| 2010 |
|
P11-2010-2 (176.182)
Puzynin I.V., Puzynina T.P., Thach V.T.
SLIPM - a MAPLE Package for Numerical Solution
of Sturm-Liouville Partial Problems Based on a Continuous
Analog of Newton's Method. I. Algorithm
We present the SLIPM (Sturm-LIouville Problem in MAPLE),
a program in the language of system computer algebras MAPLE, intended for
the numerical solution with the help of continuous analogue of Newton's
method (CANM) of Sturm-Liouville partial problems, i.e., for calculating
some eigenvalue of linear second-order differential operator and
corresponding eigenfunction satisfying homogeneous boundary conditions.
SLIPM is development written in the Fortran language of programs SLIP1
and SLIPH4: it is added by a new procedure of calculation of initial
approach to the solution {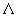 0, y0} and new ways of
calculating the initial value of iterative parameter 0, y0} and new ways of
calculating the initial value of iterative parameter  0. 0.
|
P10-2010-3 (1.031.099)
Lebedev A.A., Ososkov G.A.
Track Reconstruction in the TRD and MUCH Detectors of the CBM Experiment
Track reconstruction algorithm and its applications to the TRD and MUCH tracking detectors of the CBM experiment are described. The main components of the reconstruction package include track finding, fitting and propagation in the detector. The track finding algorithm is based on the track following method with branches. Track propagation algorithm takes into account inhomogeneous magnetic field and includes accurate calculation of multiple scattering and energy losses in the detector material. Track parameters and covariance matrices are estimated using the Kalman filter method. Developed software was included into the experiment software framework. Performance of the algorithm which shows its efficiency is presented.
|
E6-2010-4 (823.891)
Tereshatov E.E., Bruchertseifer H., Voronyuk M.G.,
Starodub G.Ya., Petrushkin O.V., Dmitriev S.N.
Isocratic Anion Exchange Separations of Group V Elements
The present study has been performed within the framework of experiments
aimed at the investigation of chemical properties of long-lived Db isotopes
in aqueous solutions. The isocratic anion exchange separations of group V
elements in the solutions containing HF have been considered. A possibility
in principle of niobium and tantalum separation in the system HF/NH4F
has been shown. Parameters of separation of dubnium homologues (Ра, Nb and
Ta) in HF/HNO3 mixed solutions have been optimized. The procedure of
separation of group V elements from multicomponent system has been
suggested.
|
P11-2010-8 (560.511)
Atanasova P.Ch. et al.
Numerical Modeling of Long Josephson Junctions in the Framework of Double Sine-Gordon Equation
The aim of this work is a mathematical modeling of the static magnetic flux distributions in long Josephson junctions (JJ)
taking into account the second harmonic in the Fourier decomposition of the Josephson current. Stability analysis is based on numerical
solution of a spectral Sturm-Liouville problem formulated for each distribution. In this approach the nullification of the minimal eigenvalue
of this problem indicates a bifurcation point in one of parameters. At each step of numerical continuation in parameters of the model,
the corresponding nonlinear boundary problem is solved on the basis of the continuous analog of Newton's method with the spline-collocation
discretization of linearized problems at Newtonian iterations. Main solutions of the double sine-Gordon equation have been found. Stability
of magnetic flux distributions has been investigated. Numerical results are compared with the results of the standard JJ model.
|
P11-2010-11 (113.201)
Bunetsky O.O. et al.
Preparation of NSC KIPT and JINR Grid-Infrastructures for Data Analysis at the CMS Experiment (CERN)
At the running phase of the LHC experiments the requirements on computing centers for the LHC experiments,
including CMS, are very strict because it would be necessary to process a huge amount of data at very high speed. For these purposes,
a special distributed global grid-infrastructure named WLCG has been constructed. JINR LIT and "Kharkov Institute of Physics and Technology"
(NSC KIPT) computing centers, intergarted into the WLCG infrastructure and certified at the CMS experiment as CMS Tier2 centers,
demonstrate a high level of reliabilty at their operation. These centers' computing resources are mostly dedicated for analysis of CMS data.
A proper WLCG elements configuration at JINR LIT and NSC KIPT grid-sites (especially Storage Elements) should be provided and actual
versions of CMS specialized software should be supported to make possible the reconstruction and analysis of data registered by the CMS detector.
Readiness of JINR LIT and NSC KIPT computing centers to the LHC start-up is discussed and the results of scale testing of JINR LIT and NSC
KIPT grid-sites are presented.
|
P15-2010-16 (147.851)
Gangrsky Yu.P., Zhemenik V.I., Markov B.N., Myshinsky G.V.
The Yield Ratio of I and Xe Isotopes in the Photofission Fragments of Heavy Nuclei
The ratios of I cumulative yields and Xe independent ones were
measured in the photofission of 232Th, 238U, 237Np,
243Am and 248Cm nuclei
by the bremsstrahlung radiation of 25 MeV boundary energy. The selective gas
transport and  -ray spectra measurements were used. A large
difference, from 34 for 238U up to 1.3 for 243Am, was observed. This difference is
discussed on the basis of modern models for fission fragments formation. -ray spectra measurements were used. A large
difference, from 34 for 238U up to 1.3 for 243Am, was observed. This difference is
discussed on the basis of modern models for fission fragments formation.
|
P13-2010-21 (277.780)
Pepyolyshev Yu.N., Popov A.K.
Limits of Safe Perturbations of External Reactivity of the IBR-2 Reactor
For the IBR-2 pulsed reactor the limits of safe perturbations of reactivity have been
defined by mathematical simulation of the reactor
dynamics.
It has been shown that during the reactor operation there occurs a
continuous narrowing of the region of permissible perturbations of
reactivity in the presence of significant fluctuations of its limit. The
safety limit for some kinds of reactivity perturbations during 20 years of
the reactor operation has decreased by more than 3 times.
The reduction of the region of permissible fluctuations of reactivity is
connected with a gradual decay of the fast power feedback. It has been
demonstrated that the most probable reason for this phenomenon is an
increase in the positive component of the feedback due to a change in
thermo-mechanical deformations of the fuel elements in the course of energy
production.
It has been noted that even in view of the continuous narrowing of the
safety limit a standard system of automatic control of the reactor reliably
ensures its safe operation.
|
E15-2010-23 (521.713)
J. Adam, A.A. Solnyshkin, M. Stefanik, V. M. Tsoupko-Sitnikov, L. Zavorka, V. Kumar, Chitra Bhatia, Aruna Bhart, S.K. Gupta
A Feasibility Study of Nonelastic Reactions in Thorium and Uranium by the Spallation Neutrons
Neutron absorption and fission reactions play an important
role in a conventional reactor but when fuel is irradiated by the
spallation neutrons then a number of nonelastic reactions will play
significant role in both multiplication of neutrons and fission
reactions. In theoretical study it has been revealed that the fertile and
fissile fuels have a different behavior in this respect. Thus, it is
imperative to understand the feasibility of such reactions taking place in
the fertile and fissile fuel elements before conducting experiment at
Phasotron. In the present study it is found that many nonelastic reactions producing fragments or residuals of half-lives greater
than several tens of minutes can be studied using the off-line gamma
spectrometry. A large amount of samples can be irradiated with the
spallation neutrons produced in 660 MeV proton +Pb collision. A tentative
design of the experimental setup is also suggested for the experiment at
Phasotron.
|
19-2010-24
Белов О. В.
Математическое моделирование индуцированного мутационного процесса в клетках Escherichia coli при действии ультрафиолетового излучения
Автореф. дис. ... канд. биолог. наук
(rus)
|
E14-2010-26 (537.382)
D.P. Kozlenko, N.T. Dang, Z. Jirak, S.E. Kichanov, E.V. Lukin, B.N. Savenko, L.S. Dubrovinsky, C. Lathe
Structural and Magnetic Phase Transitions in Pr0,15Sr0,85MnO3 at High Pressure
The crystal and magnetic structures of Pr0,15Sr0,85MnO3
manganite have been studied by means of powder X-ray and neutron diffraction
in the temperature range 10-400 K at high external pressures up to 55 and 4 GPa, respectively. A structural phase transition from cubic to tetragonal
phase upon compression was observed, with large positive pressure
coefficient of transition temperature dTct/dP = 26(2) K/GPa. The C-type
antiferromagnetic (AFM) ground state is formed below TN ~ 280 K. While at ambient pressure the structural and magnetic transition
temperatures coincide, Tct ~ TN, upon compression they
become decoupled with TN « Tct due to much weaker TN-pressure dependence with
coefficient dTN/dP = 3.8(1) K/GPa.
|
P12-2010-27 (308.363)
Maslov O.D. et al.
Uranium Extraction from the Waste Ash after Burning the Mongolian Coal
The content of natural radionuclides, as well as possibility of
uranium leaching from the brown coal ash of the Mongolian Thermal Power
Plant, was determined. Instrumental Gamma Activation Analysis (IGAA) and
X-Ray Fluorescence Analysis (RFA) for determination of the element contents
were used. Leaching of uranium from the brown coal ash was carried out by
the 8 М HNO3+HF (10%) mixture. Extraction of uranium from solution
and separation from contiguous elements were carried out by ion-exchange
resin. The natural radioelements 238U, 232Th and products of their
decay were absent in the ash sample after leaching, which allows using the
brown coal ash as building material.
|
P3-2010-29 (959.957)
Yurevich V.I., Yakovlev R.M., Lyapin V.G.
