasma
Focus" (PF-4) set-up. After irradiation, all the samples of foils were
investigated by registration of hydrogen and deuterium recoils (ERDA) on
both sides of each foil. Redistribution of hydrogen and deuterium in the
stacks of foils was found. Experimental results on ultra-deep penetration of
light gaseous impurities as hydrogen and deuterium are explained based on
the effects of shock waves on the foil and accelerated diffusion by an
external force.
|
P13-2015-62 (814.608)
Didyk A.Yu. et al.
The Distribution of Deuterium and Hydrogen in Zr, Ni and Ti Foil
Assemblies after Exposure to Pulsed High-Temperature Deuterium Plasma
The accumulation and redistribution of deuterium and hydrogen in the
assemblies of two high-purity Ni, Ti or Zr foils under high-temperature
pulsed action of deuterium plasma at the "Plasma Focus" (PF-4) set-up was
studied by the method of registration of recoil deuterons and protons
(ERDA). It was found that redistribution of implanted deuterium and hydrogen
gas impurities in the assemblies of the studied Zr, Ni and Ti foils takes
place to large depths greatly exceeding the ranges of deuterium ions (at
their maximum speeds of up to 108cm/s). As in earlier studies, the
observed phenomenon can be explained by the redistribution of the implanted
deuterium and hydrogen under the influence of powerful shock waves formed in
the metal foil under the action of high-temperature pulsed plasma, and (or)
the acceleration of the diffusion of deuterium and hydrogen atoms under the
influence of compression-expansion waves at the front of the shock wave
accompanied by redistribution of hydrogen and deuterium to great depths.
|
P10-2015-63 (280.777)
Zlokazov V.B., Morozov V.A., Morozova N.V.
VMRIA - Program for Definition of the Scintillator Decay Times at Processing 3D(E-T-N) Distributions
The program of determination of the scintillator decay time with use of an autocorrelated time spectrometer is submitted.
The result of measurement of the LaBr3:Ce decay time is given -  = 22.5(2) ns. = 22.5(2) ns.
|
P18-2015-66 (165.875)
Molokanova L.G., Orelovich O.L., Chukova S.N.
Preparation of Cleavages of Polyethylene Naphthalate Track Membranes for Investigations Using Scanning Electron Microscope
The possibility of preparing cleavages of polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) track membrane samples has been investigated for exploring the pore channel
structure along one surface to another using scanning electron microscope. On account of high radiation and thermal resistance of polyethylene naphthalate films,
thermal, ultraviolet, and radiation treatment methods used for embrittlement of such polymers as polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polycarbonate (PC),
and polypropylene (PP) are not suitable for PEN. It has been found that only exposing samples to concentrated nitric acid fumes for 1.5 months allows
embrittlement of the PEN film so that it can be broken in such a way as to obtain even-shaped cleavages.
|
E10-2015-67 (137.747)
Bogdanova N.B., Todorov S.T., Ososkov G.A.
Use of Orthonormal Polynomial Expansion Method to the Description of the Energy Spectra of Biological Liquids
Orthonormal polynomial expansion method (OPEM) is applied to the data obtained by the method of energy spectra to the liquid
of the biomass of wheat in the case when herbicides are used. Since the biomass of a biological object contains liquid composed mainly of water,
the method of water spectra is applicable to this case as well. For comparison, the similar data obtained from control sample consisting of wheat
liquid without the application of herbicides are shown. The total variance OPEM is involved including errors in both dependent and independent variables.
Special criteria are used for evaluating the optimal polynomial degree and the number of iterations. The presented numerical results show good agreement with
the experimental data. The developed analysis frame is of interest for future analysis in theoretical ecology.
|
E6-2015-69 (226.474)
Maslov O.D.
The Concentration of Short-Lived Spontaneously Fissioning Nuclides from Iron-Manganese Nodules
The paper reports on the observation of the spontaneously fissioning nuclides as a result of hydrochemical and high-temperature
processing of iron-manganese nodules. The spontaneous fission in the samples obtained was measured by the track method using electrochemical etching,
and nuclides with T1/2 = 15 d, T1/2 = 25 d (similar in chemical properties to Os) and
T1/2 = 62 d (similar in chemical properties to Pb and Ra) were detected.
|
P15-2015-71 (1.610.459)
Didyk A.Yu., Gulbekyan G.G., Myshinskiy G.V.
SEM and RMPA Research of Synthesized Particles
and Objects in Dense Xenon (270 bar) Irradiated
by Braking  -Rays with a Maximum Energy of 10 MeV -Rays with a Maximum Energy of 10 MeV
Natural xenon at an initial pressure of 270 bar in a special chamber (XeHPC) was irradiated for 43 h
(1.548  105 s) by braking 105 s) by braking  -rays with a threshold energy of 10 MeV at electron accelerator
MT-25 at an average intensity of the beam of 20-22 -rays with a threshold energy of 10 MeV at electron accelerator
MT-25 at an average intensity of the beam of 20-22  A.
