| 2007 |
|
P9-2007-2 (803.523)
Meshkov I.N., Pavlov V.N., Sidorin A.O., Yakovenko S.L.
The Cryogenic Source of Slow Monochromatic Positrons
The cryogenic source of slow monochromatic positrons based on the 22Na
isotope has been designed and constructed at JINR. Positrons emitted from
radioactive source 22Na have a very broad energy spectrum up to
0.5 MeV. To generate monochromatic beam of slow positrons the solid neon is
used as a moderator. The solid neon allows forming slow positron beam of the
energy of 1.2 eV at the spectrum width of 1 eV. The efficiency of moderation
is 1% of total positron flux.
|
E1-2007-4 (1.855.957)
Fedorishin J., Vokal S.
Search for the Ring-Like Structures in the Emission of Secondary Particles
in Central 197Au Collisions with Emulsion
Nuclei at 11.6A GeV/c
Angular spectra of the relativistic secondary particles produced
in Au + Em
nuclear collisions at 11.6A GeV/c are analyzed by the method of continuous
wavelet transform in order to search for the ring-like structures
which could indicate either the production of Cherenkov gluons
or the occurrence of Mach shock waves
in excited nuclear matter. The analysis is based
on the assumption that the presence of the above-mentioned effects would be
manifested by excess of particles at some characteristic pseudorapidities.
In addition, the involved particles are expected to be azimuthally
uniformly distributed.
The irregularities are revealed in the wavelet pseudorapidity
spectra in the scale pseudorapidity region up to 0.5.
These irregularities are interpreted as the preferred pseudorapidities of
groups of emitted particles.
The performed study of the azimuthal structure of the above-mentioned
pseudorapidity
irregularities suggests that they are not related to the sought ring-like
structures.
|
E7-2007-5 (401.351)
Popeko L.A. et al.
Thick Si(Li) Coaxial Detectors for Registration of Intermediate Energy Heavy
Ions
Thick coaxial Si(Li) detectors are fabricated to register long-range
high-ionizing reaction products with high resolution. It is shown that
charge collection efficiency and resolution strongly depend on cooling
temperature and magnitude of voltage applied. The test experiments have
shown that coaxial detectors are capable of registering the intermediate energy
heavy ions with 0.5-0.7% resolution. The energy losses in entrance window
of the detector are less than 100 keV.
|
P4-2007-6 (377.377)
Lukyanov K. V. et al.
Microscopic Approach to the Heavy Ion Scattering with Excitation of Nuclear Collective States
The density distribution of a deformed target nucleus is presented as
the spherically symmetrical (l=0) and the deformed
(l=2) parts. On this basis, the corresponding parts U0 and
Uint of a double-folding microscopic nucleus-nucleus optical
potential are obtained. Then, with these potentials and using the
coupled-channel method, the elastic and inelastic amplitudes are calculated
of the 17O heavy ion scattering on various target nuclei with
excitation of their collective 2+ states. Besides, the same cross-sections
are calculated basing on the adiabatic approach of the eikonal approximation,
where inelastic amplitude is the linear function of Uint(2). Both
results are compared with experimental data, and the capabilities of them to
search deformation parameters of nuclei are discussed.
|
E1-2007-7 (724.974)
M.I. Krivopustov, A.V. Pavliouk, A.I. Malakhov, A.D. Kovalenko,
I.I. Mariin, A.F. Elishev, J. Adam, A. Kovalik, Yu.A. Batusov, V.G. Kalinnikov, V.B. Brudanin, P. Chaloun,
V.M. Tsoupko-Sitnikov, A.A. Solnyshkin, V.I. Stegailov, Sh. Gerbish,
O. Svoboda, Z. Dubnicka, M. Kala, M. Kloc, A. Krasa, A. Kugler, M. Majerle, V. Wagner,
R. Brandt, W. Westmeier, H. Robotham, K. Simon,
M. Bielewicz, S. Kilim, M. Szuta, E. Strugalska-Gola, A. Wojciechowski,
S.R. Hashemi-Nezhad, M. Manolopoulou, M. Fragopolou, S. Stoulos, M. Zamani-Valasiadou,
S. Jokic, K. Katovsky, O. Schastny, I.V. Zhuk, A.S. Potapenko, A.A. Ternova, Zh.A. Lucashevich,
V.A. Voronko, V.V. Sotnikov, V.V. Sidorenko, W. Ensinger, D. Severin,
S. Batzev, L. Kostov, Ch. Stoyanov, O. Yordanov, P.K. Zhivkov,
V. Kumar, M. Sharma, A.M. Khilmanovich, B.A. Marcinkevich, S.V. Korneev, Ts. Damdinsuren, Ts. Togoo, H. Kumawat
About the First Experiment on Investigation of 129I, 237Np, 238Pu and 239}Pu Transmutation at the Nuclotron 2.52 GeV Deuteron Beam in Neutron Field Generated in U/Pb-Assembly "Energy Plus Transmutation"
Preliminary results of the first experiment with deuteron beam with energy
2.52 GeV at the electronuclear setup which consists of Pb-target (diameter
8.4 cm, length 45.6 cm) and natU-blanket (206.4 kg), transmutation
samples of 129I, 237Np, 238Pu and 239Pu (radioecological
aspect) are described.
Hermetically sealed samples in notable amounts are gathered in atomic
reactors and setups of industries which use nuclear materials and nuclear
technologies were irradiated in the field of neutrons produced in the
Pb-target and propagated in the natU-blanket. Estimates of
transmutations were obtained as result of measurements of gamma activities
of the samples.
The information about the space and energy distribution of neutrons in the
volume of the lead target and the uranium blanket was obtained with help of
sets of activation threshold detectors (Al, Co, Y, I, Au, Bi and others),
solid-state nuclear track detectors, 3He neutron detectors and nuclear
emulsion. Comparison of the experimental data with the results of simulation
with the MCNPX program was performed.
|
P7-2007-8 (387.590)
Artyukh A. G. et al.
Reconstruction of Parameters of Cluster Break-Up of Light Nuclei
Kinematics of the two-body Coulomb break-up of the prototype 11В nucleus into the
fragments He and Li is discussed. The analysis of factors influencing the measurement accuracy of break-up parameters
is presented. Estimates of measurement spreads for break-up parameters are deduced to use them for reconstruction
of cluster break-up primary parameters. The method of determination of unknown contamination in the target is discussed.
The procedure is used to separate the true events from the backgrounds. The background factors occurring in the
fragmentation reactions of heavy ions are described. The random coincidence rate from intensive loads of detectors
by parasitic products is estimated. The preliminary magnetic analysis of correlated clusters is proposed to reduce
the power flow background particles and to improve energy resolution.
|
P13-2007-9 (236.431)
Latuszynski A. et al.
On-Line Thermoemission Ion Source Efficiency
The calculations of thermoemission ion source efficiency were performed for
different ionizer models. The calculations show that source efficiency is
strongly influenced by geometry and dimensions of the ionizer (its length
and the size of the extraction hole). The value of extraction voltage (i.e.
voltage between the ionizer and the extraction electrode) is also very
important. The construction of the ion source should enable electric field
to penetrate deep into the ionizer volume.
|
P11-2007-11 (317.930)
Kalinnikov V. A.
New Algorithms of Discrete Transformations for Digital Spectral
Measurement of Non-Stationary Signals in Real Time
New methods of the discrete transformations for realization of reliable
spectral measurement of non-stationary signals in real time are considered.
Features of the offered mathematical methods allow one to realize in real
time effective algorithms of digital processing of signals, such as
calculation of spectral density of capacity, correlation parameters, digital
convolution, etc. which cannot be executed by classical methods of
transformations because of time restrictions. Methods of statistical
processing of dynamic modules of Fourier factors allow obtaining an
authentic spectral rating of non-stationary signals in real time.
|
P14-2007-12 (332.169)
Mamedov T.N. et al.
Investigation of the Boron Acceptor Impurity in a Synthetic Diamond by the  -SR-method -SR-method
The results in the investigation of boron acceptor centers in a synthetic
diamond by the  -SR-method are presented. Two IIa and IIb type
monocrystal samples were studied. Atoms of -SR-method are presented. Two IIa and IIb type
monocrystal samples were studied. Atoms of  -B-acceptor impurity in the
sample were created by implantation of negative muons. The polarization of
muons was studied in a magnetic field of 2.5 kG transverse to the direction
of the muon spin in the temperature range 4.2-300 K. -B-acceptor impurity in the
sample were created by implantation of negative muons. The polarization of
muons was studied in a magnetic field of 2.5 kG transverse to the direction
of the muon spin in the temperature range 4.2-300 K.
It was found that  -B acceptor in a diamond is formed mostly in
diamagnetic (ionized) state.
The hole capture rate by an ionized acceptor center in IIa and IIb types of a synthetic diamond was found at temperatures T > 80 K and T > 50 K
respectively. -B acceptor in a diamond is formed mostly in
diamagnetic (ionized) state.
The hole capture rate by an ionized acceptor center in IIa and IIb types of a synthetic diamond was found at temperatures T > 80 K and T > 50 K
respectively.
|
2007-13 (1.519.355)
Brief Review of Topmost Scientific Results Obtained in 2006 at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research
|
E17-2007-14 (261.994)
Patrick A. E.
Spherical Model in a Random Field
We investigate the
properties of the Gibbs states and thermodynamic observables of
the spherical model in a random field. We show that on the
low-temperature critical line the magnetization of the model is
not a self-averaging observable, but it self-averages
conditionally. We also show that an arbitrarily weak homogeneous
boundary field dominates over fluctuations of the random field
once the model transits into a ferromagnetic phase. As a result, a
homogeneous boundary field restores the conventional
self-averaging of thermodynamic observables, like the
magnetization and the susceptibility. We also investigate the
effective field created at the sites of the lattice by the random
field, and show that at the critical temperature of the spherical
model the effective field undergoes a transition into a
ferromagnetic phase with long-range correlations ~ r 4-d.
|
P2-2007-16 (147.911)
Beshtoev Kh.M.
Virtual Transitions (Oscillations) of
 
 K K Mesons Caused by Strangeness Violating in the Weak Interactions Mesons Caused by Strangeness Violating in the Weak Interactions
At strangeness violation by the weak interactions there should arise
mixings (transitions) between   and K and K mesons. Since
masses of these hadrons differ, these mixings (transitions)
should be virtual. The nondiagonal mass term responsible for such
mixing is computed. It is shown that two types of transitions can
take place between these mesons: mesons. Since
masses of these hadrons differ, these mixings (transitions)
should be virtual. The nondiagonal mass term responsible for such
mixing is computed. It is shown that two types of transitions can
take place between these mesons:   meson is converted into
K meson is converted into
K meson with mass changing, and without mass changing
(K meson with mass changing, and without mass changing
(K meson has mass of meson has mass of   ). Probabilities of vacuum ). Probabilities of vacuum
 
 K K virtual transitions
(oscillations) with taking into account of virtual transitions
(oscillations) with taking into account of   -meson decays
are calculated. The estimation of extreme distance R for
observation of -meson decays
are calculated. The estimation of extreme distance R for
observation of  
 K K transition is made.
The kinematics of process of K transition is made.
The kinematics of process of K meson productions, at their
transitions on mass shell, is investigated for determination of
optimum energies for observation of these transitions. meson productions, at their
transitions on mass shell, is investigated for determination of
optimum energies for observation of these transitions.
|
E10-2007-17 (383.239)
E.P. Akishina, T.P. Akishina, V.V. Ivanov, A.I. Maevskaya, O.A. Afanas'ev
Electron/Pion Identification in the CBM TRD Using a Multilayer Perceptron
The problem of electron/pion identification in the CBM experiment
based on the measurements of energy losses and transition radiation
in the TRD detector is discussed. We consider a possibility to solve
such a problem by applying an artificial neural network (ANN). As input
information for the network we used both the samples of energy losses
of pions or electrons in the TRD absorbers and the "clever" variable
obtained on the basis of the original data. We show that usage of this new
variable permits one to reach a reliable level of particle recognition no
longer than after 10-20 training epochs; there are practically no
fluctuations against the trend, and the needed level of pions
suppression is obtained under the condition of a minimal loss of electrons.
|
P18-2007-18 (399.805)
Baldin A. A., Baldina E. G., Volkov A. A.
The Physics with Lasers: from Relativistic Particle Production to Material Processing
The physics with lasers is an extremely wide field of fundamental and
applied research. The uniqueness of this field at present is that among with
recently discovered fundamentally new phenomena, its inherent element is the
applied component. In this work, a brief overview of activities in three
fields of physics with lasers at LHE JINR in the framework of the
international collaboration MARUSYA is given. These fields cover the
relativistic collective phenomena of particle and radiation production with
ultrashort laser pulses, ion and X-ray interaction with hot dense plasmas,
and nonlinear processes at laser material processing.
|
P9-2007-20 (1.470.174)
Gikal B. N. et al.
Cyclotron Based Complex IC-100 for Scientific and Applied Research
The complex based on the cyclotron IC-100 of the JINR Laboratory of Nuclear
Reactions (Dubna, Russia) provides industrial fabrication of nuclear
filters. After the modernization the cyclotron was equipped with
superconducting ECR-ion source as well as with axial injection system. The
specialized beam channel with two coordinates scanning system and equipment
for irradiation of polymer films has been installed in the implantation part
of the complex. High intensity heavy ion beams of Ne, Ar, Fe, Kr, Xe, I, W
have been accelerated to 1 MeV/nucleon energy. The investigation of
irradiated crystals features, irradiation of different polymer films have
been provided. Also a few thousands of square meters of track films with holes in
the wide range of densities have been produced. The cyclotron based complex
is capable of solving different kinds of scientific and applied problems as
well.
|
P14-2007-21 (570.145)
Balasoiu M. et al.