Neutron Production in Interaction of 2-GeV Protons with Nuclei
Neutron production double differential cross sections for reactions of 2-GeV
protons with the nuclei Be, Al, Cu, Cd and Pb have been measured by the TOF method
in the angular range above 30°. The experimental data analysis is
performed in the framework of a phenomenological model with four moving sources
including neutron emission in the first nucleon-nucleon collisions, a hot
source (fireball) decay, multifragmentation and de-excitation of nuclear
fragments by neutron evaporation. The magnitudes of temperature parameters
for all the sources are universal and practically do not depend on the
target nucleus and incident particle energy in the region above 0.5 GeV. It is
found that relative contribution of the hot source decay and
multifragmentation to the mean neutron multiplicity in the reactions is about 41%.
|
P16-2010-31 (558.493)
Brabcova K. et al.
LET Spectrometry of the Clinical 12C Ion Beam
The sets of track etched detectors for the linear energy transfer (LET)
spectrometry were exposed in 12C 290 MeV/amu natural and modified ion
beams at the HIMAC installation at NIRS, Chiba, Japan. LET spectra were
measured at various depths in 12C-ion beams with expected LET values
of primary particles from 13 keV/mm in water, through the Bragg peak
area up to the region of fragmentation behind the Bragg peak.
LET spectra measured with one type of used track
etched detectors, Page, along the beams axis at the depth up to the region
behind the Bragg peak are presented.
The dosimetric values calculated from measured LET spectra are given.
The depth distributions of absorbed dose and biological weighted effective
dose for radiation therapy are calculated. Relative biological weighted
efficiency of 12C beams at the various depths is estimated. The
depth-dose distribution calculated from LET spectra is in a good agreement
with reference measurements in HIMAC.
|
E13-2010-32 (500.674)
N. Anfimov, I. Chirikov-Zorin, A. Dovlatov, O. Gavrishchuk, A. Guskov, N. Khovanskiy, Z. Krumshtein, R. Leitner, G. Meshcheryakov, A. Nagaytsev, A. Olchevski, T. Rezinko, A. Sadovskiy, Z. Sadygov, I. Savin, V. Tchalyshev, I. Tyapkin, G. Yarygin, F. Zerrouk
Novel Micropixel Avalanche Photodiodes (MAPD) with Superhigh Pixel Density
In many detectors based on scintillators the photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) are used as photodetectors.
At present photodiodes are finding wide application. Solid state photodetectors allow operation in strong magnetic fields
that are often present in applications, e.g., some calorimeters operating near magnets, combined PET and MRT, etc.
The photon detection efficiency (PDE) of photodiodes may reach values a few times higher than that of PMTs.
Also, they are rigid, compact and have relatively low operating voltage. In the last few years Micropixel Avalanche PhotoDiodes (MAPDs)
have been developed and started to be used. The MAPD combines a lot of advantages of semiconductor photodetectors and has a high gain,
which is close to that of the PMT. Yet, they have some disadvantages, and one of them is a limited dynamic range that corresponds
to a total number of pixels. The novel deep microwell MAPD with high pixel density produced by Zecotek Company partially avoids this
disadvantage. In this paper characteristics of these photodetectors are presented in comparison with the PMT characteristics.
The results refer to measurements of the gain, PDE, cross-talks, photon counting and applications: beam test results of two different "Shashlyk"
EM calorimeters for COMPASS (CERN) and NICA-MPD (JINR) with the MAPD readout and a possibility of using the MAPD in PET.
|
E10-2010-34 (847.088)
Isupov A.Yu.
The ngdp Framework for Data Acquisition Systems
The ngdp framework is intended to provide a base for the data acquisition (DAQ) system software.
The ngdp's design key features are: high modularity and scalability; usage of the kernel context (particularly kernel threads)
of the operating systems (OS), which allows one to avoid preemptive scheduling and unnecessary memory-to-memory copying between contexts;
elimination of intermediate data storages on the media slower than the operating memory like hard disks, etc. The ngdp, having the
above properties, is suitable to organize and manage data transportation and processing for needs of essentially distributed DAQ systems.
|
E10-2010-35 (196.237)
Isupov A.Yu.
CAMAC Subsystem and User Context Utilities in ngdp Framework
The ngdp framework advanced topics are described.
Namely we consider work with CAMAC hardware,
"selfflow" nodes for the data acquisition systems with the
As-Soon-As-Possible policy, ng_mm(4) as an
alternative to ng_socket(4), the
control subsystem, user context utilities, events representation for the
ROOT package, test and debug nodes,
possible advancements for netgraph(4), etc.
It is shown that the ngdp is suitable for building lightweight
DAQ systems to handle CAMAC.
|
E14-2010-37 (154.163)
McIntyre G. et al.
Modulated Crystal Structures of VII and V Phases in (NH4)3H(SO4)2.
I. Neutron Laue Diffraction
The study of crystal structures of VII and V phases of
(NH4)3H(SO4)2 by means of neutron Laue diffraction is carried out at temperatures
from 5 to 300 K. It is found that crystal structures of VII and V phases have incommensurate
modulation with different periods, and phase transition from phase VII to phase V is transition of the first type.
|
P16-2010-38 (234.644)
Gryzinski M.A.
Determination of the Radiation Quality Factor at the Proton Beam with a Recombination Chamber
Radiation quality factor at the real session on proton therapy and the
contribution of the high LET particles to dosimetric characteristics of the
170 MeV clinical proton beam were experimentally studied using ionization
recombination chamber KR-13. Chamber electrodes were elaborated of
tissue-equivalent material containing 10.5% hydrogen, 86% carbon and
3.5% nitrogen in weight filled with ethane at pressure of 0.7 MPa.
The contribution of high LET particles to absorbed dose has been determined.
It was d2 = (30.8±3)% in the spread out Bragg peak.
Radiation quality factor in the region of the Bragg peak was Q=(4±0.4) Sv/Gy and at the entrance was Q = (1.6±0.2) Sv/Gy.
|
P16-2010-41 (652.581)
Ryom Kwang Chol, Shabalin E.P.
Possibility Research to Use a Passive Type Feeder for the Pelletized Cold
Neutron Moderator of the IBR-2M Pulsed Reactor
The investigation of the behavior of balls in a passive feeder (of a
sandwatch type) for the prospective cold moderator of the IBR-2M pulsed
reactor on the basis of the PFC-3D program intended for the analysis of
multiparticle problems with the so-called DEM method has been carried out.
Numerical experiments have shown that no jams of the flow of 4 mm balls
occured, provided that the diameter of a discharging tube is more than 13 mm. And it is also shown that balls of the boundary layer come out of the
feeder at 1.3-1.4 times more slowly than balls of the central
position. Eventually, special geometry and sizes of the discharging tube ensuring
needed (in view of admissible residence time of methane in a moderator
chamber) flow rate of balls 1-1.2 balls per second are obtained.
|
17-2010-43
Катков В. Л.
Теоретическое исследование особенностей автоэлектронной эмиссии с углеродных объектов
Автореф. дис. ... канд. физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
P5-2010-44 (146.579)
Shlyk V.A.
Decision Problems for Some Classes of Integer Partitions and Number Multisets
We show that the class of integer partitions that cannot be represented as
convex combinations of two partitions of the same numbers coincides with the
class of knapsack partitions and the class of Sidon multisets, which
includes sum-free sets and standard Sidon sets. The decision problem for
knapsack partitions is proved to be co-NP-complete and, therefore, cannot be
solved in polynomial time unless P = NP.
|
P14-2010-45 (382.629)
Mamedov T.N. et al.
Search for Magnetic-Ordered Phase Zn0.99Co0.01O by the mSR-Method
The behavior of the negative muon polarization was studied to search for possible magnetic ordered phase in
Zn0.99Co0.01O. The sample was produced by solid-phase reaction method by using ZnO и Co3O4.
Measurements were performed in transverse magnetic field 1.5 kG in the temperature range 5-300 K and in zero external magnetic field at
temperature 6 K. There were not observed any evidences for the long-range magnetic order.
|
E14-2010-50 (328.520)
T.N. Mamedov, V.D. Blank, V.N. Gorelkin, K.I. Gritsaj, M.S. Kuznetsov, S.A. Nosukhin, V.G. Ralchenko, A.V. Stoykov, R. Scheuermann, S.A. Terentiev
Behaviour of Muonium in Synthetic Diamond
The probabilities of finding the muon in various states in synthetic
single-crystal and polycrystalline diamond were studied. In the IIa-type
single-crystal sample at 150 K the contributions of the diamagnetic muon,
"normal" and "anomalous" muonium were observed to be 1.5, 57 and 8.1,
respectively. The missing fraction of muon polarization was 33.4,
which is approximately two times smaller than in the Ia-type natural diamond,
and two or three times greater than in the IIa- and IIb-type natural diamonds.
The muon spin relaxation rates at the "normal" and "anomalous" muonium states
in the synthetic and natural samples of IIa- and IIb-type are similar.
|
1-2010-51
Мушински Я.
Исследование зарядово-обменных процессов в дейтрон-протонных взаимодействиях
Автореф. дис. ... канд. физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
E6-2010-53 (356.039)
Izosimov I.N., Kalinnikov V.G., Solnyshkin A.A.
Fine Structure of the Strength Function for the b+/EC Decay of the 160mHo (5.02 h) Isomer
The strength function for the b+/EC decay of the deformed nucleus of the 160mHo (5.02 h)
isomer is obtained from the experimental data. The fine structure of the strength function Sb(E) is analyzed.
It has a pronounced resonance structure for Gamow-Teller transitions and is found to exhibit a resonance structure for first-forbidden transitions.