After opening of XeHPC both internal chambers with all structures and particles, but without gas, were
measured on A.
After opening of XeHPC both internal chambers with all structures and particles, but without gas, were
measured on  -germanium detector (Canberra) in series with the detector background measurement
to 15 h each measurement. -germanium detector (Canberra) in series with the detector background measurement
to 15 h each measurement.  -spectra of short-lived isotopes, formed as a result of exposure,
were obtained and processed. Visual inspection of the inner chambers surfaces showed visible brownish-yellowish coating
of significant thickness.
X-ray microprobe analysis (RMPA) and SEM studies allowed us to determine the composition of the synthesized
particles and structural objects. -spectra of short-lived isotopes, formed as a result of exposure,
were obtained and processed. Visual inspection of the inner chambers surfaces showed visible brownish-yellowish coating
of significant thickness.
X-ray microprobe analysis (RMPA) and SEM studies allowed us to determine the composition of the synthesized
particles and structural objects.
|
P15-2015-72 (1.934.257)
Didyk A.Yu., Gulbekyan G.G., Myshinskiy G.V.
A Study of the Element Composition and Surface Structure Changes
during Irradiation of Dense Xenon (270 atm) by Braking  -Rays with a
Maximum Energy of 10 MeV -Rays with a
Maximum Energy of 10 MeV
Natural xenon at an initial pressure of 270 atm in the high-pressure chamber (XeHPC) was irradiated for 43 hours by braking
 -rays with a threshold energy of 10 MeV at the MT-25 electron accelerator at an average beam intensity of 20-22 -rays with a threshold energy of 10 MeV at the MT-25 electron accelerator at an average beam intensity of 20-22  A. The results on gamma
activation analysis of the relevant short-lived radionuclides are presented. When opening the XeHPC, the internal assembly without xenon was installed
on the precision germanium A. The results on gamma
activation analysis of the relevant short-lived radionuclides are presented. When opening the XeHPC, the internal assembly without xenon was installed
on the precision germanium  -detector (HPGe-Canberra) for 15-hour measurements of -detector (HPGe-Canberra) for 15-hour measurements of  -spectra of radionuclides formed in XeHPC, and the background.
Visual inspection of the inside of the assembly revealed that its surface was covered with a thin film of greenish-yellow color. SEM studies and X-ray probe
microanalysis (XRPMA) have allowed us to determine the composition of the synthesized microparticles. To explain the observed anomalies in the formation
of new elements in the microparticles and microobjects, possible nuclear fission and fusion reactions are presented. -spectra of radionuclides formed in XeHPC, and the background.
Visual inspection of the inside of the assembly revealed that its surface was covered with a thin film of greenish-yellow color. SEM studies and X-ray probe
microanalysis (XRPMA) have allowed us to determine the composition of the synthesized microparticles. To explain the observed anomalies in the formation
of new elements in the microparticles and microobjects, possible nuclear fission and fusion reactions are presented.
|
P3-2015-75 (408.420)
Eganova I. A., Kallies W.
On Modeling of the Neutron in Classical Physics: A Methodical Review
In the given work it is shown that the question about the neutron as a non-elementary particle started recently
by B.V. Vasiliev in JINR Communication P3-2014-77 demands to take into conside-ration the entire system of the logically relevant and based
on experiments knowledge which was found by M. Gryzinski in the deterministic atomic physics, and also the two interpretations declared
in this communication are refuted: 1) of an electron-like elementary particle in the neutron structure that has no magnetic properties and
2) of the planetary-type model for a neutron with point objects.
|
P4-2015-76 (276.221)
Pupyshev V.V.
Two-Dimensional Coulomb Scattering of a Quantum Particle. Low-Energy Asymptotics
By assumption, a charged quantum particle moves in the
two-dimensional plane of the three-dimensional configuration space
and is scattered by a fixed Coulomb center lying in the same plane.
The expansions of the wave-functions and all radial wave-functions
of this particle over integer powers of the wave number and the
Bessel functions of real order are derived. It is proven that the
finite sums of these expansions are the asymptotics of the
wave-functions in the low-energy limit.
|
E11-2015-77 (317.249)
Mi o L., T o L., T r r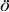 k Cs. k Cs.
Fast Algorithm for Spline Surfaces
We propose a fast algorithm for evaluation of interpolating spline surfaces with C2 continuity over
uniform grids that utilizes a recently proved approximation property between biquartic and bicubic polynomials. Thanks to this property,
the size of the tridiagonal systems are reduced to the half. The comparison of the proposed algorithm with the classical de Boor's one shows
that the former needs less multiplication operations and its explicit formulas can be parallelized automatically.
|
E3-2015-81 (145.516)
Karamian S.A., Aksenov N.V., Bozhikov G.A.