Magnetic Property Investigation of the Ferrofluid
by  SR-Spectroscopy on the DLNP JINR Phasotron SR-Spectroscopy on the DLNP JINR Phasotron
The  SR-method was applied to the study of the magnetic fluid
properties for the first time. The ferrofluid on the Fe3O4 basis
was investigated in the temperature range from 114 to 300 K at the zero and
transverse magnetic field conditions. The distinct SR-method was applied to the study of the magnetic fluid
properties for the first time. The ferrofluid on the Fe3O4 basis
was investigated in the temperature range from 114 to 300 K at the zero and
transverse magnetic field conditions. The distinct  SR-signal was
observed in both cases. In zero field measurements the drop in the
relaxation rate and polarization at T = 230 K to zero-level
followed by fast increasing of the latter in the temperature interval from
240 to 255 K were observed. SR-signal was
observed in both cases. In zero field measurements the drop in the
relaxation rate and polarization at T = 230 K to zero-level
followed by fast increasing of the latter in the temperature interval from
240 to 255 K were observed.
|
E3-2007-22 (201.546)
Sukhovoj A. M., Khitrov V. A.
Gamma-Decay of the Compound State and Change of Structure of the 124Te Excited Levels
Independent analysis of a large amount of data on the spectrum of
gamma-rays of the radiative capture of thermal neutrons in
123Te(S(ig Eg)/Bn = 0.49)
obtained in Rez made it possible to obtain new and reliable
information on the dependence of sums of radiative strength functions
of dipole gamma-transitions on the energy of levels excited by them.
These data, as does the level density in 124Te,
demonstrate a strong change of structure of the nucleus practically
for the whole region of the levels excited by a captured neutron.
As in the earlier studied nuclei (using data on the intensities
of two-step cascades), it is possible to reproduce the stated parameters
of the gamma-decay process to the accuracy of experiment only by
the models directly taking into account the coexistence and interaction
of the usual and superfluid component of the nuclear matter.
|
E3-2007-25 (612,2)
Khuukhenkhuu G. et al.
The Fast Neutron Induced (n, p) Reaction Cross Sections. Compound Reaction Mechanism
In the framework of the compound mechanism the general formula for fast
neutron induced and particle emission reaction cross section was deduced.
The evaporation model, constant nuclear temperature approximation,
semi-classical approach to an inverse reaction cross section and
Weizsacker's formula for nuclear binding energy were used.
For the systematic analysis of known experimental (n, p) cross sections
the obtained formula was used in the energy range from 6 to 16 MeV. It was found
that discrepancy between the theoretical and experimental (n, p) cross
sections increases with growth of the neutron relative excess parameter
(N-Z+1)/A. Levkovsky's conclusions were considered and revised for a wide energy range from 6 to 16 MeV.
|
E3-2007-26 (137,0)
Khuukhenkhuu G. et al.
The Fast Neutron Induced (n, p) Reaction Cross Sections. Pre-equilibrium Reaction Mechanism
In the framework of the pre-equilibrium mechanism using Griffin's exciton model
a simple formula was deduced for the fast neutron induced charged particle
emission reaction cross sections. Using the obtained formula in a wide energy
range, the systematic analysis of the experimental (n, p) cross sections was
carried out. It was shown that in the case of 14-16 MeV the theoretical formula satisfactorily
describes the experimental data, however, in the energy region from 6 to 10 MeV there is a significant
discrepancy between the theoretical and experimental cross sections.
|
E3-2007-27 (152,950)
Khuukhenkhuu G. et al.
The Fast Neutron Induced (n, p) Reaction Cross Sections. Direct Reaction Mechanism
In the framework of the direct reaction mechanism using the plane-wave Born
approximation (PWBA) a simple formula was deduced for the fast neutron induced charged particle emission
reaction cross sections. In the wide energy range from 6 to 16 MeV the systematic analysis of the (n, p)
reaction cross sections was carried out. It is shown that theoretical total cross sections calculated by statistical and exciton models
and PWBA satisfactorily agree with the experimental data.
|
E1-2007-28 (187.175)
Usubov Z.U.
Graviton Exchange Effects on Dijet
Production in pp-Interactions at 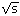 =14 TeV =14 TeV
The effects of the virtual graviton exchange on the dijet production
in proton-proton collisions in the ATLAS detector at the LHC are
considered. The high ET cross section and the angular distribution
for dijet production are examined. A sensitivity of the LHC to a parameter
of the model with extra dimensions is estimated.
|
P17-2007-29 (187.855)
Kuznetsov A.B.
On Experimental Confirmation of Ginzburg-Landau Equation
A numerical solution of the Ginzburg-Landau equation
for a single fluxoid was used to obtain an approximation formula
of ratio dependence of critical fields (of the first to the second
one) on the Ginzburg-Landau parameter. Comparison of this
formula with 46 experimental results showed their good agreement.
|
E9-2007-30 (196.084)
Zhabitsky V.M.
Transverse Emittance Blow-Up from Beam Injection Errors in
Synchrotrons with Nonlinear Feedback Systems
The problem of transverse emittance blow-up from beam injection
errors in synchrotrons with nonlinear feedback systems is
considered. The relative emittance growth is calculated for
linear and nonlinear feedback transfer functions. Effects of an
increase of the damping decrement of the beam coherent
oscillations and of a decrease of the coherent transverse
amplitude spread of different bunches in case of the damper
with a positive cubic term in the feedback transfer function
are discussed.
|
P5-2007-31 (409.419)
Lomidze I. R., Javakhishvili J. I.
Application of Orthogonal Invariants of Operators in Solving Some Physical Problems
On the base of complete set of orthogonal invariants of operators which is
built in the recently performed series of articles of one of the authors
(I.L.) the system of nonlinear differential equations (NDE) for orthogonal
invariants of ideal gas (liquid) hydrodynamic velocity's Jacobi matrix is
obtained when the flow is barochronic. It is shown that only two regimes of
barochronic flow are possible - a potential and/or a solenoidal one. Exact
solutions of the NDE system are obtained; polynomial
relations between the Jacobi matrix's invariants are found and it is proved that these relations are integrals of motion. Using the obtained results the
3-dimensional hydrodynamic Euler equations are solved and hydrodynamic
velocity's and substance density`s time and space dependence are found. It
is shown that the hydrodynamic velocity of potential barochronic flow
depends on radius-vector (for arbitrarily chosen origin of coordinates
frame) and satisfies the nonrelativistic Hubble law. This result seems
interesting taking into consideration that barochronic flow naturally
describes long-scale evolution of the Universe. The sufficient and necessary
conditions are found for the solution of hydrodynamic Euler equations of
solenoidal barochronic stream having form of the primitive wave or of the
double wave. It is shown that such a flow is isobaric.
|
P13-2007-32 (319,0)
Samatov Zh.K., Stahin A.A., Fominykh V.I.
Stabilization of Nuclear Radiation Spectra by Means of Equipment and Software Correction
Two types of the stabilizer spectra of nuclear radiations are described.
In the first event the correction of instability is produced by changing parameters of the
ADC device by presenting correcting voltages. The amplitude of analog signals changes in the
second event with leaving the linear amplifier with the help of termoresistors supplied by
heating winding. Contributing the changes is expected to the program of the accumulation of
radiation spectra for the reason of realization of executive CAMAC commands. It is shown that
by means of mathematical transformations it is possible to correct distortion spectra, caused
by instability of the equipment.
|
E6-2007-33 (159.934)
S. A. Karamian, J. J. Carrollast, S. Iliev, S. P. Tretyakova
Weak K-Hindrance Manifested in Alpha Decay of the 178m2Hf Isomer
An experiment has been performed to detect the alpha-emission mode in
178m2Hf isomer decay and a partial half-life of (2.5 ± 0.5) · 1010 years was measured.
It was concluded that  decay is strongly retarded by the centrifugal barrier arising due to the high spin of this isomeric state.
Additional analysis shows, however, that the K-hindrance in this decay is strongly retarded by the centrifugal barrier arising due to the high spin of this isomeric state.
Additional analysis shows, however, that the K-hindrance in this  decay is relatively weak, despite the strong manifestation of spin hindrance.
decay is relatively weak, despite the strong manifestation of spin hindrance.
|
P5-2007-37 (260.040)
Pupyshev V. V.
Structure of Regular Solutions to the
Schrödinger and Faddeev Equations in the Limit of the Three-Body Linear Configuration
The six-dimensional Schrödinger and Faddeev equations
for a three-body system with two-body central potentials of a more general type than the
Coulomb ones are studied. The regular general and particular
physical solutions of these equations are represented as infinite
series in integer powers of the distance between one
particle and the center of mass of two other particles and the
sought functions of other three-particle coordinates. In the
angular basis, formed by the spherical and bispherical harmonics
or the symmetrized Wigner D-functions, the construction of these
functions is reduced to solving simple algebraic recurrence
equations. For the projections of the physical solutions to the
Schrödinger and Faddeev equations onto angular basic functions
the boundary conditions in the limit of the linear three-body
configuration are derived.
|
P11-2007-38 (367.317)
Lukyanov K. V.
Double Folding Model of Nucleus-Nucleus Potential:
Formulae, Iteration Method and Computer Code
Method of construction of the nucleus-nucleus
double folding potential is described. Iteration procedure for the
corresponding integral equation is presented. Computer code and
numerical results are presented.
|
P5-2007-41 (215.656)
Pupyshev V. V.
Structure of Regular Solutions to the
Faddeev Equations in the Vicinity of the Two-Body Collision Point
The two- and three-dimensional Faddeev equations for
a three-body system with
two-body central or S-wave interactions are studied. The regular
solutions of these equations are represented as infinite series in
integer powers of the distance between two particles and the
sought functions of other three-particle coordinates. The
construction of these functions is reduced to solving algebraic
recurrence equations. For the regular solutions to the Faddeev
equations the boundary conditions at the two-body collision point
are derived.
|
P10-2007-43 (238.797)
Bunyatov S. A. et al.
Reconstruction of Trajectories in the "IHEP-JINR Neutrino Detector"
Methods and tools for recognition of trajectories and determination of their
parameters for particles registered by the upgraded experimental complex "IHEP-JINR Neutrino Detector" are presented.
Based on the regression analysis algorithms of definition of kinematic parameters are developed.
Quantitative characteristics of muon momentum estimation in the region 0.5-3.0 GeV/c are studied. The relative error on the momentum in this range is
14.6 ± 0.2 %.
|
P1-2007-46 (367.908)
Azhgirey L. S. et al.
The Measurements of the
Tensor Ayy and Vector Ay Analyzing Powers of the Deuteron
Fragmentation on Hydrogen and Carbon Nuclei at an Initial Deuteron
Momentum of 9 GeV/c with the Emission of Protons with
Large Transverse Momenta
The data on the tensor Ayy and vector Ay analyzing
powers of the deuteron fragmentation on the hydrogen and carbon nuclei
at an initial deuteron momentum of 9 GeV/c with the emission of protons with large transverse momenta are presented. The data obtained are
compared with the calculations made in the framework of light-front
dynamics using different deuteron wave functions. A better
description of the experimental data is accomplished by the use of
the relativistic deuteron wave function derived by Karmanov et al. in the
framework of the field light-front dynamics.
|
P19-2007-47 (203.218)
Belov O. V.
Modeling of Kinetics of the Inducible Protein Complexes of the SOS-System in Bacteria E. coli Which Realize TLS-Process
The mathematical model describing kinetics of the inducible genes of the
protein complexes, formed during SOS-response in bacteria Escherichia coli is developed.
Within the bounds of developed approaches the auxiliary mathematical model
describing changes in concentrations of the dimers, which are the components
of final protein complexes, is developed. The solutions of both models are
based on the experimental data concerning expression of the basic genes of the
SOS-system in bacteria Escherichia coli.
|
E2-2007-54 (103.984)
Beshtoev Kh. M.
Cherenkov Effect in the Weak Interactions Generated
by the Neutrinos and New Approach for Estimation of Neutrino Mass
It is shown that if weak interactions can generate masses and
polarize matter, then the Cherenkov effect induced by these
interactions at v > c/n appears. The effect of (resonance)
enhancement of neutrino oscillations in matter (v > c/n appears. The effect of (resonance)
enhancement of neutrino oscillations in matter (v < c/n) and
the Cherenkov (v < c/n) and
the Cherenkov (v > c/n) effect are competitive processes and
at definite neutrino energies the effect of (resonance)
enhancement of neutrino oscillations in matter will change to the
Cherenkov effect. Then neutrino vacuum oscillations will
recommence and we obtain an excellent possibility of estimating
neutrino masses. > c/n) effect are competitive processes and
at definite neutrino energies the effect of (resonance)
enhancement of neutrino oscillations in matter will change to the
Cherenkov effect. Then neutrino vacuum oscillations will
recommence and we obtain an excellent possibility of estimating
neutrino masses.
|
e2-2007-55 (289.484)
Beshtoev Kh. M.
Status of the Mechanism of Resonance Enhancement of
Neutrino Oscillations in Matter
The present status of the mechanism of resonance enhancement of
neutrino oscillations in matter has been considered by using the
existent experimental data and it is concluded that this effect
has no clear experimental confirmation. To prove that this
mechanism is realized it is necessary to fulfil precision
experiments with solar neutrinos and neutrinos which have
passed through the Earth matter.
|
E2-2007-56 (103.183)
Gevorkyan S. R. et al.