It is shown that for some excitation energies of the 160Dy daughter nucleus the probability of first-forbidden
b+/EC transitions in the decay of the 160mHo isomer is comparable with the probability of Gamow-Teller
b+/EC transitions.
|
E1-2010-54 (378.823)
Tokarev M.V. (on behalf of the STAR Collaboration)
High-pT Spectra of Charged Hadrons in Au+Au Collisions at 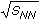 =9.2 GeV in STAR =9.2 GeV in STAR
The production of hadrons in heavy-ion collisions at high pT provides
an important information on mechanism of particle formation and
constituent energy loss in medium. Such information is needed for search
of a critical point and signatures of phase transition. Measurements by
the STAR Collaboration of charged hadron production in Au+Au collisions at
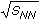 =9.2 GeV over a wide transverse momentum pT=0.2-4 GeV/c
and at mid-rapidity range are reported.
The first measurements of
the spectra of charged hadrons at high pT at this energy are presented.
The spectra demonstrate
the dependence on centrality which enhances with pT. The constituent
energy loss and its dependence on transverse momentum of particle and
centrality of collisions are estimated in the z-scaling approach. =9.2 GeV over a wide transverse momentum pT=0.2-4 GeV/c
and at mid-rapidity range are reported.
The first measurements of
the spectra of charged hadrons at high pT at this energy are presented.
The spectra demonstrate
the dependence on centrality which enhances with pT. The constituent
energy loss and its dependence on transverse momentum of particle and
centrality of collisions are estimated in the z-scaling approach.
|
P14-2010-55 (222.836)
Semina V.K.
Modification of Magnetic Structure and Properties of Metallic Alloys
Using Heavy Ion Irradiation
Based on own experimental and published data on modification of magnetic
structure and properties of metallic alloys under heavy ion irradiation the
possibility was shown to create defined laminated and two-dimensional
magnetic structures.
|
P13-2010-57 (812.430)
Budagov J. et al.
Cylindrical Niobium - Stainless Steel Transition Element Manufactured by Explosion Welding
New results in development of the Nb+stainless steel (SS) bimetallic
transition elements for the helium Vessel of the
fourth-generation ILC cryomodule are presented. Various schemes
are considered for explosion welding of the Nb+SS transition element, and
two schemes proposed by JINR are adopted: with inner cladding and with outer cladding. A new technology is optimized
for explosion welding of the necessary niobium and stainless steel
components, and four test specimens of the transition elements are made.
Preliminary tests in vacuum with thermal cycling in liquid nitrogen and
exposure to ultrasound were carried out in Sarov (RFNC) and Pisa (INFN).
Macro- and microanalyses were also given to the specimens. The tests showed
satisfactory characteristics of the Nb+SS joints. The leak rate
measured in Sarov was Q 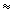 10-9 atm · cm3/s. In Pisa, after
thermal cycling and exposure to ultrasound, the upper limit of the leak rate
for all test joints was found to be Q 10-9 atm · cm3/s. In Pisa, after
thermal cycling and exposure to ultrasound, the upper limit of the leak rate
for all test joints was found to be Q  3-5 · 10-10 atm · cm3/s.
The transition elements will be tested at the helium temperature
(1.8 K) at FNAL (USA). 3-5 · 10-10 atm · cm3/s.
The transition elements will be tested at the helium temperature
(1.8 K) at FNAL (USA).
|
P13-2010-58 (441.077)
Kim Tae Gyoun, Pepyolyshev Yu.N., Rogov A.D.
Thermal Analysis Methods of a Fuel Rod in IBR-2 Pulsed Reactor
The problem of transient temperature distribution in a fuel rod of
the reactor IBR-2 is considered: in fuel (in rod-shaped pellet and in hollow-shaped pellet), in cladding of the fuel rod, and also in liquid sodium
coolant surrounding a fuel rod.
For analyzing transient thermal behaviour of a fuel rod, a program for
numerical solving of heat conduction equation in cylindrical coordinates
system by applying finite difference method to the equations of
one-dimensional transient problem of heat conduction is created. The program
is written on the basis of the algorithms used in programs FEMAXI,
FRAPTRAN and FRAPCON, but has essential difference from them as it is
focused on thermal physics of fast reactors of IBR-2 type with plutonium fuel
and sodium coolant with research possibility of very rapid thermal processes
up to microsecond duration.
The solution algorithms of transient thermal behaviour used
in the program and their implementation technique are shortly described.
|
P13-2010-59 (300.590)
Kim Tae Gyoun, Pepyolyshev Yu.N., Rogov A.D.
Thermal Analysis of a Fuel Rod in IBR-2 Pulsed Reactor (Steady-State Problem)
Computational results of a thermal analysis for a fuel rod of fast
pulsed reactor IBR-2 with plutonium as fuel and liquid sodium as coolant are
presented. The maximum temperature in the center of rod-shaped fuel
subjected to maximum thermal load (137.52 W/cm) and to average thermal load
(109.31 W/cm) is 1135 and 948 oC, respectively. And the
maximum temperature on an inner surface of hollow-shaped fuel subjected to
maximum thermal load is 944 oC. The maximum temperature of a coolant
on the output of the coolant channel with a fuel rod subjected to maximum
thermal load is 398 oC and the heating of coolant is 108 oC.
Only thermal analysis of a steady-state fuel rod is presented.
|
E1-2010-61 (878.034)
J.Adam, A.Baldin, N.Vladimirova, N.Gundorin, B.Gus'kov, V.Dyachenko,
A.Elishev, M.Kadykov, E.Kostyuhov, V.Krasnov, I.Mar'in, V.Pronskikh,
A.Rogov, A.Solnyshkin, V.Stegailov, S.Stetsenko, S.Tyutyunnikov, V.Furman, V.Tsoupko-Sitnikov
E.Belov, M.Galanin, V.Kolesnikov, N.Ryazansky, S.Solodchenkova,
B.Fonarev, V.Chilap, A.Chinenov,
E.Baldina,
A.Balabekyan, G.Karapetyan,
I.Zhuk, S.Korneev, A.Potapenko, A.Safronova, V.N.Sorokin,
V.V.Sorokin,
A.Khilmanovich, B.Marcynkevich, T.Korbut,
Ch.Stoyanov, L.Kostov, P.Zhivkov, O.Yordanov, S.Batzev,
Ch.Protohristov,
A.Kugler, V.Wagner, M.Majerle, A.Krasa, O.Svoboda,
K.Katovsky, O.Schasny,
A.Tuleushev,
K.Gudima, M.Baznat,
R.Togoo, D.Otgonsuren, Ts.Tumendelger, Ts.Damdinsuren,
M.Shuta, E.Strugalska-Gola, S.Kilim, M.Bielevicz, A.Wojeciechowsky,
V.Voronko, V.Sotnikov, V.Sidorenko,
I.Haysak,
S.R.Hashemi-Nezhad, Y.Borger,
W.Westmeier, H.Robotham,
W.Ensinger, D.Severin,
M.Rossbah, B.Thomauske,
M.Zamani, M.Manolopoulou, St.Stoulos, M.Fragopolou,
St.Jokic,
H.Kumawat,
V.Kumar, M.Sharma
Study of Deep Subcritical Electronuclear Systems and
Feasibility of Their Application for Energy Production and Radioactive Waste Transmutation
Представлено физическое обоснование для продолжения и развития исследований
новых схем электроядерного метода для производства энергии и трансмутации
долгоживущих компонентов радиоактивных отходов (РАО), основанного на ядерных
релятивистских технологиях (ЯРТ). Проект "Энергия и
трансмутация РАО" нацелен на комплексное исследование взаимодействий
релятивистских пучков нуклотрона-М с энергиями до 10 ГэВ в квазибесконечных
мишенях.
На основе анализа результатов известных экспериментальных и
расчетно-теоретических работ показано, что в рамках предлагаемой схемы можно рассчитывать на использование
природного/обедненного урана или тория для
производства энергии без добавления урана-235. Также
возможна утилизация отработанных ядерных элементов атомных электростанций.
Показано, что выполнение проекта "Энергия и трансмутация РАО" даст возможность получить
принципиально новые, отсутствующие в настоящее время совокупные данные и
расчетные методы, необходимые для начала проектирования демонстрационных
опытно-промышленных установок на основе этой схемы.
|
E17-2010-062 (860.034)
Vladimirov A.A., Ihle D., Plakida N.M.
Dynamic Spin Susceptibility of Superconducting Cuprates: A Microscopic Theory of the Magnetic Resonance Mode
A microscopic theory of the dynamic spin susceptibility (DSS) in the superconducting state within the t-J model is presented.
It is based on an exact representation for the DSS obtained by applying the Mori-type projection technique for the relaxation function in
terms of Hubbard operators. The static spin susceptibility is evaluated by a sum-rule-conserving generalized mean-field approximation,
while the self-energy is calculated in the mode-coupling approximation. The spectrum of spin excitations is studied in the underdoped and
optimally doped regions. The DSS reveals a resonance mode (RM) at the antiferromagnetic wave vector Q = p(1,1) at
low temperatures due to a strong suppression of the damping of spin excitations. This is explained by an involvement of spin excitations in the decay
process besides the particle-hole continuum usually considered in random-phase-type approximations. The spin gap in the spin-excitation spectrum
at Q plays a dominant role in limiting the decay in comparison with the superconducting gap which results in the observation of the RM even
above Tc in the underdoped region. A good agreement with inelastic neutron-scattering experiments on the RM in YBCO compounds is found.
|
P3-2010-63 (113.735)
Alexandrov Yu.A.
On the Interaction between the Neutron and the Electron. Connection with the Yukawa Meson Theory
It would be desirable to underline once again that the n-e scattering length
value, which is -1.30(3)·10-16 cm, contradicts the Yukawa meson theory and -1.60(4)·10-16 cm is in agreement with it.