Double-Neutron Capture Reaction and Natural Abundance of
183W, 195Pt, and 199Hg Isotopes
The database for neutron cross sections is well
developed over the nuclide chart for stable isotopes and not as much for the
radioactive species. Double-neutron capture experiments could be productive
to supply more data. Time-integrated mean flux of slow neutrons reaches a
value of 2.3  1012 cm-2 1012 cm-2  s-1 at the irradiation port near the
active zone of the IBR-2 pulsed reactor of JINR. This is enough to detect the
double-neutron capture products by the activation method. A high capture
cross section is deduced in the present experiment for intermediate
radioactive 182Ta and 194Ir target nuclides. Together with the
known one for 198Au, these values may prove an essential role of double-neutron capture process for nucleosynthesis of 183W, 195Pt, and
199Hg isotopes at stellar conditions. s-1 at the irradiation port near the
active zone of the IBR-2 pulsed reactor of JINR. This is enough to detect the
double-neutron capture products by the activation method. A high capture
cross section is deduced in the present experiment for intermediate
radioactive 182Ta and 194Ir target nuclides. Together with the
known one for 198Au, these values may prove an essential role of double-neutron capture process for nucleosynthesis of 183W, 195Pt, and
199Hg isotopes at stellar conditions.
|
E1-2015-83 (902.667)
Tokarev M.V. (on behalf of the STAR Collaboration)
Self-Similarity of Negative Particle Production from the Beam Energy Scan Program at STAR
We present the spectra of negative charged particle production in Au + Au collisions
from STAR for the first phase of the RHIC Beam Energy Scan Program
measured over a wide range
of collision energy 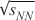 = 7.7-200 GeV,
and the transverse momentum of produced particles
in different centralities at | = 7.7-200 GeV,
and the transverse momentum of produced particles
in different centralities at |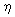 |< 0.5.
The spectra demonstrate a strong dependence on
the collision energy which enhances with pT.
An indication of self-similarity of negative charged particle
production in Au + Au collisions is found.
The constituent energy loss as a function of the energy and centrality
of collisions and transverse momentum of the inclusive particle
was estimated in the z-scaling approach.
The energy dependence of the model parameters - the fractal
and fragmentation dimensions and "specific heat" - was studied. |< 0.5.
The spectra demonstrate a strong dependence on
the collision energy which enhances with pT.
An indication of self-similarity of negative charged particle
production in Au + Au collisions is found.
The constituent energy loss as a function of the energy and centrality
of collisions and transverse momentum of the inclusive particle
was estimated in the z-scaling approach.
The energy dependence of the model parameters - the fractal
and fragmentation dimensions and "specific heat" - was studied.
|
P19-2015-89 (399.834)
Koltovaya N.A.
Cyclin-Dependent Kinase CDK1/CDC28 and Checkpoints
The genetic instability induced by defects in the cell cycle progression contributes to
different human diseases, particularly neoplastic transformation. The
control mechanisms of correct cell cycle progression are the most studied in
the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, in which checkpoint was first discovered. Many components
of these processes have been identified by now. Here, the role of the
central kinase of cell cycle CDK1/CDC28 is considered in checkpoint in different phases.
|
E7-2015-91 (230.624)
Volkov V.V., Kalandarov Sh.A.
Interpretation of the Low-Energy Fission Process in the Framework of Dinuclear System Conception
The possibility of the interpretation of fission of heavy nuclei as the process of formation, evolution,
and decay of a dinuclear system is discussed. The interpretation is based on the nuclear interaction data obtained in heavy-ion nuclear physics investigations.
|
E3-2015-94 (360.855)
Telezhnikov S.A. et al.
Precise Determination of Neutron Binding Energy of 64Cu
The neutron binding energy in 64Cu has been accurately measured in thermal neutron capture.
A composite target of natural Cu and NaCl was used on a high-flux neutron beam using a large measuring time.
The  -ray spectrum emitted in the (n, -ray spectrum emitted in the (n, )
reaction was measured with a HPGe detector in large statistics (up to 106 events per channel).
Intrinsic limitations of HPGe detectors, which restrict the accuracy of energy calibration, were determined. The value Bn
of 64Cu was determined as 7915.867(24) keV. )
reaction was measured with a HPGe detector in large statistics (up to 106 events per channel).
Intrinsic limitations of HPGe detectors, which restrict the accuracy of energy calibration, were determined. The value Bn
of 64Cu was determined as 7915.867(24) keV.
|
P13-2015-95 (509.003)
Omelyanenko M.M.
Current Regulation Unit CR-01 with Power Pass Transistor Bank in Linear Mode
The current regulation unit with a power pass transistor in linear mode is described.
The unit named CR-01 was designed for building high-speed low-noise precision current regulators for low-voltage load, for example,
to supply magnet elements of charged particle accelerators. To build the current regulator using CR-01 unit, an external D.C. power supply is needed.
The required value of output current can be achieved by parallel connection of proportionate number of units. For precision current regulation an overall
current feedback must be applied.
|