Electromagnetic Effects and Scattering Lengths Extraction from
Experimental Data on K  3 3 Decays Decays
The final state interactions in K   
 0 0 0 decays
are considered using the methods of non-relativistic quantum
mechanics. We show how to take into account the largest
electromagnetic effect in the analysis of experimental data using
the amplitudes calculated earlier. We propose the relevant
expressions for amplitude corrections valid both above and below the
two charged pion production threshold M 0 decays
are considered using the methods of non-relativistic quantum
mechanics. We show how to take into account the largest
electromagnetic effect in the analysis of experimental data using
the amplitudes calculated earlier. We propose the relevant
expressions for amplitude corrections valid both above and below the
two charged pion production threshold M 0 0 0
= 2m 0
= 2m  ,
including the average effect for the threshold bin. These formulae
can be used in the procedure of pion scattering lengths measurement
from M ,
including the average effect for the threshold bin. These formulae
can be used in the procedure of pion scattering lengths measurement
from M 0 0 0 spectrum. 0 spectrum.
|
P9-2007-59 (1.086.779)
Savchenko O. V.
Methods of Flattening Transverse Dose Distributions for the Medical Proton Beams with the Large Emittance at the JINR LNP Phasotron
Calculation methods for parameters of combining scatterers providing
flattening for transverse dose distribution of a necessary size for medical
proton beams with large emittance at the JINR LNP Phasotron are proposed and
developed. The results allow one to quickly calculate the parameters of
combining scatterers for different conditions of production of a dose field
with a wide region of flattening up to 20 cm at increasing the used part of
the proton beam about 3 to 7 times (up to 35%).
|
p9-2007-60 (619.646)
Savchenko O. V.
The Proposal and Physico-Technical Feasibility Studies of an Accelerator of New Type for the Medico-Technical Complex of the LNP, JINR
A proton accelerator of new type (a phasotron with a divided magnet or a
recirculation phasotron), in which the magnetic field in bending magnets is
constant and the frequency of the accelerating electrical field and the
gradient of the magnetic field in focusing lenses vary during the
acceleration cycle according to preset programs, is proposed.
The analysis of consistency of trajectories as well as of phase, transverse
and resonance stability, which allows making a conclusion about the
principal possibility of realizing such an accelerator, is carried out.
Some particularities of the new accelerator such as speed cycles (50-100 Hz)
and the possibility to vary the energy and the number of particles in each
acceleration cycle are the most suitable clinical requirements on proton
beams, particularly while using perspective methods of active formation of
dose fields.
A proposal on technical feasibility of realization of a new accelerator
within the building of the Medico-Technical Complex of the LNP, JINR, is
made.
|
E13-2007-61 (286,6)
Andronic A. et al.
Research and Development of Fast TRD Readout Chambers
Several fast multiwire proportional chambers and GEM based detectors were
constructed in the frame of R&D for Transition Radiation Detector for CBM experiment
planned at FAIR. The results of experiments with a beam of secondary protons at GSI let us conclude that
the multiwire proportional chamber-type detector meets all requirement to the Transition Radiation Detector of CBM high rate environment experiment.
|
E17-2007-63 (398.745)
Nietz V.V., Osipov A.A.
Шаровые солитоны в кинетике магнитных фазовых переходов первого рода
The theory of magnetic ball solitons (BS), arising as a result of the energy
fluctuations at the spin-flop transition induced by a magnetic field in
antiferromagnets with uniaxial anisotropy, is presented. Such solitons are
possible in a wide range of amplitudes and energies, including the negative
energy relative to an initial condition. When such an antiferromagnet is in a
metastable condition, ball solitons are born with the greatest probability
if the energy of solitons is close to zero. Evolution of these solitons, at
which they develop into macroscopic domains of a new magnetic phase, is
analyzed, thus carrying out full phase reorganization.
|
E14-2007-65 (835,5)
Hall P. et al.
Study of Nanocrystalline Substances with Sorbed Hydrogen by Neutron Scattering
Earlier P. Hall et al. have
shown that FeTi nanocrystalline alloys are more preferable for hydrogen
storage in comparison with those prepared by usual technology. The diffraction
and vibration spectra from nanocrystalline samples with sorbed hydrogen of
(FeTiMg)Hx, (MgTi)Hx, (MgTiPd)Hx, (FeTiMn)Hx, [(FeTiMn)Mg]Hx are obtained
by means of neutron scattering. The crystal structure peculiarities of the
samples are observed. The phonon and local vibrational modes of sorbed
hydrogen are selected and their energies are determined. It is shown that
the energies of hydrogen modes in multicomponent nanocrystalline structures
with sorbed hydrogen are not described simply by energies of hydrogen modes
observed in different single-component metal hydrides.
|
E1-2007-66 (2.007.091)
Fedorisin J., Vokal S.
Wavelet Analysis of Angular Spectra of Relativistic Particles in 208Pb Induced Collisions with Emulsion Nuclei at 158A GeV/c
The continuous wavelet transform is applied to the pseudorapidity spectra of
relativistic secondary particles created in Pb+Em
nuclear collisions at 158A GeV/c. The wavelet pseudorapidity spectra
are subsequently surveyed at different scales to look for signs
of ring-like correlations whose presence
could be explained either via the production of Cherenkov gluons
or the propagation of Mach shock waves in excited nuclear medium.
The presented approach is established
on the basic prerequisite that the both effects would lead to
excess of particles at certain typical pseudorapidities.
Furthermore, the particles contributing to the ring-like structures
are expected to have uniform azimuthal distributions.
The multiscale analysis of the wavelet pseudorapidity spectra
reveals the irregularities which are interpreted as the favoured
pseudorapidities of groups of produced particles.
A uniformity of the azimuthal structure of the disclosed pseudorapidity
irregularities is examined, eventually leading to the conclusion that the
irregularities are not related to correlations of a ring-like nature.
|
E2-2007-68 (77,892)
Konopleva N.P.
"Baldin Autumn" and Gauge Fields
The paper is the reminiscences of the participant of the gauge field theory
beginning and the first "Baldin Autumn" conference in 1969. This conference was named "Vector Mesons and Electromagnetic Interactions".
At that time, just the processes with vector mesons participation contained
some experimental indications of new universal interactions existence. Vector
dominance was the experimental evidence of physical reasons of the gauge field
theory. In the course of time the gauge field theory form, which was under
discussion thirty seven years ago, became generally recognized and
experimentally corroborated. It led to construction of the well-known Standard
Model of elementary particle interactions.
|
E2-2007-69 (89.986)
Konopleva N.P.
Relativistic Physics and Geometry
The problem of physics geometrization is considered as a part of the
problems which is the sixth Hilbert's problem talks about. This Hilbert's
problem concerns mathematical formulation of physics axioms. It is shown
that for the whole XX century this problem formed scientific research
strategies in theoretical physics and some mathematical topics, especially
in geometry. Appearance of special and general relativities as well as the
geometrical gauge field theory can be regarded as consequent stages in the
sixth Hilbert's problem solution. The present-day problem consists in
application of the geometrical gauge field theory for relativistic nuclear
physics.
|
E13-2007-70 (418,2)
Tsyganov Yu.S.
Amplitude Analysis of Highly Ionizing Particle Signals Registered with Silicon Radiation Detector. Some Remarks to Anomalies
Analysis of the registered energy amplitudes measured with silicon radiation
detector with the significant pulse height defect (PHD), namely for the
evaporation residues (EVR) and fission fragments (FF), has been performed for
rare events obtained in the heavy-ion induced nuclear reactions. It is
shown, that in some cases those measured amplitudes are quite anomalous.
|
P13-2007-71 (286.712)
Stavissky Yu. Ya.
Nuclear Energy for Space Flights
A brief review of little-known works carried out in the State Research Centre of Russian Federation
Institute of Physics and Power Engineering in 1955-1975 to construct space vehicles and power supply equipment for
space flights on the basis of chain reaction of nuclear fission is presented. The works have been carried out at the
initiative of the Director of the Institute, Corresponding Member of AS USSR D.I. Blokhintsev and with the active
support of Academician S.P. Korolyov.
|
E5-2007-72 (111.225)
Zhidkov P. E.
On the Existence of a Component-Wise Positive Radially Symmetric Solution for a
Superlinear System
The system under consideration is 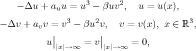 where au , av and
where au , av and  are positive constants. We prove the existence of a component-wise
positive smooth radially symmetric solution of this system. This statement is one of the results
presented in the recent paper [1]; in our opinion, our method allows one to treat the problem
simpler and shorter. are positive constants. We prove the existence of a component-wise
positive smooth radially symmetric solution of this system. This statement is one of the results
presented in the recent paper [1]; in our opinion, our method allows one to treat the problem
simpler and shorter.
|
E5-2007-73 (166.953)
Zhidkov P. E.
Existence of Positive Radial Solutions for Some Nonvariational Superlinear Elliptic
Systems
|
P9-2007-75 (227,6)
Philippov A.V. et al.
Development of the Balance Equations Model for Calculation of Ion
Charge-State Distribution in ECR Ion Sources
The investigation of the widespread model for the calculation of ion
charge-state distributions (CSD) in electron cyclotron-resonance ion
source based on the set of balance equations is given. The modification of
this model that allows one to describe the confinement and accumulation
processes of highly charged ions in ECR plasma for gas mixing case more
precisely is discussed. The new approach for the time confinement
calculation (ions and electrons) based on the theory of Pastukhov is
offered, viz. calculation of confinement times during two step
minimization of special type functionals. The results obtained by this
approach have been compared with available experimental data.
|
E1-2007-77 (1.080.471)
Artikov A., Budagov Ju., Chlachidze G., Prokoshin F., Pukhov O., Sissakian A., Giunta M., Bellettini G., Velev G.
Top Mass Measurement on 1 fb-1 Using the Three Best Combinations Method
The BLUE method is applicable to improve the precision in the Top Mass Measurement,
whenever the mass can be derived in a number of different ways for each candidate
event. This method is applied to a 1 fb-1 data sample in the semileptonic channel requiring
no b-tag information used in the Template Method. This method makes use of the mass
value returned by the most likely jet-to-parton association (out of 24). In this note the mass
information returned by the three best combinations is exploited. Simulations show that in
a significant number of cases the associations giving the second and the third best c2 are
actually the correct ones. It was found in MC that the statistical error is improved by about
10%. Combining the three best mass reconstructions by using a statistical technique called
BLUE gives Mtop 168,9  2,2 (stat.) 2,2 (stat.)  4.2 (syst.) 4.2 (syst.)  GeV/c2. GeV/c2.
|
P7-2007-78 (326,2)
Hiryanov R.M., Karpov A.V., Adeev G.D.
Stochastic Model of Fission Fragment Angular Distribution for Excited Compound Nuclei
A dynamical approach to treatment of the fission fragment
angular distribution is developed. The approach is based on
three-dimensional Langevin dynamics for shape collective
coordinates joined with Monte-Carlo algorithm for the degree of
freedom associated with projection K of the total angular
momentum of fissioning system on the symmetry axis. The relaxation
time of the tilting mode  K is estimated. From the fits to
the experimental data on the fission fragment angular
distribution of heavy fissioning compound systems the K
equilibration time is deduced to be (2-4) · 10-21 s for
the temperatures ~ 1-2 MeV. A modified one-body mechanism
of nuclear dissipation with reduction coefficient of the contribution
from the "wall" formula ks = 0.5 has been used in the calculations. K is estimated. From the fits to
the experimental data on the fission fragment angular
distribution of heavy fissioning compound systems the K
equilibration time is deduced to be (2-4) · 10-21 s for
the temperatures ~ 1-2 MeV. A modified one-body mechanism
of nuclear dissipation with reduction coefficient of the contribution
from the "wall" formula ks = 0.5 has been used in the calculations.
|
P5-2007-79 (323,2)
Pupyshev V. V.
Structure of Regular Solutions to the Schroedinger and Faddeev Equations in the Vicinity of the Triple Collision Point
Three-body systems with two-body central interactions are
considered in the vicinity of the triple collision point. The
regular Faddeev bispherical components obeying the systems of
two-dimensional integrodifferential equations are studied. It is
shown that all fundamental regular solutions to these equations
are the double series in integer powers of the hyperradius, its
logarithm and the sought functions of one hyperangle. The
construction of these functions is reduced to solving of a
recurrence chain of ordinary differential equations. The Faddeev
bispherical components are presented as infinite sums of all
regular solutions. The found expansions of these components are
used for reproduction of expansions of projections of the regular
solutions to the six-dimensional Schroedinger and Faddeev
equations onto the angular basis formed by bispherical harmonics,
hyperharmonics or the symmetrized Wigner D-functions. For all
these projections the boundary conditions at the triple collision
point are derived.
|
P9-2007-80 (1.582.500)
Gikal B. N. et al.
Experimental Results on Acceleration of Nitrogen, Argon, Krypton Ion Beams in the Frame of Starting-up Works on Isochronous Cyclotron DC-60
The heavy ion cyclotron DC-60, created in the Laboratory of Nuclear
Reactions, JINR, was started at the end of 2006 at the Interdisciplinary
Research Complex (Astana, Kazakhstan). The cyclotron complex is developed
for solving a wide range of scientifically-applied problems with the use of ion beams with energy range 0.35 to 1.77 MeV/nucleon. In the frame of
starting-up and adjustment works, the experiments on acceleration of
nitrogen, argon, krypton ion beams (14N2+, 40Ar4+, 40Ar5+,
40Ar7+, 84Kr12+) at various levels of the magnetic field
1.25-1.65 Т were made. Research and optimization of acceleration process of
ions on the fourth and sixth harmonics accelerating RF voltage is carried
out. Design parameters of the accelerated ion beams are realized.
|
E15-2007-081 (866.566)
Krasa A. et al.