Unfortunately,
practically nobody pays attention to this fact.
Because of a considerable number of difficult-to-estimate corrections, the
future experiments on the measurement of the n-e scattering length should
be performed at a rather big relative contribution of the sought-for length
to the measured value.
|
P14-2010-65 (268.259)
Krivandin A.V. et al.
Study of  -Crystallin Structure by Small-Angle Neutron
Scattering with Contrast Variation -Crystallin Structure by Small-Angle Neutron
Scattering with Contrast Variation
The structure of the oligomeric protein  -crystallin from the bovine
eye lens has been investigated by small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) by the
contrast variation method (volume fraction of D2O was 0, 23, 68 and
90%). Experiments were carried out on YuMO spectrometer (IBR-2 reactor,
JINR). From the SANS curves the match point for -crystallin from the bovine
eye lens has been investigated by small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) by the
contrast variation method (volume fraction of D2O was 0, 23, 68 and
90%). Experiments were carried out on YuMO spectrometer (IBR-2 reactor,
JINR). From the SANS curves the match point for  -crystallin (43%
D2O) and its average scattering length density at this point
(2.4 · 1010 cm-2) have been obtained. The radius of gyration
and distance distribution functions for -crystallin (43%
D2O) and its average scattering length density at this point
(2.4 · 1010 cm-2) have been obtained. The radius of gyration
and distance distribution functions for  -crystallin have been
calculated as well. On the basis of these calculations it was concluded that -crystallin have been
calculated as well. On the basis of these calculations it was concluded that
 -crystallin has a homogeneous distribution of the scattering
density in domains inaccessible for water penetration and all parts of this
protein undergo a uniform deuteration. The latter indicates that all -crystallin has a homogeneous distribution of the scattering
density in domains inaccessible for water penetration and all parts of this
protein undergo a uniform deuteration. The latter indicates that all  -crystallin
subunits have an equal accessibility for water and presumably
for some other low molecular weight substances. These conclusions on the -crystallin
subunits have an equal accessibility for water and presumably
for some other low molecular weight substances. These conclusions on the
 -crystallin structure (a homogeneous distribution of the scattering
density and an equal accessibility of all subunits for low molecular weight
substances) should be taken into account in the time of elaboration of -crystallin structure (a homogeneous distribution of the scattering
density and an equal accessibility of all subunits for low molecular weight
substances) should be taken into account in the time of elaboration of
 -crystallin quaternary structure models. -crystallin quaternary structure models.
|
P9-2010-68 (1.044.998)
Averichev et al.
Results of 40th and 41st Nuclotron
Main results of the works in the frame of the Nuclotron-M project fulfilled in the period from July
2009 till April 2010 are presented. General attention is devoted to the results of 40th and 41st Nuclotron
runs performed from 18 November to 11 December 2009 and from 25 February to 25 March 2010
correspondingly. ost sufficient achievement of the 41st run was successive acceleration and extraction
of Xe ions.
|
P13-2010-69 (449.269)
Bazylev S.N. et al.
A Prototype Coordinate Detector Based on Granulated Thin-Walled Drift Tubes
A prototype detector based on thin-walled segmented tubes was developed and its parameters were studied in JINR and on SPS (CERN).
The detector contains 360 registration channels with a diameter of 4 mm. The prototype's granularity is 4 сm2 and the insensitive
length in the region of straw internal elements is less than 5% of its full sensitive area. The time and spatial parameters of the detector
do not differ from those of ordinary track detectors based on drift tubes.
|
E18-2010-71 (439.959)
Luu Viet Hung, O.D.Maslov, Dang Duc Nhan, Trinh Thi Thu My, Phung Khac Nam Ho
Uranium Uptake of Vetiveria zizanioides (L.) Nash
Uranium uptake of vetiver grass Vetiveria zizanioides (L.) Nash) from Eutric Fluvisols (AK), Albic Acrisols (BG),
Dystric Fluvisols (HP) and Ferralic Acrisols (TC) in northern Vietnam is assessed. The soils were mixed with aqueous solution of uranyl
nitrate to make soils contaminated with uranium at 0, 50, 100, 250 mg/kg before planting the grass. The efficiency of uranium uptake by the grass
was assessed based on the soil-to-plant transfer factor (TFU, kg · kg-1). It was found that the TFU values
are dependent upon the soils properties. CEC facilitates the uptake and the increased soil pH could reduce the uptake and translocation of
uranium in the plant. Organic matter content, as well as iron and potassium, inhibits the uranium uptake of the grass. It was revealed
that the lower fertile soil, the higher uranium uptake. The translocation of uranium in root for all the soil types studied is almost
higher than that in its shoot. It seems that vetiver grass could potentially be used for the purpose of phytoremediation of soils
contaminated with uranium.
|
E10-2010-73 (689.308)
Akishina T.P., Derenovskaya O.Yu., Ivanov V.V.
Study of the Electron Energy Losses in the CBM TRD
We analyze the distributions of energy losses for electrons in the
TRD (Transition Radiation Detector) using the energy deposits in a
one-layer TRD prototype obtained during the test beam at the GSI (Darmstadt,
February 2006) and Monte Carlo simulations for the n-layered TRD realized
in the framework of the CBM ROOT for momenta
in the range of 1 to 13 GeV/c. The procedure for approximation of
the electron energy losses in one layer of the TRD is developed.
This procedure permits one to extract a transition radiation part from
the real measurements and compare it with the Monte Carlo simulation.
|
E15-2010-74 (298.622)
Baluev V.V. et al.
Experimental Search for the Radiative Capture Reaction
d + d  4He + 4He +  from the dd
from the dd Muonic Molecule State J = 1 Muonic Molecule State J = 1
A search for the muon catalyzed fusion
reaction d + d  4He + 4He +  in the dd
in the dd muonic molecule was performed using the experimental installation
TRITON with BGO detectors for muonic molecule was performed using the experimental installation
TRITON with BGO detectors for  quanta. The high-pressure target filled
with deuterium was exposed to the negative muon beam of the JINR Phasotron to
detect quanta. The high-pressure target filled
with deuterium was exposed to the negative muon beam of the JINR Phasotron to
detect  quanta with the energy of 23.8 MeV.
An experimental estimation for the yield of radiative deuteron capture
from the dd quanta with the energy of 23.8 MeV.
An experimental estimation for the yield of radiative deuteron capture
from the dd state J = 1 was obtained at a level state J = 1 was obtained at a level
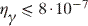 per fusion. per fusion.
|
P1-2010-75 (825.313)
Zarubin P.I. (on behalf of the BECQUEREL Collaboration)
Peripheral Fragmentation of Relativistic Nuclei
The modern concepts of nucleon clustering are described in brief. The application of experimental methods of
relativistic nuclear physics for the development of nucleon cluster physics is presented. A short review of research performed
by the nuclear emulsion technique is given. The significance of observations of coherent dissociation of relativistic nuclei
for the study of nuclear clustering is discussed. According to observations in nuclear emulsion, the degree of coherent
dissociation may reach complete dissociation both for light nuclei O, Ne, Mg and Si, and for heavy nuclei Au, Pb and U.
This phenomenon may be a source of cluster systems of unprecedented complexity. Pattern of coherent dissociation for a
large variety of nuclei, adjacent to the beginning of the table of isotopes, including radioactive ones, is studied.
|
P13-2010-76 (663.863)
Piyadin S.M. et al.
 E-E Detector for the Registration of the Protons
from the Deuteron Nonmesonic Breakup Reaction at Internal Target at Nuclotron-M E-E Detector for the Registration of the Protons
from the Deuteron Nonmesonic Breakup Reaction at Internal Target at Nuclotron-M
The design of  E-E detector
for study of the deuteron breakup reaction at the internal target at Nuclotron-M
in the deuteron energy interval 300-500 MeV is presented.
The high voltage power system for PMTs-63 that is managed by Wenzel Electronik
module with the computer control is shortly described. The light-emitting diode monitoring
of the E-E detector
for study of the deuteron breakup reaction at the internal target at Nuclotron-M
in the deuteron energy interval 300-500 MeV is presented.
The high voltage power system for PMTs-63 that is managed by Wenzel Electronik
module with the computer control is shortly described. The light-emitting diode monitoring
of the  E-E detector's work is considered.
The results of the E-E detector's work is considered.
The results of the  E-E detector tests
with cosmic muons and deuterons at Nuclotron are presented. E-E detector tests
with cosmic muons and deuterons at Nuclotron are presented.
|
P1-2010-77 (477.560)
Yurevich V.I., Yakovlev R.M., Lyapin V.G.
Neutron Production in Collisions of 2 A GeV Carbon Nuclei with C, Al, Cu, Cd and Pb Nuclei
Neutron production double-differential cross sections were measured by
time-of-flight method for interactions of carbon nuclei with energy of 2 GeV/nucleon with C, Al, Cu, Cd and Pb nuclei. The measurements were carried
out for angles 30, 53 and 90o in interval of neutron
energies from hundred keV to 300 MeV. A phenomenological model of four
moving sources is applied for analysis of the experimental results and
estimation of contributions to the neutron emission from different reaction
stages. The temperature parameters, obtained on the neutron energy spectrum
slope, are (22 2) MeV for the hot source, fireball, and (4.5 2) MeV for the hot source, fireball, and (4.5 0.3) MeV
for the stage of thermal fragmentation of highly excited heavy remnants. The
relative contribution of these two sources to total neutron yield does not
depend on target nucleus and in average it is ~ 42%. 0.3) MeV
for the stage of thermal fragmentation of highly excited heavy remnants. The
relative contribution of these two sources to total neutron yield does not
depend on target nucleus and in average it is ~ 42%.
|
P4-2010-79 (250.214)
Gusev A.V.
Electrical Field of Magnetized Sphere and Unipolar Induction
At rotation of a ball, magnetized lengthwise axis of rotation passing
through its center, a magnetic field produced by this ball does not change
in time neither in value, nor in a direction. Is it possible in this
case to speak that the field is rotated together with the magnet? How should one resolve a visible inconsistency between observation of EMF in a unipolar
generator and the Faraday induction law, which suggests that EMF = -d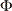 /dt = 0,
when /dt = 0,
when 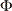 = const?
On the basis of the classic Maxwell theory, equations of lines of force of
an electrical field, derived at rotation of such a ball, are deduced and
their picture is built. The opinion of some specialists is criticized that
the magnetic field of such a ball is rotated together with a ball and
creates outside of it an electrical field with the special properties
contradicting the classic Maxwell theory. = const?
On the basis of the classic Maxwell theory, equations of lines of force of
an electrical field, derived at rotation of such a ball, are deduced and
their picture is built. The opinion of some specialists is criticized that
the magnetic field of such a ball is rotated together with a ball and
creates outside of it an electrical field with the special properties
contradicting the classic Maxwell theory.
|
P13-2010-81 (2.041.619)
Batusov V.Yu., Lyablin M.V., Topilin N.D.
The Development and Application of Hardware-Software for the Controlled
Assembly of ATLAS Hadron Tile Calorimeter
The article contains developed by the authors hardware-software
complex and geometry control methods of the main constituent elements and final
assembly of the hadron tile calorimeter. The developed complex was used at all
stages of the calorimeter creation and allowed one to reach high-design precision
when creating the world largest research ATLAS spectrometer.
|
E4-2010-83 (138.453)
Ignatovich F.V., Ignatovich V.K.
An Experiment on a Ball-Lightning Model
We discuss total internal reflection (TIR) from an interface
between glass and gainy gaseous media and propose an experiment
for strong light amplification related to investigation of a
ball-lightning model.
|
E13-2010-84 (775.938)
Balagurov A.M. et al.
Neutron Diffraction Potentialities at the IBR-2 Pulsed Reactor
for Nondestructive Testing of Structural Materials
Neutron diffraction is widely used for investigations of residual and
applied stresses in bulk materials and components. The most important factor
in these investigations is the high penetration depth of neutrons (up to 2 cm for steel).
At the IBR-2 pulsed reactor in Dubna the Fourier stress
diffractometer (FSD) has been constructed to optimize the internal stress
measurements. The FSD design satisfies the requirements of high luminosity,
high resolution and specific sample environment. The collimator system
guarantees a minimum gauge volume of 2  2 2 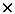 2 mm. A mechanical testing
machine allows in-situ tension or compression
measurements up to a load of 20 kN and sample temperatures up to 800 oC.
In the paper the current status of FSD is reported and potentialities are
demonstrated with several examples of investigations performed. 2 mm. A mechanical testing
machine allows in-situ tension or compression
measurements up to a load of 20 kN and sample temperatures up to 800 oC.
In the paper the current status of FSD is reported and potentialities are
demonstrated with several examples of investigations performed.
|
E2-2010-85 (104.404)
Beshtoev Kh.M.
Is Neutrino Produced in Standard Weak Interactions a Dirac or
Majorana Particle?
This work considers the following problem: what type (Dirac or
Majorana) of neutrinos is produced in standard weak interactions?
It is concluded that only Dirac neutrinos but not Majorana
neutrinos can be produced in these interactions. Then neutrino
interacts with W and Z bosons but neutrinoless double
beta decay is absent. It means that this neutrino will be produced
in another type of interaction. Namely, Majorana neutrino will be
produced in the interaction which differentiates spin projections
but cannot differentiate neutrino (particle) from antineutrino
(antiparticle). Then neutrino will interact with W and Z bosons but neutrinoless double
beta decay is absent. It means that this neutrino will be produced
in another type of interaction. Namely, Majorana neutrino will be
produced in the interaction which differentiates spin projections
but cannot differentiate neutrino (particle) from antineutrino
(antiparticle). Then neutrino will interact with W bosons
and neutrinoless double beta decay will arise. But interaction
with Z boson will be absent. Such an interaction has not been
discovered yet. Therefore, experiments with very high precision are
important to detect the neutrinoless double decays if they are
realized in the Nature. bosons
and neutrinoless double beta decay will arise. But interaction
with Z boson will be absent. Such an interaction has not been
discovered yet. Therefore, experiments with very high precision are
important to detect the neutrinoless double decays if they are
realized in the Nature.
|
E6-2010-86 (416.679)
Bunatian G.G., Nikolenko V.G., Popov A.B.
The Usage of Electron Beam to Produce Radio Isotopes
through the Uranium Fission by  -Rays and Neutrons -Rays and Neutrons
We treat the production of desirable radio
isotopes due to the 238U photo-fission by the
bremsstrahlung induced in converter by an initial electron beam
provided by a linear electron accelerator. We consider as well the
radio isotope production through the 238U fission by
the neutrons that stem in the 238U sample irradiated by
that bremsstrahlung. The yield of the most applicable radio isotope
99Mo is calculated. We correlate the findings acquired
in the work presented with those obtained by treating the nuclear
photo-neutron reaction. Menace of the plutonium contamination of an
irradiated uranium sample because of the neutron capture by
238U is considered. As we get convinced, the
photo-neutron production of radio isotopes proves to be more
practicable than the production by the uranium photo- and
neutron-fission, both methods are certain to be brought into action
due to usage of the electron beam provided by modern linear
accelerators.
|
1-2010-87 (9.435.913)
Понтекорво Д. Б.
Исседование взаимодействий пионов и антипротонов я легкими ядрами с помощью самошунтирующихся стримерных камер и ядерной фотоэмульсии
Автореф. дис. ... доктора физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
P13-2010-89 (417.285)
Mechtiyeva R.N. et al.
Calculation of the Effective Delayed Neutron Fraction and Prompt Neutron
Lifetime in the IBR-2M Reactor
Calculation of main kinetic parameters for the reactor IBR-2M is carried
out: the effective delayed neutron fraction and the prompt neutron lifetime.
The calculation is based on the use of DORT, a two-dimensional multi-group
program for resolving of neutron transport equation, and SCALE4 programs for
generating multi-group nuclear cross-sections. Calculation values of kinetic
parameters for IBR-2M in a regular mode of its work are obtained:
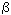 eff = 0.00216 eff = 0.00216  0.00007, 0.00007,
 = 6.5 = 6.5  10-8 s, 10-8 s,
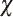 = 0.980, = 0.980, 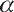 = 3.50 = 3.50  104 s-1.
The parameters 104 s-1.
The parameters 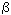 and and  are ~ 0.2% and ~5.0% greater than for
IBR-2 ( are ~ 0.2% and ~5.0% greater than for
IBR-2 (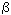 эф = 0.00216 and эф = 0.00216 and
 = (6.2 = (6.2 0.2) 0.2)  10-8 s).
It is shown that 10-8 s).
It is shown that 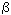 eff and eff and  increase with
reduction of the size of the active zone. Also, it is noted that for calculation of
prompt neutron lifetime it is necessary to use the S16-approximation. increase with
reduction of the size of the active zone. Also, it is noted that for calculation of
prompt neutron lifetime it is necessary to use the S16-approximation.
|
P13-2010-91 (289.768)
Kim Tae Gyoun, Pepyolyshev Yu.N., Rogov A.D.
Thermal Analysis of a Fuel Element in the IBR-2 Pulsed Reactor (Pulse Regime)
In the work computational results on transient temperature fields in a fuel rod
of the IBR-2 reactor at the rated power 2 MW and frequency of repetition of
impulses 5 s-1 are presented. And also in case of generation of power impulses from the
zero moment, the heating process of a fuel rod is considered. Calculations have shown the following.
The heating on an inner surface of hollow-shaped pellet under maximum thermal-loaded condition
does not exceed 18 oC, and average heatings on radius in the centre of a fuel rod and on fuel
volume in this fuel rod are 17.9 and 14.2 oC, respectively.
Pulsations of the average temperature of coolant at the exit from the active zone and cladding of a
fuel rod during a pulse are small and equal to 0.2 and 1.1 oC, respectively.
The value of thermal inertia of a fuel rod is equal to 8.94 s and well
coincides with the experimental estimation of the time constant of the basic
component in the power feedback.
It is emphasized that the time of achievement of thermal balance in a fuel rod is not
greater than 50 s.
|
E13-2010-92 (546.231)
Budagov J. et al.
Investigations on Helicoflex Gaskets for ILC Cavity Flanges
A reliable joint of the Nb superconducting cavities is achieved due to the
use of the conical Nb-Ti flanges
together with a Quick Disconnect System (from the Garlock company). The joint was tested at room
temperature and liquid nitrogen temperature (77 K), the measured leak level is
< 10-9 mbar · l/s. This flange
assembly simplifies the design, reduces the assembly time by an order of magnitude, and is expected to
decrease the accelerator vacuum chamber length.
|
E13-2010-93 (464.058)
Budagov J. et al.
FEM Analysis of Ultra-Flex Gasket for ILC Cavity Flanges
Numerical simulation of a new kind of metallic gasket by Garlock company, the Ultra-Flex,
has been carried out
using the ANSYS code for finite element analysis. The main purpose was to determine the optimal geometrical parameters
of the seal for our application in ILC cavity flanges. The FEA model shows that if the gasket tore diameter is
increased from 4.65 to 8 mm and its thickness is increased from 0.5 to 0.65 mm, the useful elastic recovery
(spring-back) of the gasket will drastically increase, from 0.05 to 0.2 mm.
|
P11-2010-95 (195.710)
Puzynin I.V., Puzynina T.P., Thach V.T.