Neutron Emission in the Spallation Reactions of 1 GeV Protons on a Thick Lead Target Surrounded by Uranium Blanket
A thick lead target surrounded by uranium blanket was irradiated with 1 GeV protons. Measurement of the produced
neutron field was performed by means of threshold reactions in activation foils. The experimental results were compared
with Monte Carlo calculations performed with the MCNPX 2.6. C code.
|
E15-2007-82 (597.208)
Majerle M. et al.
Monte Carlo Studies of the "Energy plus Transmutation"
"Energy plus Transmutation" setup consists of a thick lead target surrounded with uranium blanket and placed in a polyethylene box.
Relativistic protons are directed to the target. Produced neutron flux is
studied at different places of the setup using the activation detectors. The possible sources of systematic uncertainties of obtained
experimental data are analyzed using MCNPX simulations. Further, the
influence of different setup parts and uncertainties in their geometrical and
physical definitions on the neutron flux is investigated. The possibility to compare the experimental data with the results of the MCNPX
simulation code is discussed.
|
E17-2007-83 (193.158)
Adam Gh., Adam S.
Rigorous Derivation of the Mean-Field Green Functions of the
Two-Band Hubbard Model of Superconductivity
The Green function (GF) equation of motion technique for solving the
effective two-band Hubbard model of high-Tc superconductivity in
cuprates
rests on the Hubbard operator (HO) algebra. We show that, if we take into
account the invariance to translations and spin reversal, the HO algebra
results in invariance properties of several specific correlation functions.
The use of these properties allows rigorous derivation and simplification
of the expressions of the frequency matrix (FM) and of the generalized mean-field approximation (GMFA) Green functions (GFs) of the model.
For the normal singlet hopping and anomalous exchange pairing correlation
functions which enter the FM and GMFA-GFs, the use of spectral representations
allows the identification and elimination of exponentially small quantities.
This procedure secures the reduction of the correlation order to the GMFA-GF
expressions.
|
P9-2007-85 (1.232.076)
Savchenko O. V.
The Fortieth Anniversary of Proton Therapy at the JINR LNP Synchrocyclotron
and Phasotron
A survey of 40-year period of developing proton therapy first at
synchrocyclotron and then, after reconstruction of the accelerator, at the JINP LNP phasotron is given.
It is marked that the first medical proton beam in the Soviet Union (now
CIS) and also intense negative  -meson and high energy neutron beams
were produced even before reconstruction of JINR LNP synchrocyclotron.
By using such beams the radiobiological experiments were carried out and
clinical results of the initial research of treating cancer patients were
obtained on proton beams. -meson and high energy neutron beams
were produced even before reconstruction of JINR LNP synchrocyclotron.
By using such beams the radiobiological experiments were carried out and
clinical results of the initial research of treating cancer patients were
obtained on proton beams.
A many-room Medico-Technical Complex of radiation therapy with JINR
phasotron beams, produced during reconstruction of the JINR LNP
synchrocyclotron, is described in detail.
The first clinical results of treating cancer patients with proton beams at
this complex are given.
It is emphasized that construction in Dubna, as part of medical
department number 9, of a 20-bed specialized radiological hospital and also
development and use of the first in Russia three-dimensional conformal
proton therapy procedure made it possible to increase essentially a number of patients treated with proton
beams at Medico-Technical Complex, JINR LNP.
The prospects of the further development of JINR LNP Medico-Technical Complex and, in particular, the replacement of the JINR LNP phasotron by a
specialized medical accelerator, in full dedicated to proton therapy cancer
patients, are considered briefly.
|
E7-2007-86 (357.393)
Kulko A. A. et al.
Isomeric Ratios for 196, 198Tl and 196, 198Au from Fusion and
Transfer in the Interaction of 6He with 197Au
Excitation functions and isomeric cross-section ratios have been measured
for the nuclei 198m,gTl, 196m,gTl, 198m,gAu and
196m,gAu, formed in fusion-evaporation and transfer processes in
reactions of 6He with 197Au in the energy range 5-60 MeV.
The population probability of high- and low-spin states in the fusion
reaction with the formation of 198Tl and 196Tl
(Jmp = 7+,
Jgp = 2-), as well as of the transfer products
198Au and 196Au (Jmp = 12-,
Jgp = 2-),
is compared with calculations within the statistical model and with similar
results from deuteron-induced reactions.
|
p9-2007-87 (946.425)
Borisov O. N. et al.
Beam Extraction System for the DC-60 Cyclotron
The results of numerical simulation of the heavy ions beam extraction system
(A/Z=6-12, W=0,35-1,77 MeV/amu) from the DC-60 cyclotron are presented. The parameters of the extraction system elements
(electrostatic deflector and focusing magnetic channel) and diagnostic elements are chosen.
The experimental extraction efficiency of 14Ne2+ and 84Kr12+ beams is equal to
60-65% with intensity 1.5 - 2.5 muA.
|
E10-2007-88 (3.045.518)
Lebedev S., Ososkov G., Hoehne C.
Ring Recognition in the CBM RICH Detector
Two algorithms of ring recognition, a standalone ring finder (using only
RICH information) and an algorithm based on the information from vertex
tracks, are described. The fake ring problem and its solution using a set of
two-dimensional cuts or an artificial neural network are discussed. Results of
a comparative study are given. All developed algorithms were tested on large
statistics of simulated events and were then included into the CBM framework
for common use.
|
P18-2007-90 (704.920)
Molokanov A. G.
Forming of the Depth-Dose Distribution of the Radiotherapy Proton Beam of the JINR Phasotron
Radiation therapy with proton beams has a number of important advantages
over conventional radiation therapy with photons and electrons based on the
energy deposition processes which give a well defined range in а tissue, a
Bragg peak of ionization in the depth-dose distribution and slow lateral
scattering.
The radiotherapy proton beam at the JINR Phasotron is formed by means of
slowing down of the initial 660 MeV beam in the carbon degrader. For
clearance of the slowed down proton beam from contaminations of secondary
particles and improvement of the Bragg peak shape the magnetic analysis of
the beam and compensate wedge is used.
The set of ridge filters transform the Bragg peak to the depth-dose
distribution with a flat top from 2 to 5 cm for large target irradiation.
Influence of the collimators material and aperture on the shape of the
proton beam depth-dose distributions was studied. For the small sizes of
collimator aperture the shape of the depth-dose distribution is distorted
especially in collimators made of materials with large atomic number.
|
E18-2007-91 (493.336)
Rajcan M., Molokanov A. G., Mumot M.
Simulations of Proton Beam Depth-Dose Distributions
Proton beams are successfully used in radiotherapy. A correct modification
of beam parameters enables to spare normal surrounding tissues from
radiation action. Our work is focused on passive beam-shaping techniques,
which are used to modify the proton beam properties. The beam passes through
the scattering system, which consists of scattering materials, energy
degraders, drift spaces and collimators. In order to model the proton beam
transport through the scattering system, the new Monte Carlo (MC) computer
code Track has been developed. The code Track can predict output proton beam
parameters modulated by various system adjustments and helps to optimize
them. It calculates a beam profile, creates beam emittance diagram at a specified
position of the system and predicts proton beam depth-dose distribution in
a water phantom. In addition it calculates beam losses on individual
components.
We present a physical model of the beam transport calculations and algorithm
implemented in a~code Track. We compared the Track code calculations of depth-dose distributions in water phantom with experimental data and with a
set of MC calculations in the FLUKA code. The accuracy of simulation results
and calculation time in Track code are observed.
|
P13-2007-93 (660.811)
Maznyj N. G., Salamatin I. M., Salamatin K. M.
Generation of Experiment Automation Programs from Modules in Loadable Format
The work aims at searching for methods to significantly decrease periods of
ACS development and modification. The developed ACS structure includes task
preparation subsystem, operation control program (user's interface),
subsystem to control the state of monitored object (MO), and data processing
subsystem. Task preparation and its execution are arranged as separate
processes. Provided that ready program modules are available, ACS
integration and modification can be performed by the user.
|
P10-2007-94 (294.252)
Gundorin N. A. et al.
An Express-Analysis of Spectra in Precision Experiments
Some precision experiments, such as research of polarized particles and
targets, parity violations, etc., use tens hours for measurements. In this
case, significant importance is drawn to an account of possible drift of
registering system parameters in time. The aim of early detection of
significant distortions in registered spectra, of their filtration and
correction of results has been addressed to in development of the data express-analysis program.
|
P13-2007-96 (293.414)
Pepyolyshev Yu. N.
Method of Experimental Estimation of the Effective
Delay Neutron Fraction and of the Neutron Generation Lifetime in the IBR-2
Reactor
Experimental investigations of stochastic noises of the power of the IBR-2
periodic pulsed reactor carried out in the steady-state and in the pulsed modes of its operation made it possible to obtain estimations of
the main parameters of the kinetics - the effective fraction of delayed
neutrons and the average lifetime of prompt neutrons. Functionals were
measured relating the main parameters of the kinetics: the prompt neutron
decay constant (steady-state mode) and the relative dispersion of pulse
energy fluctuations. It was shown that the experimental values of parameters
of the kinetics are close to the calculated ones. In addition, the power of
the spontaneous neutron source was estimated on the basis of the analysis of
neutron noises.
|
E13-2007-97 (731.415)
Smirnov O. Ju.
An Approximation of the Ideal Scintillation Detector Line Shape with a Generalized Gamma Distribution
An approximation of the real line shape of a scintillation detector
with a generalized gamma distribution is proposed. The approximation
describes the ideal scintillation line shape better than the conventional
normal distribution. Two parameters of the proposed function are uniquely
defined by the first two moments of the detector response.
|
E13-2007-98 (1.536.024)
Batusov V. et al.
On a Laser Beam Fiducial Line Application for Metrological Purposes
The possibility of a collimated one-mode laser beam used as a fiducial line is considered. The technology of an "extended" laser beam formation and application for a much extended fiducial line is proposed.
|
E14-2007-101 (592.552)
Budzynski P., Polanski K., Kobzev A. P.
Changes of Surface Layer of Nitrogen-Implanted AISI316L Stainless Steel
The effects of nitrogen ion implantation into AISI316L stainless steel on
friction, wear, and microhardness have been investigated at energy level
of 125 keV at fluence of 1 · 1017 -1 · 1018 N/cm2. The composition of the surface layer was investigated by RBS,
XRD (GXRD), SEM and EDX. The friction coefficient and abrasive wear rate of
the stainless steel were measured in atmospheres of air, oxygen, argon, and
in vacuum. As follows from the investigations, there is an increase in
resistance to frictional wear in the studied samples after implantation;
however, these changes are of different characters in various atmospheres.
The largest decrease in wear was observed during tests in the air, and the
largest reduction in the value of the friction coefficient for all implanted
samples was obtained during tests in the argon atmosphere. Tribological
tests revealed larger contents of nitrogen, carbon, and oxygen in the
products of surface layer wear than in the surface layer itself of the
sample directly after implantation.
|
P11-2007-102 (280.965)
Gostev I.M., Sevastianov L.A.
About Identification of Smooth Spatial Curves
Methodology of forming of information properties of unclosed spatial curves
is discussed. The intrinsic geometry on the base of any class of k-jet equivalence is investigated.
For identification of its curve
some types of metrics are introduced. There is a defined conception of super slow k-jet identification
of curves and their segments. Examples and area of application of this methodology are included and the
path of next investigations is described.
|
E4-2007-103 (217.750)
Zhabitsky M. V.
Direct Calculation of the Probability of Pionium Ionization in the Target
The goal of the DIRAC experiment at CERN
is the lifetime measurement of pionium (p+p--atom).
Its lifetime is mainly defined by the charge-exchange process
p+p-  p0p0.
Value of the lifetime in the ground state
is predicted in the framework of Chiral Perturbation
Theory (ChPT) with high precision:
t1S=(2,9 ± 0,1) · 10-15 s.
The method used by DIRAC
is based on the analysis of p+p--pairs spectra
with small relative momenta
in their center-of-mass system in order to find out signal
from pionium ionization (break-up) in the target.
Pioniums are produced in proton-nuclei collisions and
have relativistic velocities (g > 10).
For fixed values of the pionium momentum and the target thickness
the probability of pionium ionization in the target depends on
its lifetime in a unique way,
thus the pionium lifetime can be deduced from
the experimentally defined probability of pionium ionization.
Based on ionization cross sections of pionium
with target atoms
we performed the first direct calculation of the pionium ionization probability
in the target. p0p0.
Value of the lifetime in the ground state
is predicted in the framework of Chiral Perturbation
Theory (ChPT) with high precision:
t1S=(2,9 ± 0,1) · 10-15 s.
The method used by DIRAC
is based on the analysis of p+p--pairs spectra
with small relative momenta
in their center-of-mass system in order to find out signal
from pionium ionization (break-up) in the target.
Pioniums are produced in proton-nuclei collisions and
have relativistic velocities (g > 10).
For fixed values of the pionium momentum and the target thickness
the probability of pionium ionization in the target depends on
its lifetime in a unique way,
thus the pionium lifetime can be deduced from
the experimentally defined probability of pionium ionization.
Based on ionization cross sections of pionium
with target atoms
we performed the first direct calculation of the pionium ionization probability
in the target.
|
P9-2007-104 (995.226)
Gikal B. et al.
Cyclotron Based Complex DC-60 for Scientific and Applied Research as well as for Industrial Application in the Nanotechnologies
The newly operating complex based on the cyclotron DC-60 has been built to
provide scientific and applied research as well as for industrial
application in the nanotechnologies. The facility has been designed and
manufactured by the Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions of the Joint
Institute for Nuclear Research (Dubna) for the International
scientific-research center at the Euro-Asia National University named after
L.N. Gumilev (Astana, Kazakhstan). High intensity beams of heavy ions of Ne, Ar, Kr and other elements have been accelerated in a wide range of masses and
energies. Irradiation of different polymer films has been provided and a few
batches of nuclear membranes have been developed in a wide range of hole
densities. The complex benefits joint development of technologies, science
and related business. The facility is intended for production of Nuclear Filters and is boosting industrial technologies by using of nano- and
microstructures based on TM and also assigned to establish scientific
environment and education in Kazakhstan.
|
P11-2007-105 (470.270)
Amirkhanov I. V. et al.
The Use of Nonlinear Thermal Spike Model for Calculations of Temperature
Effects at Two Layer Structures under Their Irradiation with High Energy Heavy Ions
Temperatures at two layer structures, presenting massive substrate and
surface cover by relatively thin layer from another material, under
irradiation with swift heavy ions with high ionizing energy loss in frame of
thermal spike model in three dimensional case were calculated. The
temperature changes near the separate boundary of such a two layer structure
on the example of Ni-W of the convective warm exchanging coefficient t
are studied in detail. Parameter t characterizes the changes of
temperature gradient near the separate boundary, i.e. determines the type of
heat contact. It was established that calculated temperatures of electronic
and lattice subsystems for nonlinear model (characterized by thermal
physical coefficients depending on the temperature) are much less than ones in
the linear model (characterized by thermal physical coefficients without
dependence on the temperature). The peculiarity of the nonlinear model is that the characteristic
time of the thermal processes in such a crystalline lattice are much slower than in the linear model.
It was shown that transition from nonideal case of heat contact to ideal case of heat contact takes
place at increasing of coefficient t.
|
P11-2007-106 (467.030)
Amirkhanov I. V. et al.
Temperature Effect Studies in Frame of Thermal Spike Model at
Highly Oriented Pyrolytic Graphite under Irradiation with 86Kr and
209Bi High-Energy Heavy Ions
The studies of temperature effects in anisotropic material - highly
oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) under irradiation with 86Kr (253 MeV)
and 209Bi (710 MeV) heavy ions in frame of three dimensional thermal
spike model were carried out. The temperature effects versus the changes of
electron-phonon interaction coefficients g are considered this model. It
was shown that the surface temperature of HOPG target under irradiation with
209Bi ions can be higher than melting temperature or evaporation
temperature of HOPG if the values of electron-phonon interaction
coefficient g satisfy the inequality g  1,5gk, where gk
= 3.12 · 1012 W/(cm3·К). Surface temperature of HOPG
under irradiation with 86Kr ions is less than melting temperature if the
values of electron-phonon interaction coefficient g satisfy the inequality
g 1,5gk, where gk
= 3.12 · 1012 W/(cm3·К). Surface temperature of HOPG
under irradiation with 86Kr ions is less than melting temperature if the
values of electron-phonon interaction coefficient g satisfy the inequality
g  4,5gk. It is possible to conclude, using made calculations and
experimental data from surface structure studies of single crystal HOPG
after irradiation with 209Bi (710 MeV) and 86Kr (253 MeV), that
developed in this work thermal spike model allows one to explain the creation of crater like structures after 209Bi ion irradiation and absence such
structures in the case of 86Kr ion irradiation. Such experimental data
can take place if electron-phonon interaction coefficients g satisfy the
inequality 1,5gk 4,5gk. It is possible to conclude, using made calculations and
experimental data from surface structure studies of single crystal HOPG
after irradiation with 209Bi (710 MeV) and 86Kr (253 MeV), that
developed in this work thermal spike model allows one to explain the creation of crater like structures after 209Bi ion irradiation and absence such
structures in the case of 86Kr ion irradiation. Such experimental data
can take place if electron-phonon interaction coefficients g satisfy the
inequality 1,5gk  g g  4,5gk. The estimations of
maximum sizes of volume in HOPG under irradiation with bismuth ions where
temperature can be higher than melting temperature are made. 4,5gk. The estimations of
maximum sizes of volume in HOPG under irradiation with bismuth ions where
temperature can be higher than melting temperature are made.
|
P9-2007-107 (305.713)
Issinsky I. B., Brovko O. I., Butenko A. V.
Research of Beam Intensity Losses at the Nuclotron (2002-2005)
Beam losses in the Nuclotron were investigated at the beginning of the
acceleration cycle. Today intensity, ~ 1010 ppp, is an order less
than projected magnitude. Variations of main accelerator parameters
permitted us to define a role each of them plays in existing losses. Each of the operation conditions changed inside small limits, and if the intensity did
not reduce in this case, the parameter was considered to have no effect on
losses.
Experiments performed with deuteron beam in 2002-2005 showed that essential
contribution to losses can be from particle scattering by residual gas. According to the measurements the mean pressure
in the beam chamber is ~ 10-5 Pa. So far it was believed that the pressure in the chamber is below
10-7 Pa and this parameter could not influence particle losses.
|
E1-2007-108 (574.626)
Janek M. et al.
Analyzing Powers Ayy, Axx, Axz
and Ay in the dd  3Hen Reaction at 270 MeV 3Hen Reaction at 270 MeV
The data on the tensor Ayy, Axx, Axz and vector Ay
analyzing powers in the dd  3Hen reaction obtained at
Td= 270 MeV in the angular range 0-1100 in the c.m. are presented. The observed negative sign of the tensor analyzing powers
Ayy, Axx and Axz at small angles clearly demonstrates the sensitivity to the ratio of the
D- and S-wave component of the 3He wave function. However, the one-nucleon exchange calculations by using the
standard 3He wave functions have failed to reproduce the strong variation of the tensor analyzing powers as a function of the angle in the c.m. 3Hen reaction obtained at
Td= 270 MeV in the angular range 0-1100 in the c.m. are presented. The observed negative sign of the tensor analyzing powers
Ayy, Axx and Axz at small angles clearly demonstrates the sensitivity to the ratio of the
D- and S-wave component of the 3He wave function. However, the one-nucleon exchange calculations by using the
standard 3He wave functions have failed to reproduce the strong variation of the tensor analyzing powers as a function of the angle in the c.m.
|
P14-2007-109 (587.919)
Aksenov V.L. et al.
Investigation of Ultrasonic Wave Influence on Magnetic Alignment in Layered Structure
20 x [Fe(20 Å)/Cr(12 Å)]/MgO
The layered structure 20 x [Fe(20 Å)/Cr(12 Å)]/MgO,
excited by ultrasonic wave, was investigated using polarized neutron reflectometry.
Magnetic domains vibrations and reduction of their effective size in magnetic field of small strength were observed.
In magnetic field close to saturation magnetic lattice is formed in the layered structure. Interplane distance of the
lattice changes with increase of magnetic field strength as well as with ultrasonic excitation of the structure.
|
E18-2007-110 (3.247.293)
Taran Yu. V. et al.
Investigation of In-Plane Biaxial Low Cycle Fatigued Austenitic
Stainless Steel AISI 321. I. Mechanical Testing on the Planar Biaxial Load Machine
During fatigue loading of structural materials such as stainless steel,
changes in the microstructure which affect the mechanical and physical
properties occur. Experimental simulation of the loading conditions that induce
the changes can be performed by mechanical loading, usually in the
form of uniaxial tension-compression cycling. However, real machines
and structures are subjected to more complex multiaxial stresses. Fatigue
and fracture under multiaxial stresses are one of the most important current
topics aimed at ensuring improved reliability of industrial
components. The first step towards better understanding of this problem is to
subject the materials to biaxial loading.
The material examined was low austenitic
stainless steel AISI 321 H. A set of the four samples of cruciform geometry was
subjected to the biaxial tension-compression fatigue cycling with the
frequency of 0.5 Hz at the applied load of 10-17 kN.
The samples are intended for the neutron diffraction measurements
of the residual stresses and the mechanical characterizations on a dedicated
stress-diffractometer.
|
E18-2007-111 (1.382.534)
Taran Yu.V. et al.
Investigation of In-Plane Biaxial Low Cycle Fatigued Austenitic
Stainless Steel AISI 321.
II. Neutron Diffraction Stress Analysis at the IBR-2 Pulsed Nuclear Reactor
The in-plane biaxial low cycle fatigued sample of the cruciform geometry
from austenitic stainless steel AISI 321 was investigated on the
time-of-flight neutron Fourier stress-diffractometer. The lattice parameters
in the austenite matrix and the martensite inclusions created during the
fatigue cycling as well as the martensite volume fraction were measured
along two mutually perpendicular planar axes of the sample of the cruciform
geometry by using the strain neutron scanner. The phase total residual
strain components were calculated using the stress equilibrium relations.
The separation of the residual stresses into macro- and microstresses was
performed using the mixture rule. The measurements of the applied load-phase
elastic strain responses were carried out on a uniaxial load machine. The
strong difference between the phase elastic moduli was found out.
|
E2-2007-112 (640.540)
Beshtoev Kh.M.
Examination of Unitarity Condition (Positive Definiteness of Expression for Transition Probabilities) at Three Neutrino Oscillations in Vacuum
This work has shown that at strict fulfilment of condition  m21 3
= m21 3
=  m21 2 + m21 2 +  m22 3 the expression
for probability m22 3 the expression
for probability  e e  e transitions
P e transitions
P e e  e(t)
is positively defined at every value of q and
b, while at any arbitrarily small deviation from this
condition it becomes negative. In order to make this expression
positively defined for probability transitions, it is necessary to
put a limitation on angle mixing b at fixed value of
q = 32,45° (i.e., the value for b must be
b e(t)
is positively defined at every value of q and
b, while at any arbitrarily small deviation from this
condition it becomes negative. In order to make this expression
positively defined for probability transitions, it is necessary to
put a limitation on angle mixing b at fixed value of
q = 32,45° (i.e., the value for b must be
b  15 15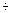 17°). 17°).
|
P13-2007-113 (535.118)
Turek M. et al.
Computer Modeling of Ion Extraction from Plasma Ion Source
Study of ion beam extraction using numerical model of plasma ion
source is presented. Current-voltage curves and the dependency of plasma
meniscus surface on extraction voltage are obtained. New concepts of dynamic perveance and effective emitting surface are introduced.
|
P11-2007-114 (255.235)
Mikheev S. A., Tsvetkov V. P.
The Bifurcation Points of Rotating Magnetic Newtonian
Polytrops with a Coefficient Close to Unit
This investigation has proved for the first time that there are
bifurcations of Newtonian rotating polytropic curves over the
range of the polytropic coefficient 0.9989 < n  1.0795,
where the solutions asymmetric with respect to the rotation axis,
that describe a density distribution, are derived. It has been
shown that within this interval, the n parameter of the
rotation rapidity takes the values 0.0442 > єk 1.0795,
where the solutions asymmetric with respect to the rotation axis,
that describe a density distribution, are derived. It has been
shown that within this interval, the n parameter of the
rotation rapidity takes the values 0.0442 > єk  0 in critical points єk. 0 in critical points єk.
|
P17-2007-115 (182.575)
Golubok D.S., Didyk A.Yu., Hofman A.
Estimation of Damage Dose at Fe77Ni2Si14B7 Amorphous Alloy Irradiated with Neutrons on IBR-2
Damage creation in amorphous alloy Fe77Ni2Si14B7 under
irradiation at IBR-2 reactor of the Frank Laboratory of Neutron Physics is
considered. The influence of a-particles with energies of 1.77 MeV (yield 93%) and 1.46 MeV (yield 7%) and 7Li
recoils with energies 1.01 MeV (yield 93%) and 0.84 MeV (yield 7%) produced at thermal neutrons capture reactions and light 10B isotopes on
radiation defects creation
is calculated. It was shown the production of damage at the elastic
scattering processes by a-particles and 7Li recoils is more than one order value bigger in comparison with production
by fast neutrons elastic scattering processes. The absorption coefficient of thermal neutrons at
their passing through the amorphous Fe77Ni2Si14B7 samples versus the depth is presented.
The estimations of relative quantities of
a-particles and 7Li recoils produced in the capture
reactions at the distances from the lateral surfaces of samples less than
their projected ranges and having possibilities to fly out from irradiated
Fe77Ni2Si14B7 alloy samples, thus contributing little to damage creation, are presented.
Approximate analytical dependence of damage dose versus the depth between the lateral surfaces is obtained.
|
P17-2007-116 (154.172)
Didyk A.Yu., Hofman A.
Peculiarities of Neutron Interaction of Fast Neutron Reactor IBR-2
with Boron-Containing Semiconductor Single Crystals BN, BP(AIIIBV) and B4C(AIIIBIV)
Calculations of damage creation at semiconductor single crystals B4C(AIIIBIV) and BN, BP(AIIIBV)
under their irradiation in fast neutron
reactor IBR-2 with fission spectrum neutrons were carried out. It was shown
that damage creation by elastic scattering mechanism on semiconductor atoms
of fission fragments as 4a2+-particles and nuclear
recoil 7Li produced by thermal neutrons in nuclear reactions
with light isotope of 10B is more than two orders higher than damage creation by fast neutrons
(En > 0.1 MeV). Calculation shows that such irradiations allow creating developed vacancies structure at single crystal semiconductors
(SCS) with homogeneous vacancy distribution. This effect can be used for technological applications, for example for more effective
diffusion of technological chemical impurities using vacancies mechanism
after covering of SCS surface or its implantation to the layer near surface
at the processes of annealing.
|
P10-2007-118 (252.937)
Zlokazov V. B., Bobrikov I. A., Balagurov A. M.