SLIPM - a MAPLE Package for Numerical Solution of Sturm-Liouville Partial Problems Based
on a Continuous Analog of Newton's Method: II. Program Realization
SLIPM (Sturm-LIouville Problem in MAPLE) is a program complex written in the language
of the computer algebras system MAPLE. It consists of the main program SLIPM.mw and
of some procedures. It is intended for a numerical solution with
the help of the continuous analog of Newton's method (CANM) of
Sturm-Liouville partial problems, i.e., for calculating some
eigenvalue of linear second-order differential operator and a
corresponding eigenfunction satisfying homogeneous boundary
conditions of the general type.
SLIPM is the development of the program complexes SLIP1 and SLIPH4 written in the Fortran language. It is added by
two new ways of calculating the initial value of iterative parameter  0,
by a procedure for calculating a higher precision solution (eigenvalue and corresponding eigenfunction) with the
help of Richardson's extrapolation method, by graphical visualization procedures of intermediate and final results
of the iterative process and by saving of the results on a disk file. The descriptions of the procedures purposes
and their parameters are given. 0,
by a procedure for calculating a higher precision solution (eigenvalue and corresponding eigenfunction) with the
help of Richardson's extrapolation method, by graphical visualization procedures of intermediate and final results
of the iterative process and by saving of the results on a disk file. The descriptions of the procedures purposes
and their parameters are given.
|
P11-2010-96 (366.520)
Amirkhanov I.V. et al.
Investigation of Solutions of Boundary Problems
for the Quasipotential Equation Using the Shift Operator
The quasipotential equations are widely applied to the relativistic
description of a system of two particles, for example, a quark and an
antiquark. In the work, using the shift operator 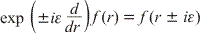 ,
the solutions of boundary problems for the
quasipotential equation with the Coulomb potential, containing the
functional ,
the solutions of boundary problems for the
quasipotential equation with the Coulomb potential, containing the
functional 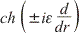 , at various values
of parameter , at various values
of parameter 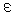 are investigated. It is established that, at are investigated. It is established that, at
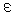  0 there is a solution which aspires to
the Schr 0 there is a solution which aspires to
the Schr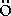 dinger
equation solution. Besides, the so-called frontier layer solutions and transition of one type
of the solution into another are found out. Investigations are
carried out using the system of symbolical evaluations MAPLE. dinger
equation solution. Besides, the so-called frontier layer solutions and transition of one type
of the solution into another are found out. Investigations are
carried out using the system of symbolical evaluations MAPLE.
|
E11-2010-101 (188.535)
Sitnik I.M.
Modification of the FUMILI Minimization Package-2
FUMILI renovation-2 (FUMILIM) is suggested which has the following advantages:
a more convenient and friendly user interface; no restriction
to the number of parameters and experimental points; speed advantage
when the number of parameters is high enough; a possibility to define
analytically an arbitrary number of parameter derivatives.
An additional package of the track reconstruction in straw
chambers is suggested.
The solution speed for the specific tasks was increased many times
in comparison with the previous version of FUMILIM.
All programs are written using FORTRAN-77.
|
P1-2010-102 (1.017.525)
Adam J. et al.
Lead-Graphite Setup "Gamma-3" for the Study of
Transmutation of Long-Lived Radionuclides at JINR LHEP Nuclotron
Particle Beams. P.1. Design. Determination of the Neutron Flux per
One 2.33 GeV Deuteron
Description of "Gamma-3" setup designed for the study
of transmutation of long-lived radionuclides is presented. The setup
is represented by a lead neutron-generating target with the dimensions
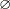 8 8 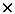 60 cm, surrounded with graphite and irradiated
by 2.33 GeV deuteron beam. The dimensions of the graphite assembly are
110 60 cm, surrounded with graphite and irradiated
by 2.33 GeV deuteron beam. The dimensions of the graphite assembly are
110 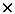 110 110 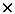 60 cm. Within the extent of the graphite assembly
channels for the placement of activation detectors and radionuclide samples
are made. Experimental results on the determination of the neutron flux per
one accelerated deuteron are given. Numerical calculations of neutron spectra
and fluxes in the channels of the setup are performed and a comparison with
the obtained experimental data is carried out. 60 cm. Within the extent of the graphite assembly
channels for the placement of activation detectors and radionuclide samples
are made. Experimental results on the determination of the neutron flux per
one accelerated deuteron are given. Numerical calculations of neutron spectra
and fluxes in the channels of the setup are performed and a comparison with
the obtained experimental data is carried out.
|
P2-2010-104 (299.871)
Kuraev E.A.
Some Problems of Mathematical Physics
Several problems arising in investigation of mechanical systems, electromagnetic fields,
electric chains, electron radiation are collected. A set of useful definite integrals,
in addition to the known textbooks, is presented as well. Most of the considered items can be
subject to further investigation by students.
The reader is supposed to be acquainted with the university course of mathematics and physics.
|
P13-2010-105 (182.993)
Davkov K.I., Myalkovskiy V.V., Peshekhonov V.D., Savenkov A.A.
Development of the Reading Cable with Small Quantity of Substance
for Segment Drift Tubes
Manufacturing techniques and key parameters of the developed samples of a
flat cable are discussed for segment detectors based on thin-film drift
tubes. Multiwire cables possess a small quantity of their own substance
simultaneously providing transmission of high voltage and reading the
signals from the anode segment on one common trunk. Dark currents of the
outflow do not exceed 1 nA and the cross-current value between the trunks of
the multiwire cable is less than 1%.
|
P18-2010-107 (330.727)
Barashkova I.I., Bunyatova E.I., Kravets L.I.
Polypropylene Track Membranes - a Promising Material for Thin Targets with Polarized Protons
With the purpose of creating a new working substance of a polarized target
it has been suggested to use polypropylene track membranes produced by
irradiation of polypropylene films by a high-energy heavy ion beam and a
subsequent chemical etching of the latent tracks of these particles. In
order to provide the membranes with paramagnetic properties required for
realization of the process of dynamic polarization of nuclei, a nitroxyl
radical 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-piperidine-1-oxyl was introduced into the sample
by the method of thermal diffusion. By the electronic paramagnetic resonance
method information was received about paramagnetic centers in the polymeric
matrix of the membranes, a concentration of the nitroxyl radical and a
rotary mobility of the spin probe in them were determined.
|
E14-2010-108 (796.420)
Smirnov L.S. et al.
Study of Ammonium Molecular Ion Impurity Modes
in Rb1-x(NH4)xI Mixed Crystals
by Inelastic Incoherent Neutron Scattering
The study of ammonium dynamics in Rb1-x(NH4)xI
mixed crystals
was carried out by inelastic incoherent neutron scattering in the
concentration region of orientationally disordered  -phase,
0.0 < x < 0.40, at temperature range from 2 to 150 K. The observed
resonance modes correspond to three energy regions: 0.19-0.481 (I), 0.56-3.0 (II) and 4.0- 10.0 (III) meV.
The modes of region I could be described by
rotational tunneling energies of the multipole moments of ammonium ions. The
modes within energy region II correspond to the calculated rotational
tunneling energies between splitted levels of the ground librational level
of ammonium ion. The modes of region III can be described as local gap modes
of ammonium ion because they are located between acoustic and optic branches
of RbI phonon density of states. -phase,
0.0 < x < 0.40, at temperature range from 2 to 150 K. The observed
resonance modes correspond to three energy regions: 0.19-0.481 (I), 0.56-3.0 (II) and 4.0- 10.0 (III) meV.
The modes of region I could be described by
rotational tunneling energies of the multipole moments of ammonium ions. The
modes within energy region II correspond to the calculated rotational
tunneling energies between splitted levels of the ground librational level
of ammonium ion. The modes of region III can be described as local gap modes
of ammonium ion because they are located between acoustic and optic branches
of RbI phonon density of states.
|
P7-2010-110 (221.912)
Nasirov A.K., Tashkhodjaev R.B., Abdurazakov O.O.
True Ternary Fission of 236U: Sequential Mechanism?
The mechanism is offered and calculations were performed to explain the true
ternary fission of 236U which was revealed experimentally by the
"missed mass" method. The calculated yield of the primary excited nucleus
72Ni after emission of neutrons corresponds to the observed most
probable yield 68Ni. The good agreement of theoretical results with
experimental data means that the assumption about the sequential mechanism
of the true ternary fission is reasonable and including the shell effects in
a theoretical model is important
|
P6-2010-111 (387.555)
Aksenov N.V. et al.
Coprecipitation of Ti, Zr and Hf as Homologues of Rf
with Lanthanum Fluoride from Hydrofluoric Acid Solutions
The longer half-lives of radionuclides of transactinides
104267Rf and 105268Db discovered in the
An + 48Ca reactions expand the application of radiochemical techniques for
their chemical characterization and to elucidate the influence of
relativistic effects on the chemical properties within a group in the
periodic table. Here we report the coprecipitation behavior of Ti, Zr and Hf
as lighter homologues of Rf with lanthanum fluoride. The kinetics of
coprecipitation and distribution of group 4 elements between the liquid and
solid phase, both preformed and formed during the distribution process, was
studied as a function of concentration of the micro- and macrocomponent,
foreign multivalent ions, HF, pH in solution. The solid phase of prepared
samples was characterized by electron microscopy (SEM and TEM). The results
show that the coprecipitation mechanism of Zr and Hf with LaF3 is
different from Ti and Th and can be assigned to heterovalent isomorphism. A
possibility of using coprecipitation with lanthanum fluoride for
investigation of the behavior of Rf in HF solutions was demonstrated.
|
P1-2010-113 (994.069)
Azhgirey L.S. et al.