Program VMRIA for Analysis of Powder Magnetic Neutron Diffraction Data
At the IBR-2 pulsed reactor at FLNP, JINR, investigations of the atomic and
magnetic structure of crystals are carried out. For the analysis of the
obtained diffraction spectra with the help of the Rietveld method, the program
package MRIA (Multiphase Rietveld Analysis) has been used for a long time.
At the present time a new version of this package, VMRIA, is in operation.
This version is developed using the visual object-oriented programming
language DELPHI. Apart from being a very convenient interface for the
interaction with the user, the program contains the algorithm for the
analysis of collinear magnetic structures.
In the paper, the general information about analysis of diffraction spectra by the Rietveld method is given, and specific
features of the magnetic structure analysis by the program VMRIA are discussed.
|
P9-2007-120 (314.102)
Dolya S.N., Reshetnikova K.A.
Heavy Ions Accelerator by the Spiral Waveguide
Heavy ions accelerator contains two sections 16 and 13 meters long. Ions of uranium with
the charge Z = +32 have energy from 84 keV/nucl. to
8 MeV/nucl. at the end. Generator power is 3 MW (each channel), frequency is f = 150 MHz. The radius of the spiral waveguide r0 changes
from r0 = 2.6 cm at the beginning to r0 = 1 cm at length l = 7 m and then became permanent. The radius of outside cylinder is R = 7.5 cm,
the step of spiral waveguide changes from h= 2.1 mm at the beginning
to h = 4.5 mm at the end.
Beam focusing is provided by the solenoid magnetic field B = 6 T.
The fields are calculated taking into account the power losses in the cupper spiral waveguide covered with silver.
|
P9-2007-122 (265.387)
Borisovskaya Z.V., Goncharov I.N.
The Calculation of Magnetic Field in the Vicinity of "Window Frame" Dipole Winding for Particle Accelerators
The necessity of such calculations in design of superconducting dipole
magnets (DM) is explained by the following circumstances. First, there is
strong enough decreasing dependence of critical current of superconducting
cable on magnetic field value Ic (B). It requires knowledge of maximum magnetic field that is
"seen" by winding turns to estimate its operation current. Second, we need to know the relation of Bmax
values in inner and outer layers of DM winding to select the optimal number of winding
layers (1 or 2) and optimal DM operation current. As long as DM length is usually many times more than its transverse
size, all calculations of
B(x,y) have been performed only in transverse plane, containing the DM
center. The value of B(0,0) = 2 T was selected for this point (this is
typical operation value close to maximum one for this type of DM).
This work contains the results of B(x,y) calculations for single- and
two-layer winding with 8 or 16 turns made of hollow composite cable.
|
123(P3-2007-123) (511.623)
Andrianov V.R.,
Measurement of Delayed Neutron Yields from Thermal Neutron Induced Fission
of 245Cm
The paper reports on the measurement of the absolute overall delayed neutron
yield from thermal neutron induced fission of 245Cm nucleus. The
experimental researches of the characteristics of delayed neutrons of
fission of series of reactor isotopes started in 1997, were continued on the
modernized "Isomer-M" installation by a method based on periodic irradiation of sample in pulsed
neutron beam IBR-2 reactor with the
subsequent registration of neutrons emitted after fission in intervals
between pulses. The value of the absolute overall delayed neutron yield from
thermal neutron induced fission of 245Cm obtained in the present
experiment  d = (0.64 d = (0.64  0.02) % has twice best accuracy in
comparison with value measured earlier. 0.02) % has twice best accuracy in
comparison with value measured earlier.
|
P19-2007-125 (1.217.098)
Koltovaya N.A.
Interactions of Checkpoint-Genes RAD9, RAD17, RAD24 and RAD53
Determining Radioresistance of Yeast Saccharomyces Cerevisiae
The mechanisms of genetic control of progress through the division cell cycle
(checkpoint-control) in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae have been studied intensively.
To investigate the role of checkpoint-genes RAD9, RAD17, RAD24,
RAD53 in cell radioresistance we have investigated cell sensitivity of double mutants
to  -ray. Double mutants involving various combinations with rad9D
show epistatic interactions, i.e. the sensitivity of the double mutants to -ray. Double mutants involving various combinations with rad9D
show epistatic interactions, i.e. the sensitivity of the double mutants to  -ray was
no greater that of more sensitive of the two single mutants. This suggests that all these
genes govern the same pathway. This group of genes was named RAD9-epistasis group.
It is interesting to note that genes RAD9 and RAD53 have positive effect
but RAD17 and RAD24 have negative effect on radiosensitivity of yeast cells.
Interactions between mutations may differ depending on the agent -ray was
no greater that of more sensitive of the two single mutants. This suggests that all these
genes govern the same pathway. This group of genes was named RAD9-epistasis group.
It is interesting to note that genes RAD9 and RAD53 have positive effect
but RAD17 and RAD24 have negative effect on radiosensitivity of yeast cells.
Interactions between mutations may differ depending on the agent  -ray or UV-light,
for example mutations rad9D and rad24D show additive effect
for -ray or UV-light,
for example mutations rad9D and rad24D show additive effect
for  -ray and epistatic effect for UV-light. -ray and epistatic effect for UV-light.
|
P19-2007-126 (2.106.059)
Koltovaya N.A. et al.
Interactions of Checkpoint-Genes RAD9, RAD17, RAD24, RAD53 with Genes SRM5/CDC28, SRM8/NET1 and SRM12/HFI1
in Determining Radioresistance of Yeast Saccharomyces Cerevisiae
In yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae checkpoint-genes RAD9, RAD17, RAD24, RAD53 and genes SRM5/CDC28,
SRM8/NET1, SRM12/HFI1 have been found to belong to one epistasis group with the exception of SRM12/HFI1 as regards cell
sensitivity to gamma radiation. This group was named RAD9-group. Analysis of radiosensitivity of double mutants has revealed
that mutation cdc28-srm is hypostatic to each of rad9D, rad17D and
rad24D. Mutation net1-srm is hypostatic to rad9D and rad53,
but additive to rad17D and rad24D. Mutation hfi1-srm has additive
effect in compound with mutations rad24D and rad9D.
So investigations of interactions mutations rad with mutations srm have demonstrated a branched of RAD9-dependent pathway
of radioresistance. The studied genes can participate in a minor mechanism involved in determining the cell radiation sensitivity independently of
mentioned RAD9-dependent pathway.
|
P11-2007-127 (582.644)
Zhidkov E.P. et al.
Methods of Modeling of Operation Modes of Multi-Purpose Isochronous Cyclotron
The methods of modeling of operation modes of multi-purpose isochronous
cyclotron are described. The traditional method is based on a simultaneous
finding of currents in all trim coils. The new method is iterative and is
based on a consecutive finding of currents in each of the considered trim
coils. All accounts are carried out at a certain level of current in the
main coil. At account of values of currents in trim coils an incorrect task
is solved (non-uniform system of the linear algebraic equations (SLAE) is
ill-conditioned, as its determinant has a value equal to machine zero). The
solution of the incorrect task is unstable in relation to a mistake of
measurement of magnetic field maps used at account. The iterative method,
as against the traditional one, enables an indirect estimation of quality of the initial data (measured magnetic field maps) used at account through an
estimation of convergence of the solution. The work on the regularization of the solution of the submitted incorrect task is being conducted at present.
|
P9-2007-128 (1.072.001)
Borisov O.N., Gikal B.N., Ivanenko I.A., Kazarinov N.Ju., Samsonov E.V.
The Beam Dynamics in the DC-60 Isochronous Cyclotron
At the present work the dynamic characteristics of the magnetic field of
cyclotron DC-60 are considered on the basis of the trajectory analysis. The
purpose of the analysis was the optimization of the acceleration conditions
in the central area of the cyclotron, in the main area of acceleration and
in the area of the beam extraction from the cyclotron. The analysis was
carried out for three characteristic modes of the acceleration: on the upper
(1.65 Т), average (1.43 Т) and lower (1.25 Т) magnetic field levels. The
calculations and later, the experiments have shown that the formed magnetic
field of the DC-60 cyclotron provides the focusing and the good efficiency
of the ion beams acceleration.
|
P13-2007-129 (226.270)
Boguslavsky I.V. et al.
Measurement of the Anode Tension for the Segmented Straws
The opportunity of measurement by an acoustic method of a tension of the
anodes of segment straws is shown. The correction factors providing
calculation of a tension by the formula connecting frequency of fluctuation
of the anode with his tension are determined.
|
P6-2007-131 (472.150)
Alyoshin V.I. et al.
Sensitivity of Experiment on Double Beta Decay of 150Nd Search
The possibility of using big area scintillation plates on the basis of
polystyrene for creation of the detector of neutrinoless 150Nd
double beta decay with sensitivity to half-life period of 1025 years
is investigated. The estimations of necessary isotope mass depending on the
energy resolution are demonstrated. It is shown that given sensitivity can
be realized by means of such a detector at isotope mass about 85 kg.
|
P19-2007-132 (479.925)
Koltovaya N.A.
Activation of Repair and Checkpoints by Double-Strand Breaks of DNA. Activational Cascade of Protein Phosphorylation
Molecular mechanisms of double-strand breaks repair and checkpoints include
phosphorylations of repair and checkpoint-proteins by protein kinases.
Chemical modification of proteins has different consequences including
activation, changing of affinity to proteins and localization.
|
E17-2007-135 (134.201)
Tonchev N.S.
The Casimir Effect and Critical Phenomena
In the present review we focus our
attention on the theory and the experimental confirmations of the Casimir
effect in critical phenomena. Since the effect is related to the boundary
conditions imposed on a system undergoing a phase transition and its
consequences, the theory of critical phenomena in finite-size systems is an
indispensable part of the theoretical description. Experiments with liquid
films near a critical point are of particular experimental relevance to the
studied phenomenon.
|
P6-2007-136 (292.725)
Tereshatov E.E., Bruhertzajfer H., Bozhikov G.A., Aksenov N.V., Starodub G.Ja., Vostokin G.K.,
Belov A.G., Shishkin S.V., Dmitriev S.N., Geggeler H.V., Ajhler R., Shumann D.
Cation Exchange Separation of the Group 5 Elements
In the framework of the investigation of chemical properties of long-lived
Db isotopes by means of liquid chemistry methods the procedure of cation
exchange separation of the group 5 elements and their isolation from Zr, Hf
and lantanides by diluted HCl/HF solutions has been developed. Based on the
derived data, it is possible to suggest the following order of stability of
fluoride complexes of the elements of groups 4 and 5: Nb  Ра > Zr > Hf > Ta. The order of the complex formation is in agreement
with earlier investigations and theoretical predictions.
Ра > Zr > Hf > Ta. The order of the complex formation is in agreement
with earlier investigations and theoretical predictions.
|
E18-2007-142 (479.925)
Bystritsky V.M. et al.
DViN - Stationary Setup for Identification of Explosives
A stationary system for identification of hidden explosives has been
developed and constructed at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR).
The results of the examination of the system as well as the operation
principle of the system and design of the main elements are presented in this
paper.
|
P13-2007-144 (193.143)
Li Yong Chan, Pepyolyshev Yu.N., Rogov A.D.
he Change of Reactivity Effect in the IBR-2 Pulsed Reactor Related to
Burn-up in the Period 1982-2006
From the analysis of operation data of the IBR-2 pulsed reactor in the
period 1982-2006 the dependence of extra reactivity as a function of
energy production of the reactor has been obtained. It shows that at the
beginning of the reactor operation in addition to the pure burn-up effect,
there is also a positive effect probably related to the densification of
fuel and structural changes of materials in the core. The effect decreases
with time and tends to zero. Only the effect of pure burn-up remains after
the 40000 MW·h burn-up, and from this point the extra reactivity is linearly
decreased with the coefficient kB = - 4,2975·10-5%/MW·h.
The formula to calculate the energy production coefficient of reactivity at
any time of the reactor operation has also been obtained. The energy
production coefficient of reactivity consists of two components: the
coefficient of pure burn-up and additional positive coefficient of
reactivity.
|
P14-2007-147 (355.551)
Chernenko L.P.
On the Limit Possibilities of the Polarized Neutron Reflection
Method in the Study of Fe/Cr Superlattices
The calculations of polarized neutron reflection coefficients for
Fe/Cr superlattices show the neutron reflection method possibilities of the
main reflection channel. The reflection of films which have the giant
magnetic resistance was considered. The limit sensitivity of the polarized
neutron specular reflection method for the nanolayer mixing type of
interfaces is observed.
|
P11-2007-148 (560.768)
Amirkhanov I.V. et al.
Solution of Boundary-Value Problems for Singular Perturbed Differential Equations of High Order
Two boundary-value problems of the singular
perturbed equation of the 4th order with small parameter e at higher derivative are investigated for the Coulomb and oscillator
potentials. It is shown that at diminution of a small parameter
value e eigenvalues of both boundary-value problems
converge to eigenvalues of the Schrödinger equation. However
derivatives from eigenfunctions of the first boundary-value problem,
as opposed to the second boundary-value problem in a vicinity of a
boundary r=0 (r - argument of eigenfunction) have boundary
layers and do not converge to derivatives of eigenfunctions of the
Schrödinger equation. At increasing of parameter e from small up to final quantities the eigenfunctions of both boundary
problems are expanding to the side of increasing of r. Thus,
eigenfunctions and eigenvalues of the first boundary-value problem
are changing grossly in comparison with their values for the second
boundary-value problem. The equidistance property of eigenvalues of
the Schrödinger equation with the oscillator potential does not hold
true for the equation of the 4th order.
|
P13-2007-149 (426.135)
Tsulaia M.I., Alfimenkov V.P.
Facility "Polarized Nuclear Target" (PNT) for Neutron Investigations
A facility "Polarized Nuclear Target (PNT) for Neutron Irvestigations" has been created at the IBR-2 pulsed reactor
of the Frank Laboratory of Neutron Physics of JINR. A 3He/4He dilution cryostat with a superconducting solenoid has
been constructed for the facility. The temperature at a sample is 23 mK at a 3He circulation rate of 1.07 · 10-3 mol/s.
Maximum magnetic field is H = 6600 Oe. The facility makes it possible to orient nuclei in a wide range of mass numbers using the "brute force"
method. Also, provision is made for the dynamical polarization of nuclei.
|
P13-2007-150 (258.166)
Li Yong Chan, Pepyolyshev Yu.N.
The Dynamical Model of Power Feedback in the IBR-2 Pulsed Reactor Taking
into Account Slow Components
The dynamical model of full-range feedback has been proposed and the method
to determine the dynamical parameters of slow components in power feedback
for individual operation cycles of the IBR-2 pulsed reactor has been
studied. Using the quasistationary equation of reactivity balance, the total
effect of power feedback which is the sum of fast and slow components of
reactivity change has been calculated. The shape of curves of this effect
shows that the dynamical model of power feedback in the IBR-2 pulsed reactor
consists of three components: a proportional block and two inertial blocks
of slow action (faster block with positive transfer coefficient and time
constant of several hours, and slower block with negative transfer
coefficient and time constant of several tens of hours). The parameters of
slow dynamical process have also been determined. Curves of reactivity
change obtained from the model are in good agreement with the ones from the
experiments.
|
P3-2007-151 (373.451)
Zamyatnin Yu.S., Shikanov A.E.
50 Years of Pulsed Neutron Logging (1955-1958, G.N.Flerov)
The first part of this paper presents the history of creation of pulsed neutron
logging (PNL) foundation by G.N.Flerov ruling. Promising modifications of PNL methods based
on analyses of thermal neutron,  quanta of inelastic scattering, radiation capture and
neutron activation fields in wells by means of achievements in modern nuclear physics, mathematics
and computer technique are considered. Schemes for creation of new PNL apparatus complexes using
the recent developments of portable neutron generator are presented. Perspectives of further improving
of PNL methods and apparatus are discussed. quanta of inelastic scattering, radiation capture and
neutron activation fields in wells by means of achievements in modern nuclear physics, mathematics
and computer technique are considered. Schemes for creation of new PNL apparatus complexes using
the recent developments of portable neutron generator are presented. Perspectives of further improving
of PNL methods and apparatus are discussed.
|
P13-2007-152 (228.268)
Pepyolyshev Yu.N., Popov A.K.
Model Study of an Automatic Controller of the IBR-2 Pulsed Reactor
For calculation of power transients in the IBR-2 reactor a special
mathematical model of dynamics taking into account the discontinuous jump of
reactivity by an automatic controller with the step motor is created. In the
model the nonlinear dependence of the energy of power pulse on the
reactivity and the influence of warming up of the reactor on the reactivity
by means of introduction of a nonlinear feedback "power-pulse energy -
reactivity" are taken into account. With the help of the model the
transients of relative deviation of power-pulse energy are calculated at
various (random, mixed and regular) reactivity disturbances at the reactor
mean power 1.475 MW. It is shown that to improve the quality of processes
the choice of such regular values of parameters of the automatic controller
is expedient, at which the least effect of smoothing of a signal acting on
an automatic controller and the least speed of an automatic controller are
provided, and the reduction of efficiency of one step of the automatic
controller and introduction of a five-percent dead space are also
expedient.
|
P13-2007-153 (164.853)
Marachev A.A., Pepyolyshev Yu.N., Popov A.K.
Statistically Optimal Filter for an Estimation of the Mean Power of the
IBR-2 Pulsed Reactor
The IBR-2 reactor is characterized by a wide spread of amplitudes of power
pulses relative to the mean value. For safe work of the IBR-2 reactor the
operation of its emergency protection is provided at double excess or
decrease of amplitude of a power pulse relative to the mean value, and at
spillover of the mean value of amplitude beyond the set limits, which
requires an estimation of current value of the mean power. As a result of
application of the method of statistically optimal regulation of a pulsed
reactor [1], statistically optimal algorithm, according to which current
value of the mean power is formed at an output of the filter, is obtained.
It is shown that the optimal algorithm is realized by the filter in the
form of an inertial element and that the most acceptable results are
reached, when the time constant of the filter is more than the period of
pulses by a factor of 3-7.
|
P13-2007-154 (197.483)
Testov D. et al.
Applications of 3He Neutron Detector
Neutron detectors utilizing 3He-filled proportional counters are
described. Applications of these detectors in measuring the probabilities of
neutron emission, especially multiple emission, after the b-decay of
neutron-rich nuclei as well as in investigations of rare events of
spontaneous fission of super heavy nuclei are considered.
|
P13-2007-155 (170.220)
Testov D.A. et al.
Measurement of Quadrupole Deformation for the Nuclei of Actinide Elements
The method of determination of the quadrupole deformation parameter is
discussed. This method is based on splitting of the giant dipole resonance.
The experimental setup including an avalanche-meter and the method of
reconstruction of cross-section are described. The cross-section was
reconstructed from the measured dependence of the photofission yield on
the boundary energy of bremsstrahlung. The results of a setup test on the
microtron bremsstrahlung beam (MT-25, FLNR, JINR) [1] including measurement of the excitation
function for the photofission of 238U are presented.
|
P9-2007-156 (836.672)
Gikal B.N. et al.
Vacuum System of the DC-60 Heavy Ion Cyclotron Complex
The vacuum system of the DC-60 heavy ion cyclotron complex constructed at
the Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions, JINR, for the interdisciplinary
research complex, Astana, Kazakhstan, is described. The results of a
numerical simulation of the transmission efficiency of ions being
accelerated in process of recharge on the residual gas that determined the
main parameters of the vacuum system are presented. Due to successful
realization of the project of the DC-60 cyclotron complex the heavy ion
beams are accelerated. The obtained parameters of the vacuum system are in
full agreement with the calculations that form the basis of the project.
|
E4-2007-157 (793.154)
Kondratyev V.N., Kadenko I.M.
Nuclide Creation and Annealing Reactor Waste in Neutron Fields
We consider chemical elements in the Universe (their properties and
transmutations) as a fuel powering an evolution of stars, galaxies, etc. The
nuclear fusion reactions represent an energy source of stars and, in
particular, the Sun fitting the life on the Earth. This brings a question on
an origin and conditions for creation of life. We discuss some specific
features of nuclear reaction chains at the hydrostatic burning of nuclides
in stars and treaties for development of thermonuclear fusion reactors at
the Earth based environment. The nova and supernova give promising
astrophysical site candidates for synthesis of heavy atomic nuclei and
renewing other nuclear components. Such an explosive nucleosynthesis yields
the actinides containing basic fuel for nuclear fission
reactors, among others. We briefly outline the e-, s-, and r-processes while
accounting for ultra-strong stellar magnetization, and discuss some
ideas for annealing the radioactive toxic nuclear waste.
|
E10-2007-158 (677.791)
Akishina E.P. et al.
Distributions of Energy Losses of Electrons and Pions in the CBM TRD
The distributions of energy losses of electrons and pions in the TRD
detector of the CBM experiment are considered. We analyze the measurements of the energy deposits in one-layer TRD prototype obtained during the test beam
(GSI, Darmstadt, February 2006) and Monte Carlo simulations
for the n-layered TRD realized with the help of GEANT in frames of
the CBM ROOT. We show that: 1) energy losses both for real measurements
and GEANT simulations are approximated with a high accuracy by a
log-normal distribution for p and a weighted sum of two log-normal
distributions for e; 2) GEANT simulations noticeably differ from real
measurements and, as a result, we have a significant loss in the
efficiency of the e/p identification. A procedure to control and
correct the process of the energy deposit of electrons in the TRD is developed.
|
E9-2007-161 (168.875)
Philippov A.V.
A New Approach for Calculation of Volume Confined by ECR Surface and Its Area in ECR Ion Source
The volume confined by the resonance surface and its area are important
parameters of the balance equations model for calculation of ion
charge-state distribution (CSD) in the electron-cyclotron resonance (ECR)
ion source. A new approach for calculation of these parameters is given.
This approach allows one to reduce the number of parameters in the balance
equations model.
|
E2-2007-162 (798.790)
Zborovsky I., Tokarev M.V.
Scaling Features of Particle Production in A+A Collisions at RHIC in z-Presentation
New arguments in favor of self-similarity of the inclusive
particle production in high energy collisions of hadrons and
nuclei are discussed. Scaling features of hadron spectra from
nuclear interactions are compared with the z-scaling observed in
p+p collisions. The microscopic scenario on the energy losses of
particles
in the framework of z-scaling is
discussed. The performed analysis is based on the phenomenological
study of data obtained at FNAL, CERN, and BNL.
|
P18-2007-163 (129.250)
Baljinnyam N. et al.
Determination of Gold and Silver in Fire Assaying Regulus of the
Copper Concentrate of the Mining "Erdenet" by Multielemental Photon
Activation Analysis
Multielemental Photon Activation Analysis (MPhAA) for determination of gold
and silver in fire assaying regulus of the copper concentrate of the ore
mining and processing enterprise "Erdenet" is described using
bremsstrahlung of high energy electrons on the microtron MT-25, FLNR, JINR. The concentrations of gold and silver in the copper concentrate of the ore
mining and processing enterprise "Erdenet" are estimated.
It has been shown that the detection limit is 1 mg/kg for gold and 0.5 mg/kg for silver when
using the combined fire assaying and MPhAA methods.
|
E18-2007-164 (174.771)
Baljinnyam N. et al.
Possibility of 117mSn Production Using High-Energy Electron Bremsstrahlung
The method of 117mSn production using an electron accelerator is described and its photonuclear reaction yield
and specific activities for 117mSn and enriched isotope 118Sn are estimated. The specific activities and photonuclear
reaction yields of 117mSn and 111In are also estimated using the high-energy electron bremsstrahlung of the linear
electron accelerator of the IREN facility, FLNP, JINR at irradiation of high-purity tin targets.
|
E1-2007-165 (266.835)
Azhgirey L.S., Gurchin Ju.V., Isupov A.Ju., Khrenov A.N., Kiselev A.S., Kurilkin A.K.,
Kurilkin P.K., Ladygin V.P., Litvinenko A.G., Peresedov V.F., Pijadin S.M., Reznikov S.G.,
Rukojatkin P.A., Tarasov A.V., Vasiliev T.A., Zhmyrov V.N., Zolin L.S.
Observation of Tensor Polarization of Deuteron Beam
Traveling through Matter
The tensor polarization of the deuteron beam arising as deuterons
pass through a carbon target was measured. The experiment was
performed at an extracted unpolarized 5-GeV/c deuteron beam of the
Nuclotron. The effect observed is compared with the calculations
made within the framework of the Glauber multiple scattering theory.
|
E1-2007-166 (128.528)
Azhgirey L.S., Tarasov A.V.
Calculation of Spin Alignment of Deuterons Traveling through Matter
Calculations of the spin alignment of the relativistic deuteron beam
passing through matter are described. The tensor polarization is
calculated within the framework of the Glauber multiple scattering
theory. The calculation results are compared with the
recent experimental data.
|
P4-2007-167 (290.967)
Gaponov Yu.V.
New Approach to Description of Majorana Properties of Neutral Particles
Two mathematical models based on Pauli transformations
including U(1) chiral group and Pauli SU(2) group, that mixes
particle and antiparticle states, are developed for description of
Majorana properties of neutral particles. The first one describes
a system, incorporating left- and right-handed fermions of the
same flavor, and it is a generalization of the Majorana model
of his pioneer article published in 1937. The second describes
a two-flavor neutrino system with quantum numbers of
Zel'dovich-Konopinsky-Mahmoud (ZKM) type. For massless
fermions the Pauli symmetry is exact and leads to the conserved
generalized lepton charge. It is a Pauli isospace vector, whose
different directions are coordinated with Dirac or generalized
Majorana properties. In nonzero-mass case the models describe
the combined Dirac-Majorana properties of neutral particles,
which are characterized either by the generalized lepton charges of
ZKM-type or by the eigenvalues of the operator that is the product
of the charge operator and chirality. The latter is connected with
operator of the structure of Lagrangian mass term or with the generalized
flavor number of the second model. The choice of the basic operator
depends on the inversion classes (A-B or C-D-types) of the particles
with respect to the space inversion. The modified second model can be
used for description of neutrino oscillation in the simplest two-flavor case.
|
P19-2007-168 (965.322)
Kadyshevskaya E.Yu., Koltovaya N.A.
SRM5/CDC28, SRM8/NET1 and SRM12/HFI1 Genes Participates in Activation of Checkpoints of Yeast Saccharomyces Cerevisiae
It's known about twenty checkpoint genes in yeast Sacharomyces cerevisiae. We are studying
participation of SRM} genes, selected as genes affecting genetic stability and
radiosensitivity [1-3]. It was shown
that srm5/cdc28-srm, srm8/net1-srm, srm12/hfi1-srm mutations prevent checkpoint activation by DNA damage,
particularly G0/S-checkpoint (srm5, srm8), G1/S-checkpoint (srm5, srm8, srm12), S-checkpoint (srm5, srm12) and
G2-checkpoint (srm5). These data indicate, at least in budding yeast,
CDC28/SRM5, HFI1/ADA1/SRM12 and NET1/SRM8 genes mediate cellular response induced by DNA damage including
checkpoint control.
|
E2-2007-169 (125.218)
Beshtoev Kh.M.