Study of Short-Range Deuteron Spin Structure at the Fragmentation
of Polarized Deuterons into the Cumulative Pions
Data are presented of the vector Ay and
tensor Ayy
analyzing powers at fragmentation of the polarized 5 and 9 GeV/c
deuterons into the high-momentum pions in the kinematic region corresponding
to the pion production on the strong correlated nucleon pair (cumulative
regime).
Observed momentum and angular dependence of pion yields
The momentum and angular behaviours of Ayy are not described by
the impulse approximation calculations with the standard deuteron
wave functions. It seems, to explain the data one needs to construct
models, which consider the deuteron core as some multi-quark
configuration,
6q cluster, the large orbital momentum of which at D-wave state of the
deuteron can be a reason of the strong tensor analyzing power dependence
on the pion transverse momentum as it is observed in the
A(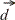 , ,  )X
reaction. )X
reaction.
|
E5-2010-115 (178.626)
Shlyk V.A.
Polyhedral Approach to Integer Partitions
This paper develops the polyhedral approach to integer partitions.
We consider the set of partitions of an integer n as a polytope 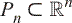 .
Vertices of Pn form the class of partitions that provide the first basis for the whole set of partitions of n.
Moreover, we show that there exists a subclass of vertices, from which all others can be generated with the use
of two combinatorial operations.
Numerical experiments demonstrate considerable decrease in the cardinality of these classes of basic partitions.
We focus on the vertex enumeration problem for Pn.
We prove that vertices of all partition polytopes form a partition ideal of Andrews' partition lattice.
This allows us to construct vertices of Pn by a lifting method, which requires examining
only certain partitions of n.
A criterion of whether a given partition is a convex combination of two others connects vertices
with knapsack partitions, sum-free sets, Sidon sets, and Sidon multisets introduced in the paper.
Albeit verifying the criterion condition was proved to be an NP-hard problem,
it recognizes almost all nonvertices for small n's.
We also prove several easy-to-check necessary conditions for a partition to be a vertex. .
Vertices of Pn form the class of partitions that provide the first basis for the whole set of partitions of n.
Moreover, we show that there exists a subclass of vertices, from which all others can be generated with the use
of two combinatorial operations.
Numerical experiments demonstrate considerable decrease in the cardinality of these classes of basic partitions.
We focus on the vertex enumeration problem for Pn.
We prove that vertices of all partition polytopes form a partition ideal of Andrews' partition lattice.
This allows us to construct vertices of Pn by a lifting method, which requires examining
only certain partitions of n.
A criterion of whether a given partition is a convex combination of two others connects vertices
with knapsack partitions, sum-free sets, Sidon sets, and Sidon multisets introduced in the paper.
Albeit verifying the criterion condition was proved to be an NP-hard problem,
it recognizes almost all nonvertices for small n's.
We also prove several easy-to-check necessary conditions for a partition to be a vertex.
|
P13-2010-116 (2.294.100)
Balagurov A.M. et al.
A New Diffractometer at the IBR-2M Reactor for Real-Time Studies of
Irreversible Processes
At the FLNP at the IBR-2 pulsed reactor, diffraction and small-angle neutron
scattering are used to study irreversible processes in condensed matter in situ
in real time. Often only this mode with a continuous recording of
experimental information allows obtaining the necessary data for the
interpretation of an irreversible process. One of the crucial parameters of
such experiments is the minimum time interval over which the necessary
statistics can be collected. The minute and sometimes second range of
collecting diffraction and SANS patterns have already been realized at the
IBR-2. Estimations show that at the upgraded IBR-2M reactor the conditions
exist for a significant improvement in time resolution while reducing
the mass of the sample. In this report the construction of the specialized
spectrometer at the IBR-2M is proposed, which offers a substantially new
possibility for real-time experiments. Thus, in favorable cases, the time
resolution of the spectrometer will be fractions of milliseconds, which is
currently possible only at high-brightness synchrotron radiation sources.
|
P18-2010-117 (791.044)
Kravets L.I. et al.
Structure and Electrochemical Properties of the Track Membranes
Modified by Tetrafluoroethane Plasma
A structure and charge transport properties of the poly(ethylene
terephthalate) track membrane modified by the 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane
plasma have been studied. It has been found that the polymer deposition on
the surface of a track membrane via the plasma polymerization of
1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane results in the creation of bilayered composite
membranes that possess a conductivity asymmetry in electrolyte solutions -
a rectification effect similar to that of a p-n junction in semiconductors.
This effect is caused by an important reduction of the pore diameter in the
polymer layer that leads to changing the pore geometry as well as by
existence of an interface between two layers with different concentrations
of carboxyl groups. Information about the charge transport in the studied
membranes has been obtained by the method of impedance spectroscopy.
|
P4-2010-119 (276.504)
Ignatovich V.K., Ignatovich F.V.
Optics of Anisotropic Media
Electromagnetic waves in anisotropic media, their reflection and
refraction at interfaces are considered. It is shown that only two
linearly polarized modes of plain waves can propagate inside
anisotropic media. Reflection from interface with isotropic
media is accompanied by double ray splitting, and at sufficiently
small grazing angles a surface wave is created on the interface.
|
P13-2010-121 (576.250)
Gurchin Yu.V. et al.
Detection Equipment of the Experiment for dp-Elastic
Scattering Study at the Internal Target Station of the Nuclotron
The detection equipment for dp-elastic scattering study at the internal target
of the Nuclotron is presented. Results of the scintillation detectors
optimization and results of test experiments using deuteron beam are shown.
|
E1-2010-122 (517.217)
Gurchin Yu.V. et al.
Status of Preparation of dp-Elastic Scattering
Study at the Extracted Beam of the Nuclotron
A selection of dp-elastic scattering events at energies of 1.6 and 2.0 GeV
by using scintillation counters has been performed. The procedure of the
CH2-C subtraction has been established. The dependence of the elastic
events yield on the filter thickness has been investigated. This method can
be used to develop the efficient high-energy deuteron beam polarimetry.
|
1-2010-123
Земляничкина Е. В.
Определение вклада странных кварков в спин нуклона по результатам эксперимента COMPASS (CERN)
Автореф. дис. ... канд. физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
P13-2010-124 (488.683)
Panteleyev Ts.Ts. et al.
A Neutron Spectrometer on the Basis of a Proton Telescope
with Electronic Collimation of Recoil Protons
A gas recoil neutron spectrometer for measuring the energy distribution of
fast neutron fluxes was constructed and its characteristics have been
studied. It is based on measurement of the kinetic energy of protons elastically
scattered at small angles from (n, p) reaction in the hydrogen gas
media. The spectrometer is composed of two cylindrical proportional counters
with common anode wire in the centre. The counting efficiency for neutrons
with kinetic energies in the interval from 150 keV to 14 MeV is expected to
be 10-4-10-6. The estimated energy resolution is about 1.5%.
|
E10-2010-127 (649.409)
Tsyganov Yu.S.
C++ Builder 6.0 CEDV Code for Files Processing
A RAD C++ Borland's Builder 6.0 code CEDV under Windows XP
has been designed for visualizing data obtained from heavy-ion-induced
complete fusion reactions at the main U-400 cyclotron of FLNR. The main
purpose of the code is processing the data from the experiments aimed at
studying chemical properties of SHE. Data from the Dubna Gas-Filled Recoil
Separator could be processed too. Some subroutines for estimating
statistical parameters are also presented; these are based on modified BSC
(background signal combination) approaches.
Examples of application both for chemistry experiments and the experiments
performed at the Dubna Gas-Filled Recoil Separator are presented.
|
13-2010-128
Лебедев А. А.
Алгоритмы и программное обеспечение для реконструкции треков в детекторе переходного излучения и в мюонной системе эксперимента СВМ
Автореф. дис. ... канд. физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
E2-2010-130 (509.149)
Manjavidze J.
On the Connection between Quantum and Classical Descriptions
The review paper presents generalization of d'Alembert's variational
principle: the dynamics of quantum system for an external observer is
defined by the exact equilibrium of all forces acting in the system,
including the random quantum force 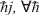 . Spetial attention is dedicated to the
systems with (hidden) symmetries. It is shown how the symmetry reduces the
number of quantum degrees of freedom down to the independent ones. The
sin-Gordon model is considered as an example of such a field theory with
symmetry. It is shown why the particles S-matrix is trivial in that model. . Spetial attention is dedicated to the
systems with (hidden) symmetries. It is shown how the symmetry reduces the
number of quantum degrees of freedom down to the independent ones. The
sin-Gordon model is considered as an example of such a field theory with
symmetry. It is shown why the particles S-matrix is trivial in that model.
|
P13-2010-131 (252.299)
Sobolev Yu.G. et al.
Active Collimators in Experiments with Exotic Nuclear Beams
The active collimator method for experiments with exotic nuclear beams at
the energies near Coulomb barrier of nuclear reactions is described. The
apparatus consists of two blocks of microchannel plates (MCP) and thin
strips of metallic foils (Au, Ag, Al), oriented along X and Y axes. MCPs
register electron emission during penetration of exotic nuclei through these
foils. It gives possibility to obtain information about particle trajectory
and time mark of the event. The proposed technique provides the
smallest amount of matter on the particle path (< 8.0  1017 cm-2),
high efficiency
( 1017 cm-2),
high efficiency
(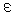 ~ 90% for every
MCP), good time resolution for additional identification of radioactive
nuclei using the time-of-flight method ~ 90% for every
MCP), good time resolution for additional identification of radioactive
nuclei using the time-of-flight method
|
P13-2010-132 (401.699)
Volkov A.D.
The Use of the МЕТ1003 Seismic Detector in Experimental Equipment
A possibility of using the MET1003 molecular seismic detector in
experimental equipment is examined. The detector is characterized by a high
sensitivity, which is 5-10 times higher than the sensitivity of
piezoelectric sensors and Bruel & Kjaer Vibro transducers. The МЕТ1003
monitor allows detection of the vibration frequency accurate to better than
0.2 Hz and amplitude accurate to better than 0.1  m in the range
1 to 200 Hz. Working temperature range of the detector is -40 m in the range
1 to 200 Hz. Working temperature range of the detector is -40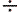 +50 oC. Owing
to its high sensitivity and small size, the detector has a wide field of
application. +50 oC. Owing
to its high sensitivity and small size, the detector has a wide field of
application.
|
P6-2010-133 (281.720)
Karivai A., Zuzaan P., Gustova M.V.
X-Ray Fluorescence Method for Determination of Some
REE and Its Correlation with Thorium
This paper presents a simple procedure for simultaneous determination of
rare earths and some trace elements in REE ores in Mongolia using energy
dispersive X-ray spectrometer and describes correlation of REEs and thorium.
Gamma activation, classic chemical methods and X-ray fluorescence analysis
results of mineral resources were used for description of correlation.
|
P1-2010-134 (464.799)
Kladnitskaya E.N. et al.
Dependences of Kinematical Characteristics for Secondary
Particles in dC,  C and CC Interactions on
Event Collision Centrality at Incident Momentum 4.2 GeV/c per
Nucleon C and CC Interactions on
Event Collision Centrality at Incident Momentum 4.2 GeV/c per
Nucleon
We present the centrality dependence of momenta, transverse momenta,
rapidities and polar angles distributions for  mesons and protons
in dC, mesons and protons
in dC,  C and CC interactions at incident
momentum 4.2 GeV/c per nucleon. As a measure for collision centrality
the number of proton participants in the event has been taken. The mean
values of all variables are obtained at different centralities of
collisions. C and CC interactions at incident
momentum 4.2 GeV/c per nucleon. As a measure for collision centrality
the number of proton participants in the event has been taken. The mean
values of all variables are obtained at different centralities of
collisions.
|
10-2010-135
Лебедев А. А.
Алгоритмы и программное обеспечение для реконструкции треков в детекторе переходного излучения и в мюонной системе эксперимента СВМ
Автореф. дис. ... канд. физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
P13-2010-136 (155.898)
Brudanin V.B. et al.
Large-Volume HPGe Detectors for Registration of Rare Events with Low Energy
Techniques of fabrication and main characteristics of large-volume HPGe
detectors with capacitance about 0.5 pF are presented. The
elaborated methods have allowed making a detector with a mass similar to
coaxial HPGe detectors. Its energy resolution and threshold are close to
typical parameters of small X-ray HPGe detectors.
|
2-2010-137
Арбузов А. Б.
Ведущее и следующее за ведущим логарифмические приближения в КЭД
Автореф. дис. ... канд. физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
2010-141 (387.618)
Краткий обзор важнейших научных результатов Объединенного института ядерных исследований в 2010 году
|
E15-2010-142 (540.345)
Bystritsky V.M. et al.
Measurement of Astrophysical S-Factors and Electron Screening
Potentials for d(d,n)3He Reaction in ZrD2, TiD2, D2O and
CD2 Targets in the Ultralow Energy Region Using Plasma
Accelerators
The present paper is devoted to study of electron
screening effect influence on the rate of d(d,n)3He reaction in the
ultralow deuteron collision energy range in the deuterated polyethylene
(CD2), frozen heavy water (D2O) and deuterated metals (ZrD2
and TiD2). The ZrD2 and TiD2 targets were fabricated via
magnetron sputtering of titanium and zirconium in gas (deuterium)
environment. The experiments have been carried out using high-current plasma
pulsed accelerator with forming of inverse Z-pinch (HCEI, RAS, Russia) and
pulsed Hall plasma accelerator (NPI at TPU, Russia). The detection of
neutrons with an energy of 2.5 MeV from dd reaction was done with eight plastic
scintillation spectrometers. As a result of the experiments, the energy
dependences of astrophysical S-factor for the dd reaction in the deuteron
collision energy range of 2-7 keV and the values of the electron screening
potential Ue of interacting deuterons have been measured for the targets indicated above:
Ue(CD2)  40 eV;
Ue(D2O) 40 eV;
Ue(D2O) 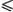 6 eV;
Ue(ZrD2) = (157 6 eV;
Ue(ZrD2) = (157  43) eV;
Ue(TiD2) = (125 43) eV;
Ue(TiD2) = (125  34) eV.
The value of astrophysical S-factor, corresponding to the deuteron
collision energy equal to zero, in the experiments with D2O target is
found: Sb(0) = (58.6 34) eV.
The value of astrophysical S-factor, corresponding to the deuteron
collision energy equal to zero, in the experiments with D2O target is
found: Sb(0) = (58.6  3.6) keV 3.6) keV  b
(D2O). The paper
compares our results with results of other available published experimental
and calculated data. b
(D2O). The paper
compares our results with results of other available published experimental
and calculated data.
|
E2-2010-143 (99.299)
Beshtoev Kh.M.
Distinction between the Model of Vector Dominance and the Model of Oscillations
The distinction between the model of vector dominance and the
model of oscillations is considered on the example of 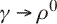 transitions. It is shown that transition
probabilities in these cases differ by a factor of 2. The physical
reason of these transition schemes is also discussed.
transitions. It is shown that transition
probabilities in these cases differ by a factor of 2. The physical
reason of these transition schemes is also discussed.
|
E3-2010-144 (266.230)
Bunatian G.G., Nikolenko V.G., Popov A.B.
On the E-Linac-Based Neutron Yield
We treat neutron generating in high atomic number
materials due to the photonuclear reactions induced by the
bremsstrahlung of an electron beam produced by linear electron
accelerator (e-linac). The dependence of neutron yield on the
electron energy and the irradiated sample size is considered for
various sample materials. The calculations are performed without
resort to the so-called «numerical Monte Carlo simulation». The
acquired neutron yields are well correlated with the data asserted
in investigations performed at a number of the e-linac-driven
neutron sources.
|
P11-2010-145 (604.864)
Dimitrov V.T.
Specification Problems of Business Process Semantics
In this paper genesis of the term «business process» is discussed: from the
business to Informatics. Special attention is given to this term in
Informatics in the context of current business development and its
requirements on the software. Specification and implementation of business
processes with Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) based technologies have
specific issues. Business demands are for fastest implementation of business
process software, but SOA standards are still not mature. As a result of that,
software tools are realized that permit business process with contradictive
semantics to be specified and even to generate non-working code. Here, the
main notations for business process specification are analyzed: WS-BPMN,
WS-BPEL and UML activity diagrams.
|
2-2010-146
Калиновская Л. В.
Однопетлевые КЭД и электрослабые поправки для процессов физики частиц при высоких энергиях
Автореф. дис. ... доктор физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
E14-2010-148 (220.334)
Balasoiu M. et al.
Structural Investigation of Biogenic Ferrihydrite Nanoparticles Dispersion
Structural properties of biogenic ferrihydrite nanoparticles produced by
bacteria Klebsiella oxytocaare investigated. Investigations of morphology and size of
particles dispersed in water by means of high-resolution transmission
electron microscopy and small angle X-ray scattering measurements were
performed. By model calculations followed by fitting procedure the
structural parameters of a cylinder of radius R =(4.87  0.02)
nm and height L =(2.12 0.02)
nm and height L =(2.12  0.04) nm are obtained. 0.04) nm are obtained.
|
E2-2010-149 (108.214)
Shirokov M.I.
My Papers on Quantum Physics
This is an autobibliographical list of papers on quantum physics
supplemented by comments.
|
P9-2010-150 (204.865)
Dolya S.N.
Linear-Circular Proton Accelerator with Energy 0.8 GeV
on the Basis of a Rectangular Cavity with Wave E110
We consider the acceleration of protons in the cavity with parameters:
length l = 10 m, width b = 20 m, height a = 1.01 m, located between the two steering
(180o) magnets with isochronous magnetic field. The resonator is loaded with rows
of plates (tubes) of the drift, it is excited by a wave of type E110 at a frequency of
f0 = 148.5 MHz, the excitation power P1 = 5.65 MW. Additionally,
the cavity is fed
power P2 = 8 MW, which is transmitted into a beam of protons with the parameters: the
final energy 0.8 GeV, the pulse beam current I = 10 mA, pulse width 25  s,
repetition rate 10 Hz.
We discuss the possibility of creating, on the basis of such an accelerator, a pulsed neutron source with
intensity In = 3 s,
repetition rate 10 Hz.
We discuss the possibility of creating, on the basis of such an accelerator, a pulsed neutron source with
intensity In = 3  1014 s-1. 1014 s-1.
|
P2-2010-152 (156.355)
Gusev A.A., Kosmachev O.S.
Structural Kinematical Approach in Elementary Particle Physics
Unique approach is proposed for constructing of relativistic lepton wave
equations. It is kinematical approach because it is exact results based on
few conventional fundamental principles. Arising structural constituents of
equations and particles are corollary of discrete symmetries or connected
components of Lorentz group. Generality and accuracy of the developed method
allow one to put the question of its extension on the hadron sector. The conditions
for solving of the named problem are discussed such as unification of the
mathematical formalism and some widely used notions.
|