Majorana Neutrino. Is Double Neutrinoless Beta Decay Possible
in the Framework of the Weak Interactions? How to Prove that
Neutrino is a Majorana Particle
Usually it is supposed that Majorana neutrino is produced in the
superposition state cL = nL + (nL)c and then follows
the neutrinoless double beta decay. But since weak interactions
are chiral-invariant, the neutrino at production has definite
helicity (i.e., nL and (nL)c neutrinos are separately
produced and then neutrino is not in the superposition state).
This helicity cannot change after production without any external
interactions. Thus, we see that for unsuitable helicity the
neutrinoless double b decay is not possible even if neutrino
is a Majorana particle. Also transition of Majorana neutrino into
antineutrino at their oscillations is forbidden since helicity in
vacuum holds. Then the only possibility to prove that neutrino is a
Dirac but not Majorana particle is detection of transition of nL
neutrino into (sterile) antineutrino 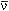 R (i.e., nL R (i.e., nL 
 R) at neutrino oscillations. Transition of Majorana neutrino
nL into (nR)c (i.e., nL R) at neutrino oscillations. Transition of Majorana neutrino
nL into (nR)c (i.e., nL
 (nR)c) at
oscillations is unobserved since it is supposed that the mass of
(nR)c is very big. (nR)c) at
oscillations is unobserved since it is supposed that the mass of
(nR)c is very big.
|
P13-2007-170 (362.337)
Zhuravlev V.V. et al.
Control System of Executive Mechanisms of a Spectrometer on the Reactor IBR-2 as a Modern Local Network of Controllers CAN
Controllers SMC-32 and SMC-32-CAN as elements of control systems by
executive mechanisms of spectrometers IBR-2 are submitted.
Controllers provide management of executive mechanisms of spectrometers on
consecutive communication line RS232, RS422 (SMC-32, SMC-32-CAN), and on
local network CAN (SMC-32-CAN).
Control systems of executive mechanisms are easily modernized due to
connection of additional elements of local network CAN. Dynamic
characteristics of executive mechanisms of spectrometers are essentially
improved. For example, it was possible to lift frequency of rotation of step
motor DSHI-200 up to 10000 pps.
|
P1-2007-171 (221.770)
Janek M., Ladygin V.P., Uesaka T.
Investigation of Extracted Nuclotron Beam Parameters for the Experiments on the Study of the Light Nuclei Structure at LHE
The parameters of the deuteron extracted beam from Nuclotron have been investigated for the experiments on the study of the light nuclei structure in the binary reaction at the intermediate energies.
|
P1-2007-172 (590.890)
Anikina M.Kh. et al.
Interference Analysis of the Expanding Pion Production Volume for Hadron-Hadron and Nuclei-Nuclei Collisions at Momenta 3.8-5.2 GeV/c
Direct proof of the expansion of the pion production volume for
np-interactions within 3.8-5.2 GeV/c was obtained by
means of interference correlation method. Identity of
the interference picture for np and MgMg interactions
was shown too.
It was demonstrated that velocity of the expansion does not depend
on kind (from np and e+e- to PbPb) and
energy (3.4-200 GeV) of interacting particles.
It was shown that measurement of the production volume size is
suitable for limited, practically stationary in their rest frame,
elements of the whole production region. Any change of kinematic
limits of the analyzed sub-ensembles changes size and form of the
elements.
|
E14-2007-173 (514.365)
Khalil A.S. et al.
Surface Modifications by Swift Heavy-Ion Irradiation of Indium Phosphide
InP (001) samples were irradiated with 200 MeV Au ions at different
fluences. The surface nanotopographical changes due to increasing fluence of
swift heavy ions were observed by Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM), where the
onset of large increase in surface roughness for fluences sufficient to
cause complete surface amorphization was observed. Transmission Electron
Microscopy was used to observe formed bulk-ion tracks in InP and high
resolution TEM (HRTEM) revealed that single-ion tracks might not be
amorphous in nature. Surface-ion tracks were observed by AFM in the form of
ill-defined pits (hollows) of ~ 12nm in diameter (width). In addition,
Rutherford backscattering was utilized to follow the formation of disorder
to amorphization in the irradiated material. The interpretation of large
increase in surface roughness with the onset of amorphization can be
attributed to the plastic phenomena induced by the change of states from
crystalline to amorphous by ion irradiation.
|
2007-177 (rus, 1.517.806)
Brief Review of Topmost Scientific Results Obtained in 2007 at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research
|
P1-2007-180 (560.472)
Baldin A.A., Gus'kov B.N., Kadykov M.G., Mihajlov K.V., Salmin R.A., Semashko S.V., Strokovskij E.A.
Asymmetries in Inclusive Spectra of  +, p and d at Interaction
of Polarized Proton and Deuteron Beams with Carbon Nuclei Obtained at the MARUSYA Setup +, p and d at Interaction
of Polarized Proton and Deuteron Beams with Carbon Nuclei Obtained at the MARUSYA Setup
The new experimental data on one-spin analyzing powers in production
of  +, p, d at interactions of 3.3 GeV/с polarized protons and of 5 GeV/с
polarized deuterons with carbon target are presented. Particles were measured at
26o in the momentum range of 0.6-1.2 GeV/с. +, p, d at interactions of 3.3 GeV/с polarized protons and of 5 GeV/с
polarized deuterons with carbon target are presented. Particles were measured at
26o in the momentum range of 0.6-1.2 GeV/с.
|
P15-2007-182 (950.784)
Kamanin D.V. et al.
Studying of the Reaction 235U(nth,f) at the Reactor IBR-2 Using MiniFOBOS Spectrometer
First results of the experiment on studying the reaction
235U(nth,f) are presented. It was performed at the IBR-2 reactor
using double-armed time-of-flight spectrometer of heavy ions miniFOBOS. The
experiment joined forces of two scientific groups from the Flerov Laboratory of
Nuclear Reactions and the Frank Laboratory of Neutron Physics of the JINR. Full
confirmation of the previous results concerning the field of our interest was
obtained. We mean a new channel of multibody decays called "collinear
cluster tripartition" and fine structure of the mass-energy distribution of
fission fragments.
|
P2-2007-183 (844.472)
Eganova I.A., Samojlov V.N., Struminskij V.I., Kallis V.
Certain Gravitation Problems and Research Opportunities in Geophysics Monitoring
The growing interest to theoretical and experimental studies of
the gravitation properties and the existing "experiment claim" gave rise to discussions of the mass variation as a consequence of
the change in the matter "state" on the micro level. This
phenomenon opens up an opportunity to obtain radically new
experimental information that concerns the fundamental general
physics notion - the mass, whose quantitative theory has not been established
so far. Peculiarities of the mass monitoring in controlled
conditions are considered. First results are given of the
practically continuous monitoring that showed variation of the
matter mass in the absence of a possibility to change its
quantity.
|
E13-2007-184 (958.820)
Belushkin A.V.
Modern Trends in Position-Sensitive Neutron Detectors Development for Condensed Matter Research
Detecting neutrons is a more complicated task compared to the detection of
ionizing particles or ionizing radiation. This is why the variety of neutron
detectors is much more limited. Meanwhile, different types of neutron
experiments pose specific and often contradictory requirements for detector
characteristics. For experiments on the high-intensity neutron sources, the
high counting rate is one of the key issues. This is very important, for
example, for small-angle neutron scattering and neutron reflectometry. For
other experiments, characteristics like detection efficiency, high position
resolution, high time resolution, neutron/gamma discrimination, large-area
imaging, or compactness, are very important. Today, the cost of the
detector also became one of the most important factors. There is no single type
of detector which satisfies all the above criteria. Therefore, compromise is
inevitable and some of the characteristics are trade off in favor of others.
Present report gives an overview of detector systems presently operating at
the leading neutron scattering facilities as well as some development work
around the globe.
|
E1-2007-185 (519.549)
Sitnik I.M.
Relevance of New Measurements of Light Nuclei Breakup at a Zero Angle
The importance of investigation of light-nuclei breakup reactions in a wide region of internal
momenta at Serpukhov energies is discussed. The experimental test for the choice of adequate
variable for the description of the breakup reactions is suggested. It is shown that the precise measurement of T20 of the deuteron
breakup reaction at small internal momenta is important for the polarimetry. The experimental difficulties of measurements in this region are discussed.
|
E6-2007-186 (589.380)
Zeynalova O., Zeynalov Sh., Hambsch F.-J., Oberstedt S.
Digital Signal Processing Algorithms for Nuclear Particle Spectroscopy
Digital signal processing algorithms for nuclear particle spectroscopy are
described along with a digital pile-up elimination method applicable to
equidistantly sampled detector signals pre-processed by a charge-sensitive
preamplifier. The signal processing algorithms are provided as recursive
one- or multi-step procedures which can be easily programmed using modern
computer programming languages. The influence of the number of bits of the
sampling analogue-to-digital converter on the final signal-to-noise ratio of
the spectrometer is considered. Algorithms for a digital shaping-filter
amplifier, for a digital pile-up elimination scheme and for ballistic
deficit correction were investigated using a high purity germanium detector.
The pile-up elimination method was originally developed for fission fragment
spectroscopy using a Frisch-grid back-to-back double ionization chamber and
was mainly intended for pile-up elimination in case of high
alpha-radioactivity of the fissile target. The developed pile-up elimination
method affects only the electronic noise generated by the preamplifier.
Therefore, the influence of the pile-up elimination scheme on the final
resolution of the spectrometer is investigated in terms of the distance
between piled-up pulses. The efficiency of the developed algorithms is
compared with other signal processing schemes published in literature.
|
E11-2007-187 (1.497.119)
Donets E.E., Hayryan E.A., Streltsova O.I.
Blow-up/Scattering Alternative for a Discrete Family of Static
Critical Solutions with Various Number of Unstable Eigenmodes
Decay of regular static spherically symmetric solutions in the SU(2)
Yang-Mills-dilaton (YMd) system of equations under the independent
excitation of their unstable eigenmodes has been studied self-consistently
in the nonlinear regime. We have obtained strong numerical evidences that
all static YMd solutions are distinct local threshold configurations,
separating blow-up and scattering solutions, and the main unstable eigenmodes
are only those responsible for the blow-up/scattering alternative. On the
other hand, excitation of higher unstable eigenmodes always leads to
finite-time blow-up. The decay of the lowest N = 1 static YMd solution
is an exceptional case because the resulting waves reveal features peculiar
to solitons. Applications of the obtained results to Type-I gravitational
collapse of massless fields are briefly discussed.
|
P14-2007-188 (510.148)
Baturin A.S. et al.
Features of Acceptor Center Formation by Negative Muon and Behavior of the Muon Polarization in Diamond
An explanation is given to dramatic distinctions between the acceptor center
(AC) formation by negative muon in diamond and in silicon. It is shown that
in diamond the impurity center mB- formation by muon occurs
not so fast as in silicon and takes more than 10-9 s, because in
contrast to silicon the probability of electron capture from valence band
due to Auger effect is negligible. The damping of the muon spin polarization
in diamond at temperatures higher than 40 K is explained by hole capture on
ionized acceptor center mB-. The calculated charge-carriers
density near the ionized AC dramatically and non-monotonically depends on
the impurity concentration for time less than 10-13 s. This
dependence notably affects the dynamics of the AC state and behavior of the
muon spin polarization at times ~ 10-7 s.
|
P15-2007-191 (184.032)
Badamsambuu J. et al.
Excitation Functions and Yields at the Photofission of 238U
The yields and reaction cross-sections of 92Sr, 97Zr, 97Nb
and 135I at the photofission of 238U were measured. These
fission-fragments have some peculiarities in nuclear structure or in
practical using. The measurements were performed on the bremsstrahlung of
FLNR JINR microtron, in the electron energy range 10-22 MeV. The activation
method with Ge(Li) detector was used in these measurements.
|
P19-2007-192 (230.518)
Chausov V.N. et al.
The Regularities of the Induction and Reparation of DNA Double Strand Breaks in Human Lymphocytes after Irradiation with Accelerated Heavy Ions of Different Energy
The regularities of the induction of DNA double strand breaks (DSB) in human
lymphocytes after irradiation with different doses of accelerated lithium and
carbon ions (33 and 480 MeV/nucleon, LET = 20 and 10.2 keV/mm,
respectively) and g-rays 60Со by using of comet assay were
investigated. It was shown that dependence of DSB formation increases
linearly with growing of the dose of lithium and carbon ions and g-rays. The biological effectiveness of carbon ions with high energy was
similar to g-rays, lithium ions possess greater biological
effectiveness in comparison with g-rays and value of RBE of lithium
ions amount to 1.6 ± 0.1. The kinetics of DSB reparation in human lymphocytes after irradiation with lithium and carbon
ions and g-rays was studied. It is revealed that the reparation proceeds effectively with heavy-ion and
g-ray irradiation by exponential kinetics.
|
P15-2007-194 (433.681)
Brudanin V.B. et al.
Neutrino Helicity Measurement with Compton Polarimeter (Project of the Experiment)
The project devoted to neutrino helicity measurement by means of Compton
polarimeter is considered. The main advantage over previous experiments of
that kind is simultaneous measurement of polarimeter efficiency. Earlier the
efficiency could be only calculated giving rise to additional systematic
uncertainty in the final result. Experimental setup, performed tests are
described, the necessary statistics and source activity are estimated.
|
|
